Infrared Ship Target Detection Algorithm Based on Improved Faster R-CNN
-
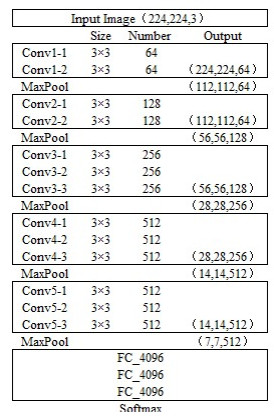
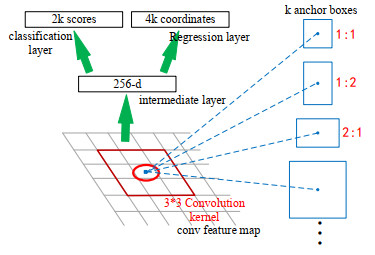
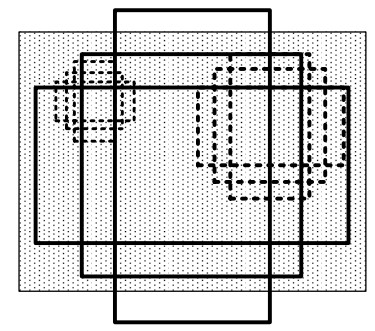
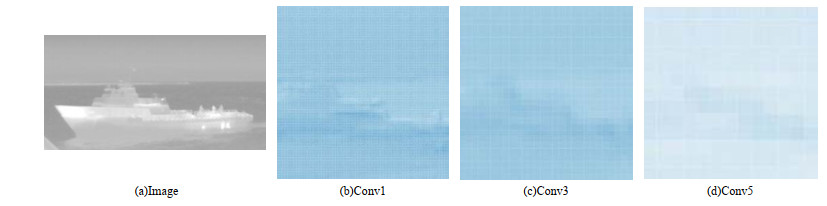
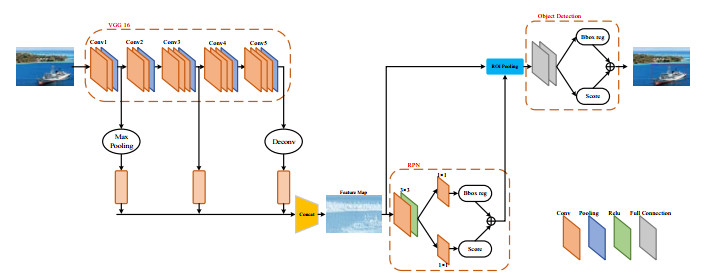
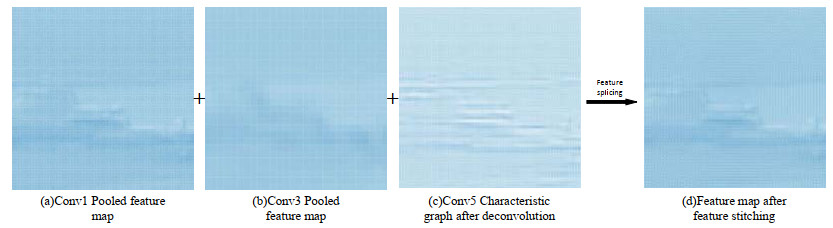
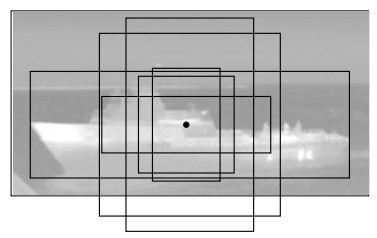
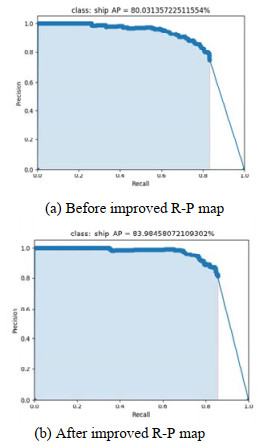
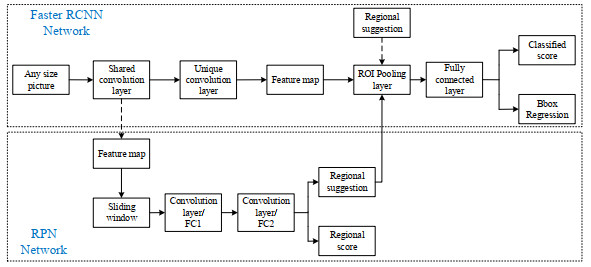
摘要: 针对Faster R-CNN算法中对于红外舰船目标特征提取不充分、容易出现重复检测的问题,提出了一种基于改进Faster R-CNN的红外舰船目标检测算法。首先通过在主干网络VGG-16中依次引出三段卷积后的3个特征图,将其进行特征拼接形成多尺度特征图,得到具有更丰富语义信息的特征向量;其次基于数据集进行Anchor的改进,重新设置Anchor boxes的个数与尺寸;最后优化改进后Faster R-CNN的损失函数,提高检测算法的整体性能。通过对测试数据集进行分析实验,结果表明改进后的检测算法平均精确度达到83.98%,较之于原Faster R-CNN,精确度提升了3.95%。
-
关键词:
- 深度学习 /
- 目标检测 /
- 舰船目标 /
- 红外图像 /
- Faster R-CNN
Abstract: To solve the problem of insufficient feature extraction and repeated detection of infrared ship targets by the Faster R-CNN algorithm, a ship target detection algorithm based on an improved Faster R-CNN is proposed. First, three feature graphs are drawn from the backbone network, VGG-16, after a three-segment convolution, and the features are spliced to form a multi-scale feature graph to obtain a feature vector with richer semantic information; second, the Anchor is improved based on the dataset, and the number and size of the Anchor boxes are reset; finally, the loss function of the improved Faster R-CNN is optimized to improve the feature extraction ability of the target. An analysis of the experimental results on the test dataset demonstrates that the average accuracy of the improved detection algorithm was 83.98%, which is 3.95% higher than that of the original Faster RCNN.-
Keywords:
- deep learning /
- target detection /
- ship target /
- infrared image /
- Faster R-CNN
-
-
表 1 分类结果判别表
Table 1 Classification result discriminant table
