Stability Control Method for Infrared Search and Track System Based on Mobile Platform
-
摘要:
基于移动平台的红外搜索跟踪系统已成为新一代光电搜索跟踪系统的主流趋势,小型化和轻量化是其高机动性的保证。载体运动姿态变化耦合的角速度扰动和系统内部力矩干扰将对其搭载的光电载荷视轴稳定控制带来严峻挑战,基于多轴多框架和高精度陀螺反馈控制相结合的传统视轴稳定方法已无法适用。本文针对两轴两框架移动平台红外搜索跟踪系统的光电载荷视轴稳定控制,提出了基于平方PI和Luenberger扰动观测前馈的双速度闭环同阶串级控制方法。仿真和实验表明,相对于传统的单陀螺闭环和双速度闭环稳定控制方法,该稳定控制方法有效提升了载体运动低频扰动下的视轴稳定精度。1°/1 Hz扰动下,仿真稳定精度达到2.7817 μrad,实验稳定精度达到35.85 μrad。1°/2 Hz扰动下,仿真稳定精度达到38.199 μrad,实验稳定精度达到119.1 μrad。最终,利用本文提出的稳定控制方法,两轴两框架移动平台红外搜索跟踪系统有效克服了行进间载体运动姿态变化耦合的低频角速度扰动,实现了高平稳高动态的光电载荷视轴指向控制性能。
Abstract:Infrared search and tracking systems based on the mobile platform have become the mainstream trend of the new generation in optoelectronic search and track systems, and miniaturization and lightweight guarantee high mobility. The angular velocity disturbance, coupled with the carrier's motion attitude change and internal torque disturbance of the system, raises serious challenges to the optical-axis stability control of the optoelectronic load. The traditional optic-axis stability method based on a combination of multi-axis, multi-frame, and high-precision gyro feedback control, is no longer applicable. In this study, a double-velocity closed-loop same-order cascade control method is proposed based on square PI and Luenberger disturbance observation and feedforward, for the optical axis stability control of the optoelectronic load on a two-axis two-frame mobile platform infrared search and tracking system. Simulations and experiments show that compared with the conventional single-gyro closed-loop and double-velocity closed-loop stability control methods, the proposed stability control method can effectively improve the stability accuracy of the optical axis under low-frequency disturbance of the carrier's motion. Under a disturbance of 1°/1 Hz carrier motion, the stability accuracy of the simulated optical axis improved to 2.7817 μrad and that of the actual experiment improved to 35.85 μrad. Under a disturbance of 1° /2 Hz carrier motion, the stability accuracy of the simulated optical axis improved to 38.199 μrad and that of the actual experiment improved to 119.1 μrad. Finally, using the stability control method proposed in this study, the two-axis two-frame infrared search and track system based on the mobile platform effectively overcame the low-frequency angular velocity disturbance coupled with the carrier's motion attitude change between marching, to realize a highly stable and highly dynamic optical-axis-oriented control performance of the optoelectronic load.
-
0. 引言
红外搜索跟踪系统利用红外成像原理实现目标被动探测,具备优异的静谧探测能力,被广泛地应用于目标的搜索、定位与跟踪等领域[1-2]。近年来,随着目标形态和运动姿态的多样化,常规的车载雷达和固基平台红外搜索跟踪系统已无法满足应用需求。基于移动平台的红外搜索跟踪系统可以隔离载体运动姿态变化的扰动,在视线坐标系下保持光轴角速度稳定,确保光电探测器在其曝光积分时间内对场景的“凝视”,提高对“低小慢”红外目标的探测性能。因此,基于移动平台的搜跟系统已逐渐成为新一代红外搜跟系统升级与发展的主流趋势。
从工作原理上可知,红外搜索跟踪系统不仅受到来自系统内部的电磁转矩波动、轴承摩擦、动密封摩擦和线缆应力变化等带来的力矩干扰,还受到行进间载体运动姿态变化耦合的随机角速度扰动。内外部扰动都将使光轴在探测器积分时间内产生角运动,进而影响成像质量,降低系统对弱小目标的探测能力[3-5]。在工程实现上,提高红外搜索跟踪系统的视轴稳定性能主要从多框架或多阶执行结构分级隔离扰动的框架结构改进和高精度视线角速度控制两方面入手。其中,增加结构框架或执行机构不利于控制搜索跟踪系统的体积、重量和成本。鉴于移动平台应用的小型化、轻量化要求,本文着重从稳定控制的角度讨论改进视轴稳定性能的方法。
为优化和提高视轴稳定控制性能,研究人员进行了很多的工作。姬伟等升级了单速度环的稳定控制方式,提出采用直流测速机和陀螺反馈实现双速度闭环串级控制的方法,并通过实验证明了双速度闭环控制方法对系统抗扰性、鲁棒性等的改善效果[6];方超宇等设计了含有降阶扩张状态观测器的自抗扰控制器,对扰动总和实时观测并进行线性化前馈补偿,有效提高了两轴四框架稳定平台的扰动隔离性能[7];孔德杰等基于双速度闭环控制结构,分析了高增益提高扰动抑制能力和降低系统稳定性的矛盾,提出引入加速度反馈和引入扰动观测器两种等效方法,在改善系统动态响应性能的同时,有效增强了扰动抑制能力[8];魏伟等从系统受到的扰动入手,融合自抗扰控制和重复控制的方法,有效拓宽了扰动隔离带宽,显著提高了两轴四框架搜索跟踪平台的视轴稳定性能[9];蔡华祥等提出基于扩张状态观测器的扰动补偿控制方法,有效补偿了望远镜稳定平台的非线性扰动影响[10];刘京等利用滑膜控制器和滑膜观测器组成复合控制,有效改善了望远镜伺服系统在复杂扰动环境下的跟踪性能[11];唐涛等将PI-PI(proportion integral-proportion integral)控制器引入到具有输出延迟的快速倾斜镜控制系统中,在不增加系统闭环带宽的前提下,有效提高了CCD闭环的低频闭环增益和低频扰动抑制能力[12];张良总等利用Stewart平台和TTM(tip-tit mirror)倾斜校正系统的双阶闭环控制,解决了空间望远镜稳定平台的隔振和跟踪性能矛盾[13]。但是,这些研究主要基于两轴四框架结构的光电吊舱系统或两轴两框架+快返镜结构的望远镜固基平台开展的。这类系统通过多层框架结构或多阶执行机构的分级隔离,大大降低了内外扰动对视轴稳定性能的影响,因此系统稳定控制的要求相对较低。
两轴两框架光电稳定平台,因其没有分级隔离结构,且转动惯量较小,稳定控制要求相对较高[3, 14]。目前,国外代表性的两框架光电系统主要有美国的Skyball-SA-144/18,视轴稳定精度达到35 μrad[15];国内主要以长光所等的产品为代表,视轴稳定精度达到40 μrad,甚至最新研究表明已实现23.6 μrad的视轴稳定精度[16-17]。但是,这些研究都主要应用于机载光电侦察领域。对于移动平台红外搜索跟踪系统领域,目前相关研究和应用较少。
本文以两轴两框架移动平台红外搜索跟踪系统为对象开展研究,首先从红外搜索跟踪系统稳定控制原理入手,分析现有双速度闭环稳定控制方法存在的不足。然后,针对移动平台红外搜索跟踪系统的应用需求,改进双速度闭环控制结构:前馈电机速度构成双速度闭环同阶串级控制,分开处理系统内部力矩扰动和载体运动姿态变化耦合的角速度扰动,用高带宽的框架速度回路来抑制具有高频特性的内部力矩扰动,用低带宽的稳定回路来抑制载体运动耦合的角速度扰动,并用平方PI控制策略来提高回路的低频增益,从而综合提高反馈回路的抗扰动能力;同时,利用Leunberger扰动观测与前馈扰动解耦的方法来进一步提高系统的抗扰性能。最后,通过数学仿真和实物实验,验证了本文提出的基于平方PI和Leunberger扰动观测前馈的双速度闭环同阶串级控制方法对移动平台红外搜索跟踪系统抗扰动性能的改善作用,得到了较好的视轴稳定效果。
1. 红外搜索跟踪系统的稳定控制实现与分析
红外搜索跟踪系统将红外探测器等光电载荷置于稳定平台内框上,利用稳定平台在方位、俯仰方向上的旋转运动,控制视轴的空间运动,实现光电载荷对目标的搜索、探测、识别、跟踪和定位等功能。系统伺服控制的实质是实现视轴的“静”稳定与“动”跟踪。一方面要隔离扰动,保证视轴惯性空间内的稳定,并以此作为指示基准;另一方面,要不断调整视轴指向以跟随目标姿态的变化[6, 18]。
传统的稳定控制方法,利用陀螺获取光电载荷视轴的角速度姿态,计算光电载荷视轴偏离目标视线的误差,并由此给出控制量调整视轴指向,从而达到稳定视轴基准的目的。
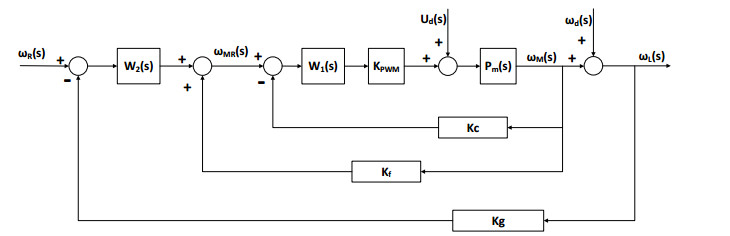
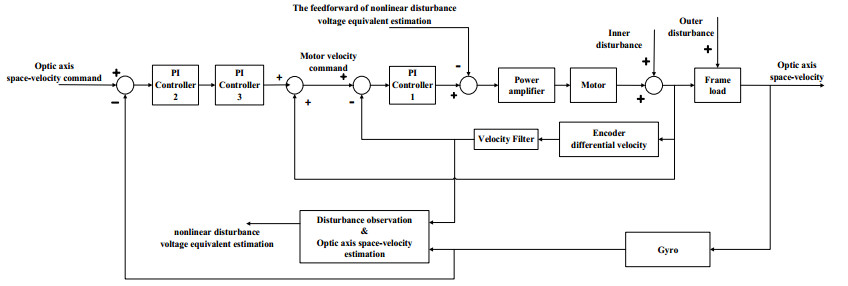
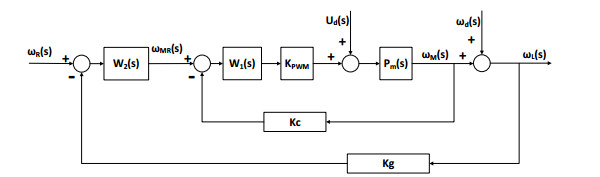
然而,受模型差异、电磁转矩波动、摩擦力矩变化、质心不平衡、载体振动和颠簸等内外部干扰,单一的速度稳定环难以协调各种干扰的影响和相互牵制[6, 19]。另外,单速度闭环稳定精度受限于陀螺器件的精度,且高精度光纤陀螺器件的成本通常都很高。实际工程应用中,红外搜索跟踪系统通常采用如图 1所示的双速度闭环稳定控制模型。
图 1中:ωR(s)、ωMR(s)、ωM(s)、ωL(s)分别表示视轴空间速度指令、电机速度指令、电机速度输出和视轴空间速度;W1(s)和W2(s)分别表示内环和外环稳定控制器;Ud(s)表示内部力矩干扰等效的电压量;ωd(s)表示载体运动姿态变化耦合的视轴角速度偏移量;kg和kc分别表示陀螺和编码器标度因子;Pm(s)表示电机及其框架的传递函数;KPWM表示功率放大器的放大系数。
由图 1可得,双速度闭环稳定控制系统视轴空间速度ωL(s)输出的传递函数,如式(1)所示:
$$ \begin{array}{l} {\omega _{\rm{L}}}(s) = \frac{{{W_2}(s){W_1}(s){K_{{\rm{PWM}}}}{P_m}(s)}}{{1 + [{k_{\rm{g}}}{W_2}(s) + {k_{\rm{c}}}]{W_1}(s){K_{{\rm{PWM}}}}{P_m}(s)}}{\omega _{\rm{R}}}(s) \\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ + \frac{{{P_m}(s)}}{{1 + [{k_{\rm{g}}}{W_2}(s) + {k_{\rm{c}}}]{W_1}(s){K_{{\rm{PWM}}}}{P_m}(s)}}{U_{\rm{d}}}(s) \\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ + \frac{{1 + {k_{\rm{c}}}{W_1}(s){K_{{\rm{PWM}}}}{P_m}(s)}}{{1 + [{k_{\rm{g}}}{W_2}(s) + {k_{\rm{c}}}]{W_1}(s){K_{{\rm{PWM}}}}{P_m}(s)}}{\omega _{\rm{d}}}(s) \end{array} $$ (1) 利用信噪比指标衡量伺服系统的抗扰性能,信噪比越大,抗扰性能越强[6]。式(1)变形可分别获得双速度闭环下系统对于内部力矩干扰Ud(s)和外部载体运动姿态变化耦合角速度扰动ωd(s)的信噪比,分别如式(2)和式(3)所示。
$$ {A_{{\rm{d1}}}} = \frac{{{\omega _{\rm{L}}}(s)/{\omega _{\rm{R}}}(s)}}{{{\omega _{\rm{L}}}(s)/{U_{\rm{d}}}(s)}} = {W_2}(s){W_1}(s){K_{{\rm{PWM}}}} $$ (2) $$ {A_{{\rm{d2}}}} = \frac{{{\omega _{\rm{L}}}(s)/{\omega _{\rm{R}}}(s)}}{{{\omega _{\rm{L}}}(s)/{\omega _{\rm{d}}}(s)}} = \frac{{{W_2}(s){W_1}(s){K_{{\rm{PWM}}}}{P_{\rm{m}}}(s)}}{{1 + {k_{\rm{c}}}{W_1}(s){K_{{\rm{PWM}}}}{P_{\rm{m}}}(s)}} $$ (3) 对于固基平台或者多轴多框架的红外搜索跟踪系统,图 1所示的双速度闭环控制已经能使系统获得很好的视轴稳定性能。相比较下,两轴两框架移动平台红外搜索跟踪系统转动惯量较小,动密封带来的可变摩擦力矩干扰和行进间载体运动姿态变化耦合的角速度波动直接作用在视轴上,其稳定控制的挑战更加严峻。特别是行进间载体运动姿态的突然变化,耦合到视轴的阶跃角速度扰动容易在低速跟踪时引起控制震荡,降低视轴控制的稳定性。与此同时,陀螺器件精度与体积大小、成本等的矛盾严重制约着移动平台红外搜索跟踪系统在边防、海防和城市治安、森林监控等民用领域的推广[20]。
为此,本文改进现有双速度闭环稳定控制方法,使其不受限于框架组成和陀螺精度,能够快速补偿行进间载体运动姿态变化耦合的角速度扰动,使移动平台红外搜索跟踪系统获得更高的视轴稳定精度。
2. 基于移动平台红外搜索跟踪系统的稳定控制方法研究
2.1 双速度闭环同阶串级控制结构的设计
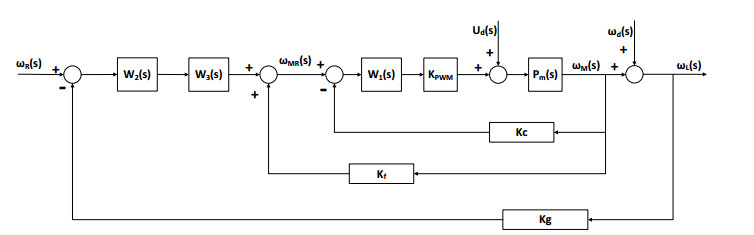
图 1所示控制模型中,陀螺稳定外环的输出直接作为电机速度内环的指令。根据串级控制降阶特性,内环带宽需远远大于外环,才能保证控制的稳定性。在移动平台红外搜跟系统机动过程中,为克服载体运动姿态变化耦合的阶跃角速度干扰,外环控制输出指令将会在内环引入指令阶跃输入和控制连续输出的矛盾,严重影响控制系统的稳定性能。
为此,本文提出前馈电机速度构成双速度闭环同阶串级控制的改进方法。如图 2所示,电机速度前馈量与陀螺速度外环的输出调整量相叠加,作为电机速度内环的指令。kf表示上一帧速度前馈的比例系数。另外,在前馈通路上引入带宽匹配滤波环节,以匹配内外速度环带宽。
由此,计算得到双速度闭环同阶串级控制系统的传递函数,如式(4)所示。
$$ \begin{array}{l} {\omega _{\rm{L}}}(s) = \frac{{{W_2}(s){W_1}(s){K_{{\rm{PWM}}}}{P_{\rm{m}}}(s)}}{{1 + [{k_{\rm{g}}}{W_2}(s) + ({k_{\rm{c}}} - {k_{\rm{f}}})]{W_1}(s){K_{{\rm{PWM}}}}{P_{\rm{m}}}(s)}}{\omega _{\rm{R}}}(s) \\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ + \frac{{{P_m}(s)}}{{1 + [{k_{\rm{g}}}{W_2}(s) + ({k_{\rm{c}}} - {k_{\rm{f}}})]{W_1}(s){K_{{\rm{PWM}}}}{P_{\rm{m}}}(s)}}{U_{\rm{d}}}(s) \\ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ \ + \frac{{1 + ({k_{\rm{c}}} - {k_{\rm{f}}}){W_1}(s){K_{{\rm{PWM}}}}{P_{\rm{m}}}(s)}}{{1 + [{k_{\rm{g}}}{W_2}(s) + ({k_{\rm{c}}} - {k_{\rm{f}}})]{W_1}(s){K_{{\rm{PWM}}}}{P_{\rm{m}}}(s)}}{\omega _{\rm{d}}}(s) \end{array} $$ (4) 对于内部力矩干扰Ud(s)和外部载体角速度扰动ωd(s)的信噪比,分别如式(5)和式(6)所示:
$$ {A_{{\rm{d1}}}}_{\_1} = \frac{{{\omega _{\rm{L}}}(s)/{\omega _{\rm{R}}}(s)}}{{{\omega _{\rm{L}}}(s)/{U_{\rm{d}}}(s)}} = {W_2}(s){W_1}(s){K_{_{{\rm{PWM}}}}} $$ (5) $$ \begin{array}{l} {A_{{\rm{d2}}\_1}} = \frac{{{\omega _{\rm{L}}}(s)/{\omega _{\rm{R}}}(s)}}{{{\omega _{\rm{L}}}(s)/{\omega _{\rm{d}}}(s)}} = \hfill \\ \quad \frac{{{W_2}(s){W_1}(s){K_{{\rm{PWM}}}}{P_{\rm{m}}}(s)}}{{1 + ({k_{\rm{c}}} - {k_{\rm{f}}}){W_1}(s){K_{{\rm{PWM}}}}{P_{\rm{m}}}(s)}}\quad \quad \hfill \end{array} $$ (6) 分别比较式(2)、式(5)和式(3)、式(6),可得:
$$ \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\Delta {A_{{\text{d1}}}} = \frac{{{A_{{\rm{d1}} - 1}}}}{{{A_{{\rm{d1}}}}}} = 1} \\ {\Delta {A_{{\rm{d2}}}} = \frac{{{A_{{\rm{d2}}\_1}}}}{{{A_{{\rm{d2}}}}}} = \frac{{1 + {k_{\rm{c}}}{W_1}(s){K_{{\rm{PWM}}}}{P_{\rm{m}}}(s)}}{{1 + ({k_{\rm{c}}} - {k_{\rm{f}}}){W_1}(s){K_{{\rm{PWM}}}}{P_{\rm{m}}}(s)}}} \end{array}} \right. $$ (7) 若控制器设计时,在工作带宽范围内满足式(8)所示的简化条件:
$$ \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\left| {1 + {k_{\rm{c}}}{W_1}(s){K_{{\rm{PWM}}}}{P_{\rm{m}}}(s)} \right| \gg 1} \\ {\left| {1 + ({k_{\rm{c}}} - {k_{\rm{f}}}){W_1}(s){K_{{\rm{PWM}}}}{P_{\rm{m}}}(s)} \right| \gg 1} \end{array}} \right. $$ (8) 则,式(7)简化为:
$$ \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\Delta {A_{{\text{d1}}}} = \frac{{{A_{{\rm{d1}} - 1}}}}{{{A_{{\rm{d1}}}}}} = 1} \\ {\Delta {A_{{\rm{d2}}}} = \frac{{{A_{{\rm{d2}}\_1}}}}{{{A_{{\rm{d2}}}}}} \approx \frac{{{k_{\rm{c}}}}}{{{k_{\rm{c}}} - {k_{\rm{f}}}}}} \end{array}} \right. $$ (9) 式(9)表明,前馈电机速度构成双速度闭环同阶串级控制的方法,在保持双速度闭环串级控制对内部力矩扰动抑制能力的基础上,增大了对行进间载体运动姿态变化耦合的角速度扰动的抑制能力。
2.2 平方PI控制策略的分析与实现
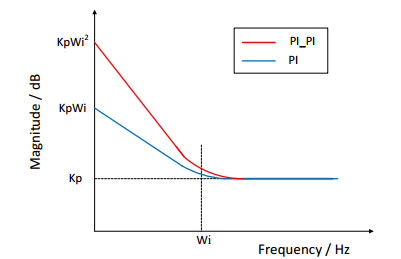
扰动响应和指令响应都可以增大回路增益来加以改善[21]。考虑到移动平台红外搜索跟踪系统的扰动响应更多关注载体运动姿态变化耦合的角速度扰动,本文基于图 2双速度闭环同阶串级控制结构,提出陀螺速度外环采用平方PI的控制策略,在系统机械谐振频率不变的情况下,增大陀螺速度外环低频段的开环增益和斜率,进而提高稳定平台对载体运动姿态变化耦合的角速度扰动的隔离能力,如图 3所示。
单PI控制器和平方PI控制器的传递函数如式(10)所示[21]:
$$\left\{\begin{array}{c} W_{\mathrm{PI}}(s)=k_{\mathrm{p}}\left(1+W_{\mathrm{i}} \frac{1}{s}\right) \\ W_{\mathrm{PI}-\mathrm{PI}}(s)=k_{\mathrm{p}}\left(1+W_{\mathrm{i}} \frac{1}{s}\right)^2 \end{array}\right.$$ (10) 由图 4所示的定性Bode图可知,在控制参数kp和Wi相同的情况下,平方PI控制器在低频段具有很高的开环增益。在工作频率远远小于转折频率时,两类控制器开环传递函数可如式(11)简化。可知,平方PI控制器将低频段的开环幅频增益近似增大Wi倍。
$$ \left\{ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{W_{{\rm{PI}}}}(s) = {k_{\rm{p}}}{W_{\rm{i}}}} \\ {{W_{{\rm{PI}}\_{\rm{PI}}}}(s) = {k_{\rm{p}}}{W_{\rm{i}}}^2} \end{array}} \right.(w \ll {W_{\rm{i}}}) $$ (11) 一般情况下,载体运动姿态变化耦合的角速度扰动为频率小于5 Hz的低频扰动。因此,陀螺速度外环采用平方PI的控制策略,能够有效提高移动平台红外搜索跟踪系统对行进间载体运动姿态变化耦合的角速度扰动的隔离能力,获得良好的视轴稳定精度。
2.3 基于Leunberger的扰动观测与前馈解耦
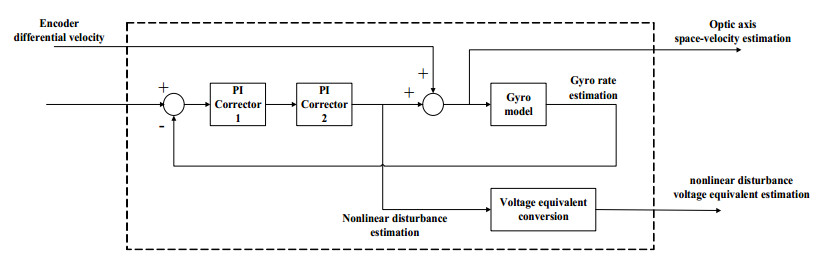
由2.2节分析可知,平方PI控制策略大大提高了低频段的开环增益和斜率。但是,根据经典控制理论频域响应分析可知:积分控制器的增加,将减小相位裕度,降低伺服系统的稳定性能。本文利用Luenberger扰动观测器观测红外搜索跟踪系统行进间受到的载体运动姿态变化扰动,并将估计得到的扰动电压等效值前馈至功率驱动器前端直接输出,削弱平方PI控制引入的相位滞后影响。
平方PI校正的Luenberger扰动观测器控制框图如图 5所示。其中,陀螺速度模型采用式(12)所示的低通滤波器表示,陀螺带宽对应为滤波器截止频率ω0。
$$ W(s) = \frac{{{\omega _0}}}{{{s^2} + 2\xi {\omega _0}s + \omega _0^2}} $$ (12) 另外,扰动观测器采用平方PI校正策略,提高陀螺速度外环的控制带宽,替代在电机速度前馈时引入的带宽匹配滤波模块,使稳定控制算法更简化和更具操作性。
最终,基于移动平台红外搜索跟踪系统的应用,本文在双速度闭环稳定控制的基础上做出改进,设计了基于平方PI和Luenberger扰动观测前馈的双速度闭环同阶串级控制的视轴稳定方法,控制框图如图 6所示。
3. 实验与结果分析
3.1 数学仿真分析
基于MATLAB仿真平台,搭建某两轴两框架红外搜索跟踪系统俯仰框架稳定控制的数学仿真模型,对比传统单速度闭环、传统双速度闭环和本文设计的视轴稳定方法的性能。
基本电气参数如表 1所列,单PI控制器和双PI控制器传递函数如式(10)所示。单速度闭环控制参数为kp=70,Wi=60;双速度闭环和本文改进的双速度闭环同阶串级控制中,电机框架速度内环控制参数为kp=75,Wi=30;陀螺速度外环控制参数为,kp=1.3,Wi=70。
表 1 俯仰框架基本电气参数Table 1. Basic electrical parameters of pitching frameParameters Value Unit Moment of inertia 0.014 kg⋅m2 Armature resistance 14 Ω Armature inductance 7.5 mH Back-emf coefficient 0.28 V/rad/s Moment coefficient 0.28 Nm/A Gyro filter frequency 50 Hz 3.1.1 双速度闭环同阶串级控制结构的扰动响应分析
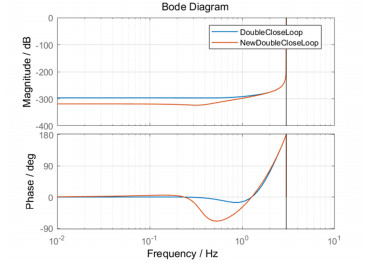
对比了传统双速度闭环和本文双速度闭环同阶串级控制两种视轴稳定方法的抗扰动性能,扰动响应曲线如图 7所示。
分析图 7可知,相对于传统双速度闭环控制,本文设计的双速度闭环同阶串级控制的视轴稳定方法在低频段具有更好的扰动抑制能力。其扰动响应低频段的增益最大降低约23.5 dB,且出现明显的相位滞后。由此,验证了2.1节和式(9)分析的正确性。
3.1.2 平方PI控制分析
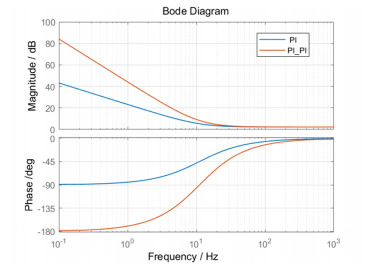
首先对比了单PI控制和平方PI控制的开环频率响应特性,其次在双闭环同阶串级控制结构的基础上,对比陀螺速度外环采用单PI控制器和平方PI控制器后的视轴稳定性能。
图 8为单PI控制和平方PI控制的开环频率响应曲线。可以看出:相比单PI控制方法,平方PI控制在不改变转折频率的情况下,提升约2倍的低频段的开环增益;但是,平方PI控制引入了很大的相位滞后,最大将引起90°的相位滞后,严重降低整个控制系统的相位裕度。
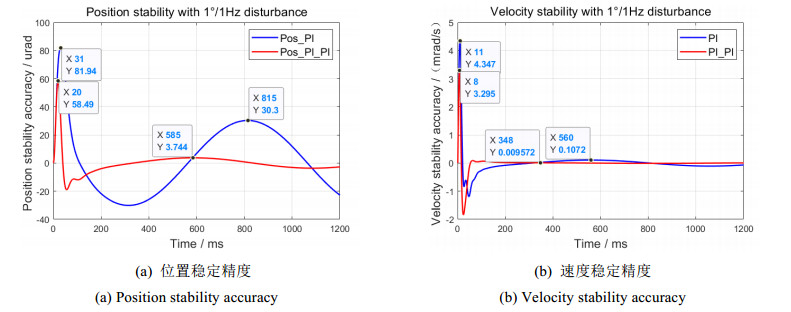
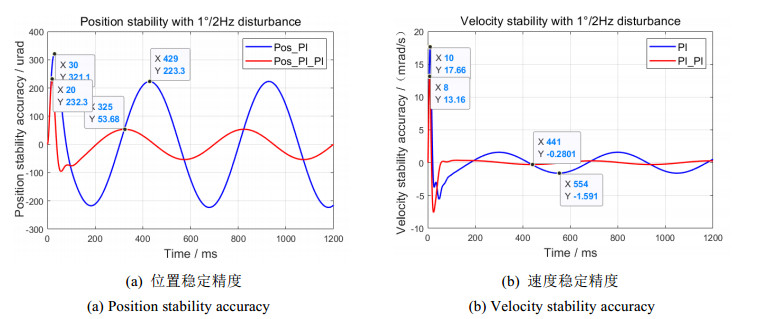
图 9和图 10分别表示在双闭环同阶串级控制结构基础上,1°/1 Hz和1°/2 Hz扰动下单PI和平方PI陀螺外环控制的视轴稳定响应曲线。对比可知,相对于单PI的陀螺外环控制,平方PI的陀螺外环控制有效改善了位置和速度的最大偏移量、稳定精度及稳定快速性能:
1)1°/1 Hz扰动下,位置最大偏移量为58.49 μrad,降低23.45 μrad;位置稳定精度为3.744 μrad,提升26.556 μrad,稳定时间缩短230 ms(图 9(a));速度稳定精度为0.009572 mrad/s,提升0.097628 mrad/s,稳定时间缩短212 ms(图 9(b))。
2)1°/2 Hz扰动下,位置最大偏移量为232.3 μrad,降低88.8 μrad;位置稳定精度为53.68 μrad,提升169.62 μrad,稳定时间缩短104 ms(图 10(a));速度稳定精度为0.2801 mrad/s,提升1.3109 mrad/s,稳定时间缩短113 ms(图 10(b))。
3.1.3 扰动观测前馈分析
在平方PI控制的双速度闭环同阶串级控制系统基础上,首先对比加入Luenberger扰动观测前馈对视轴稳定性能的影响,其次对比观测校正器采用平方PI控制的改进效果。
单PI校正器和平方PI校正器传递函数如式(10)所示,控制参数为kp=1.25,Wi=70。图 11表示Luenberger扰动观测前馈加入前后不同扰动下的视轴稳定响应曲线。
可以看出:
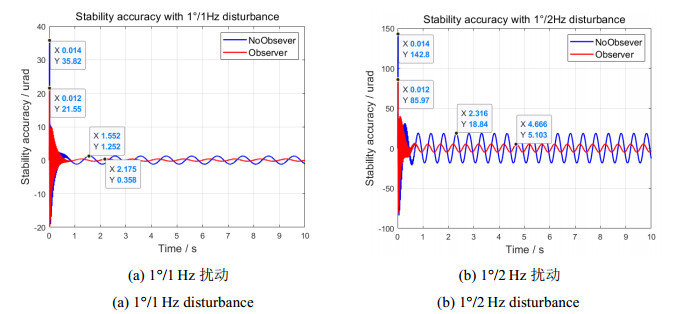
1)1°/1 Hz扰动时,Luenberger扰动观测前馈的引入,位置最大偏移量为21.55 μrad,减少14.27 μrad,稳定精度为0.358 μrad,提升0.894 μrad,相位超前约90°(图 11(a));
2)1°/2 Hz扰动时,Luenberger扰动观测前馈的引入,位置最大偏移量为85.97 μrad,减少56.83 μrad,稳定精度为5.103 μrad,提升13.737 μrad,相位超前约90°(图 11(b))。
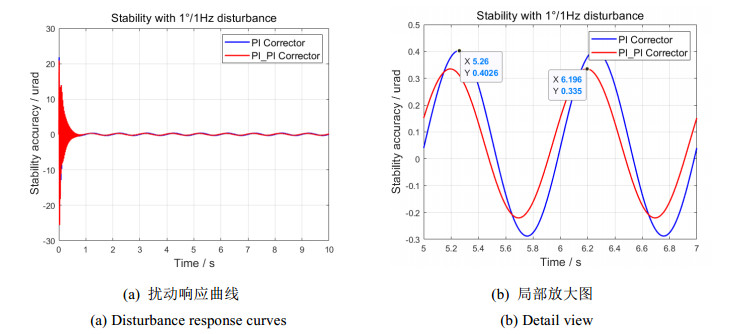
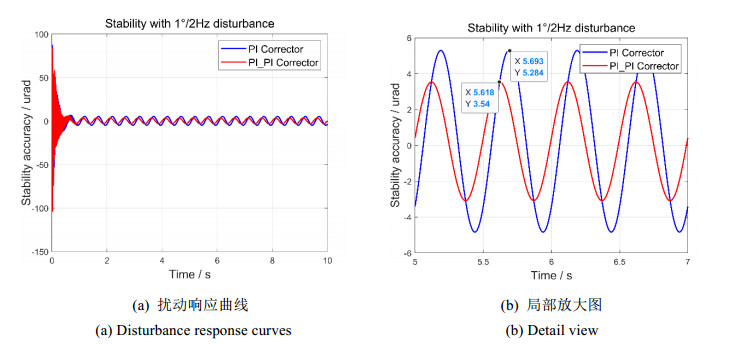
图 12和图 13分别表示单PI校正和平方PI校正的1°/1 Hz和1°/2 Hz扰动响应曲线。平方PI校正方法的使用更进一步改善了视轴稳定控制的最大偏移量、稳定精度和控制系统相位裕度。
最终,Luenberger扰动观测前馈和平方PI校正环节的引入,进一步改善了视轴稳定精度。相比较未使用观测器的稳定性能,1°/1 Hz扰动下,视轴最大偏移量降低15.24 μrad,稳定精度提升0.9623 μrad;12 Hz扰动下,视轴最大偏移量降低61.74 μrad,稳定精度提升15.481 μrad。
3.2 算法改进的有效性分析
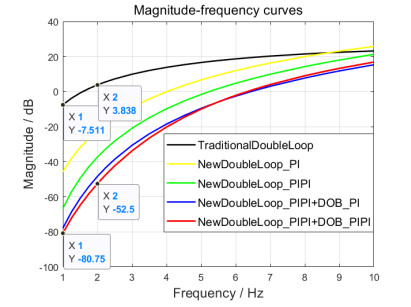
表 2和图 14分别表示了不同算法作用的视轴稳定精度和扰动幅频响应曲线。
表 2 不同算法作用的视轴稳定精度Table 2. Optical axis stability accuracy for different algorithmsμrad Disturbance Traditional double-closed loop Improved double-closed loop Singer PI Square PI Square PI+DOB_PI Square PI+DOB_PI-PI 1°/1 Hz 1168 30.3 3.744 2.85 2.7817 1°/2 Hz 2161 223.3 53.68 39.943 38.199 分析可知,本文通过双速度闭环同阶串级的改进、陀螺外环平方PI控制、Luenberger扰动观测前馈和平方PI校正等步骤,逐步提升了两轴两框架红外搜索跟踪系统的视轴稳定精度。1°/1 Hz扰动下,稳定精度达到2.7817 μrad,扰动抑制性能提升73.293 dB;1°/2 Hz扰动下,稳定精度达到38.199 μrad,扰动抑制性能提升56.338 dB。因此,本文稳定控制方法改进有效,两轴两框架红外搜索跟踪系统的视轴稳定精度达到国内外先进水平。
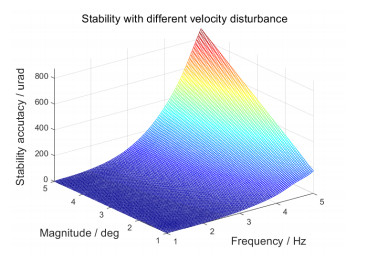
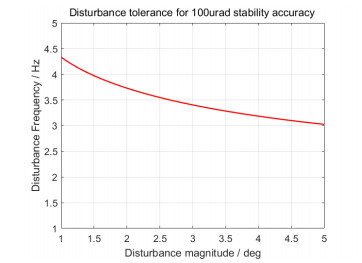
图 15和图 16分别表示了本文稳定控制算法在不同角速度扰动下的稳定性能和基于100 μrad稳定精度要求的扰动容限。分析可知,本文稳定控制算法具备很高带宽的扰动抑制能力。1°小幅值角速度扰动,本算法能最大有效抑制4.5 Hz带宽的扰动影响。
3.3 实验验证与结果分析
利用六自由度摇摆台模拟移动平台红外搜索跟踪系统行进间受到的载体运动姿态变化扰动,搭建如图 17所示的实验平台,验证某两轴两框架移动平台红外搜索跟踪系统的视轴稳定效果。
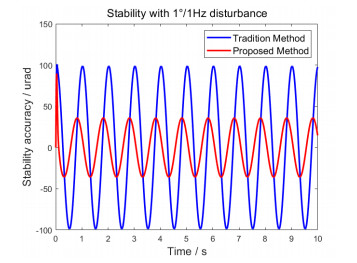
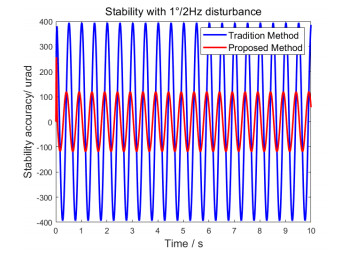
俯仰框架视轴稳定结果如图 18和图 19所示,具体数据如表 3所列。对比可知:相比较传统单PI控制单陀螺速度闭环的稳定控制方法,本文设计的稳定方法在1°/1 Hz载体运动扰动下,视轴稳定精度提升62.63 μrad(63.60%);在1°/2 Hz载体运动扰动下,稳定精度提升275.3 μrad(69.80%)。
表 3 摇摆台不同扰动条件下俯仰框架的视轴稳定精度Table 3. Pitch-optical-axis stability accuracy with different disturbance of swing platformDisturbance Single closed-loop/μrad Our method/μrad Decreasing percentage/% 1°/1 Hz 98.48 35.85 63.60 1°/2 Hz 394.4 119.1 69.80 实验结果表明:本文稳定控制方法的应用,使该移动平台红外搜索跟踪系统有效地克服了载体运动姿态变化对光电载荷视轴的扰动影响,周扫搜索过程中图像清晰不拖尾,目标跟踪过程中目标视场中心位置稳定不晃动,获得了高精度的视轴稳定效果。
表 4比较了基于本文稳定控制方法的移动平台红外搜跟系统和国内外代表性两轴两框架光电吊舱的稳定精度。分析可知,1°/1 Hz扰动下,基于本文稳定控制方法的两轴两框架移动平台红外搜跟系统实现35.85 μrad的视轴稳定精度,已达到国内外先进水平。
表 4 与部分代表性光电系统的稳定精度对比Table 4. Comparison of stability accuracy with some representative optic-electric systems但是,1°/2 Hz扰动下视轴稳定精度为119.1 μrad。同时,对比表 2和表 3数据可知,虽然视轴稳定精度的改善趋势相同,但数学仿真和实验还存在一定差异。因此,为增强移动平台红外搜跟系统在复杂应用场景下的视轴稳定精度和性能可靠性,还需通过优化对绕线阻力矩、非线性摩擦力矩等的估计来提高系统建模精度,进一步改善基于本文稳定控制方法的移动平台红外搜跟系统视轴稳定精度。
4. 结论
本文针对两轴两框架移动平台红外搜索跟踪系统的光电载荷视轴稳定控制,提出了基于平方PI和Luenberger扰动观测前馈的双速度闭环同阶串级控制方法。仿真和实验表明,相对于传统的单陀螺闭环和双速度闭环稳定控制方法,该稳定控制方法有效提升了移动平台红外搜索跟踪系统在载体运动低频扰动下的视轴稳定精度。1°/1 Hz运动载体扰动下,仿真稳定精度达到2.7817 μrad,实际实验稳定精度达到35.85 μrad。1°/2 Hz运动载体扰动下,仿真视轴稳定精度达到38.199 μrad,实际实验稳定精度达到119.1 μrad。由此,两轴两框架移动平台红外搜索跟踪系统有效克服了行进间载体运动姿态变化耦合的角速度扰动,实现了高平稳高动态的光电载荷视轴指向控制性能。
-
表 1 俯仰框架基本电气参数
Table 1 Basic electrical parameters of pitching frame
Parameters Value Unit Moment of inertia 0.014 kg⋅m2 Armature resistance 14 Ω Armature inductance 7.5 mH Back-emf coefficient 0.28 V/rad/s Moment coefficient 0.28 Nm/A Gyro filter frequency 50 Hz 表 2 不同算法作用的视轴稳定精度
Table 2 Optical axis stability accuracy for different algorithms
μrad Disturbance Traditional double-closed loop Improved double-closed loop Singer PI Square PI Square PI+DOB_PI Square PI+DOB_PI-PI 1°/1 Hz 1168 30.3 3.744 2.85 2.7817 1°/2 Hz 2161 223.3 53.68 39.943 38.199 表 3 摇摆台不同扰动条件下俯仰框架的视轴稳定精度
Table 3 Pitch-optical-axis stability accuracy with different disturbance of swing platform
Disturbance Single closed-loop/μrad Our method/μrad Decreasing percentage/% 1°/1 Hz 98.48 35.85 63.60 1°/2 Hz 394.4 119.1 69.80 表 4 与部分代表性光电系统的稳定精度对比
Table 4 Comparison of stability accuracy with some representative optic-electric systems
-
[1] 刘忠领, 于振红, 李立仁, 等. 红外搜索跟踪系统的研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 现代防御技术, 2014, 42(2): 95-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDFJ201402019.htm LIU Zhongling, YU Zhenhong, LI Liren, et al. Status and development trend of infrared search and track system[J]. Modern Defence Technology, 2014, 42(2): 95-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDFJ201402019.htm
[2] 吴晗平. 红外搜索系统[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2013. WU Hanping. Infrared Search System[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2013.
[3] 熊辉, 林宇, 张雁伟, 等. 一种基于小惯量红外稳定平台的复合电流控制方法[J]. 红外技术, 2021, 43(2): 116-126. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/cn/article/id/ad79c87b-95eb-4f5a-b6ff-92dda5b2dc72 XIONG Hui, LIN Yu, ZHANG Yanwei, et al. A composite current control method based on small inertia infrared stable platform[J]. Infrared Technology, 2021, 43(2): 116-126. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/cn/article/id/ad79c87b-95eb-4f5a-b6ff-92dda5b2dc72
[4] 唐涛, 马佳光, 陈洪斌, 等. 光电跟踪系统中精密控制技术研究进展[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(10): 3-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDGC202010001.htm TANG Tao, MA Jiaguang, CHEN Hongbin, et al. A review on precision control methodologies for optical-electric tracking control system[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2020, 47(10): 3-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDGC202010001.htm
[5] 谢瑞宏. 机载光电平台伺服系统稳定与跟踪控制技术的研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所, 2017. XIE Ruihong. The Research of Stabilization and Tracking Control Techniques on Airborne Opto-electric Platform Servo System[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Science, 2017.
[6] 姬伟. 陀螺稳定光电跟踪平台伺服控制系统研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2006. JI Wei. Research on Servo Control System of Gyro Stabilized and Opto-Electronic Tracking Platform[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2017.
[7] 方宇超. 光电跟踪稳定平台控制系统关键技术研究[D]. 长春: 长春理工大学, 2018. FANG Yuchao. Research on Key Technologies of Control System for Photoelectric Tracking Stabilized Platform[D]. Changchun: Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2018.
[8] 孔德杰. 机载光电平台扰动力矩抑制和改善研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院长春光学机密机械与物理研究所, 2013. KONG Dejie. Restraints and improvement of disturbance torque of airborne optoelectronic platform[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2013.
[9] 魏伟. 高精度机载光电平台视轴稳定技术研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院长春光学机密机械与物理研究所, 2015. WEI Wei. The Research of Optical axis stabilization of the Airborne Photoelectric Platform[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015.
[10] 蔡华祥. 望远镜中跟踪架的扰动补偿及精密控制技术研究[D]. 成都: 中国科学院光电技术研究所, 2016. CAI Huaxiang. Disturbance Compensation and Precision Control Techniques of Tracking Gimbal on Telescope[D]. Chengdu: Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016.
[11] 刘京. 基于永磁同步电机的大型望远镜低速伺服系统研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所, 2018. LIU Jing. Research on Low-Speed Servo System of Large Telescope based on Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2018.
[12] 唐涛, 杨涛, 黄永梅, 等. 具有延迟特性的FSM系统中PI-PI控制器[J]. 光电工程, 2013, 40(5): 1-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDGC201305003.htm TANG Tao, YANG Tao, HUANG Yongmei, et al. PI-PI controller for the time delay control system of FSM[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2013, 40(5): 1-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDGC201305003.htm
[13] 张良总, 杨涛, 吴云, 等. 基于图像测量的Stewart平台双阶控制技术[J]. 光电工程, 2022, 49(8): 220019. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDGC202208006.htm ZHANG Liangzong, YANG Tao, WU Yun, et al. Image measurement-based two-stage control of Stewart platform[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2022, 49(8): 220019. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDGC202208006.htm
[14] 嵇婷, 纪明, 胥青青, 等. 机载光电稳定平台建模及动态特性分析[J]. 激光与红外, 2021, 51(2): 206-211. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGHW202102013.htm JI Ting, JI Ming, XU Qingqing, et al. Modeling and dynamic characteristics analysis of airborne photoelectric stabilization platform[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2021, 51(2): 206-211. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGHW202102013.htm
[15] 任维. 运动平台下光电跟踪系统的抗扰控制技术研究[D]. 成都: 中国科学院光电技术研究所, 2020. REN Wei. Research on Anti-interference Control Technology of Optoelectronic Tracking System Under Moving Platform[D]. Chengdu: Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020.
[16] 王正玺. 机载光电侦察平台高精度视轴稳定及像移补偿控制技术研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所, 2019. WANG Zhengxi. Research on High Precision LOS Stabilization and Image Motion Compensation Control Technology of Aeronautical Photoelectric Stabilization Platform[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019.
[17] 夏先齐. 航空光电稳定平台粗精双稳定控制研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所, 2021. XIA Xianqi. Research on Coarse and Fine Dual Stability Control of Aviation Photoelectric Stabilized Platform[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2021.
[18] 张艳, 张淑梅, 乔彦峰, 等. 基于舰载光电设备参考模型扰动估计的前馈控制[J]. 光学精密工程, 2013, 21(5): 1213-1221. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXJM201305016.htm ZHANG Yan, ZHANG Shumei, QIAO Yanfeng, et al. Feedforward control based on reference model disturbance observer of carrier-based optoelectronic theodolite[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2013, 21(5): 1213-1221. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXJM201305016.htm
[19] MA Rongqi, WANG Qiang, XIA Yunxia, et al. Disturbance com-pensation of a multiaperture imaging system based on a coupling rotating prism using an improved model compensation control[J]. Applied Optics, 2021, 60(16): 4798-4806.
[20] 阎歆婕, 林宇, 李建, 等. 温度约束的MEMS陀螺零漂补偿模型[J]. 红外技术, 2017, 39(1): 73-80. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/cn/article/id/hwjs201701014 YAN Xinjie, LIN Yu, LI Jian, et al. Compensation model of MEMS gyroscope's null shift based on temperature constraint algorithm[J]. Infrared Technology, 2017, 39(1): 73-80. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/cn/article/id/hwjs201701014
[21] 乔治∙埃利斯. 控制系统设计指南[M]. 4版: 汤晓君译. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2016. George Ellis. Control System and Design Guide[M]. 4th Edition: Tang Xiaojun translated. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2016.
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 陆玉. 基于大数据分析的红外图像非均匀性自动化校对. 佳木斯大学学报(自然科学版). 2025(01): 39-42 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 院霖享,董霙达,多化琼,王