Real situation Discriminant result Positive example Counter example Positive example TP(True positive example) FN(False Counter example) Counter example FP(False positive example) TN(True Counter example) 表 2 改进前后算法性能对比
Table 2 Comparison of algorithm performance before and after improvement
Model name AP/% mAP/% Time/s Faster R-CNN 80.03 80.03 0.3128 Improved Faster R-CNN 83.98 83.98 0.3384 -
[1] 施泽浩, 赵启军. 基于全卷积网络的目标检测算法[J]. 计算机技术与发展, 2018(5): 55-58. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-629X.2018.05.013 SHI Zehao, ZHAO Qijun. Target detection algorithm based on full convolution network[J]. Computer Technology and Development, 2018(5): 55-58. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-629X.2018.05.013
[2] Uijlings J R R, Sande K E A V D, Gevers T, et al. Selective search for object recognition[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2013, 104(2): 154-171. DOI: 10.1007/s11263-013-0620-5
[3] Girshick R. Fast R-CNN[C]//Proceedings of ICCV, 2015, 2015: 1440-1448.
[4] Kaiming H, Georgia G, Piotr D, et al. Mask R-CNN[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 18(11): 1-1.
[5] Ren S, He K, Girshick R, et al. Faster r-cnn: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[C]//IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137-1149.
[6] Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, et al. You only look once: unified, real-time object detection[C]//Proceedings of CVPR, 2015: 779-788.
[7] Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017, 12(7): 6517-6525.
[8] LIU W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, et al. SSD: single shot multibox detector[C]//Computer Vision-ECCV 2016, Cham: Springer, 2016, 9905: 21-37.
[9] FU C Y, LIU W, Ranga A, et al. DSSD: deconvolutional single shot detector[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2017: 2999-3007.
[10] Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLO v3: An incremental improvement [C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018, 24(9): 2458-2476.
[11] 李慕锴, 张涛, 崔文楠. 基于YOLOv3的红外行人小目标检测技术研究[J]. 红外技术, 2020, 42(2): 176-181. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/hwjs202002012 LI Muyi, ZHANG Tao, CUI Wennan. Research on infrared pedestrian small target detection technology based on YOLO v3[J]. Infrared Technology, 2020, 42(2): 176-181. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/hwjs202002012
[12] 崔少华, 李素文, 黄金乐, 等. 改进的CNN用于单帧红外图像行人检测的方法[J]. 红外技术, 2020, 42(3): 238-244. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/hwjs202003006 CUI Shaohua, LI Suwen, HUANG Jinle, et al. Improved CNN square method for human detection of single-frame infrared image[J]. Infrared Technology, 2020, 42(3): 238-244. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/hwjs202003006
[13] 向涛. 一种基于显著区域提取的红外图像舰船目标检测方法[J]. 电讯技术, 2020, 60(7): 50-56. XIANG Tao. A ship target detection method based on salient region extraction in infrared image[J]. Telecommunication Technology, 2020, 60(7): 50-56.
[14] 邢莎, 吉林, 雍杨, 等. 基于梯度统计特性的自动红外舰船目标检测[J]. 数字技术与应用, 2013(10): 66-68, 70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZJT201310047.htm XING Sha, JI Lin, YONG Yang, et al. Automatic infrared ship target detection based on gradient statistics[J]. Digital Technology and Applications, 2013(10): 66-68, 70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SZJT201310047.htm
[15] 宫剑, 吕俊伟, 刘亮, 等. 红外偏振图像的舰船目标检测[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2020, 40(2): 586-594. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN202002052.htm GONG Jian, LV Junwei, LIU Liang, et al. Ship target detection based on infrared polarization image[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2020, 40(2): 586-594. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN202002052.htm
[16] 吴天舒, 张志佳, 刘云鹏. 基于改进SSD的轻量化小目标检测算法[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2018(7): 37-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYJ201807007.htm WU Tianshu, ZHANG Zhijia, LIU Yunpeng. Lightweight small beacon detection algorithm based on improved SSD[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2018(7): 37-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYJ201807007.htm
[17] WANG Zijie J, Robert Turko, Omar Shaikh, et al. CNN explainer: learning convolutional neural networks with interactive visualization[J]. Journal of Sensors, 2019(6): 1-13. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8941872/
[18] Zeiler M D, Fergus R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks[C]// Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2014, 8689: 818-833.
-
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 王振,刘磊. 基于改进分水岭算法的电力设备红外图像分割. 红外技术. 2025(04): 484-492 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 刘强,刘志国. 室外动态车标图像关键特征边缘识别仿真. 计算机仿真. 2024(03): 487-491 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李双营,邵亚飞. 城市周边流域有机污染物不同分布特征提取. 计算机仿真. 2024(07): 281-284+365 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王洁,伍弘,詹仲强,李金良,金铭,陈文涛. 基于Lazy Snapping混合模拟退火算法的高压开关柜温度场红外三维图像重建仿真. 红外技术. 2023(03): 276-281 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 刘训星,张海民. 基于数学形态学的路面裂纹图像分割方法. 辽东学院学报(自然科学版). 2023(02): 130-135 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 周建起,刚建华. 数字全息技术的激光超精密加工表面检测研究. 激光杂志. 2023(08): 243-247 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 翁宇游,郑州,郭俊,赵志超,谢炜,胡雨. 改进U-Net网络的接地网图像超像素分割. 激光与红外. 2023(08): 1196-1202 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 黄祥声,乐治济,吴敏辉,倪秀楠,钟茗秋,陈川. 基于改进时域高通滤波红外图像的海上风机塔架腐蚀速率预测. 激光与红外. 2023(10): 1527-1533 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 朱笑,袁丽华. 基于红外热成像的CFRP复合材料低速冲击损伤表征. 复合材料学报. 2022(08): 4164-4171 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 何翠萍. 应用区域生长的无人船红外图像精确分割方法. 信息与电脑(理论版). 2022(24): 81-83 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)



 下载:
下载: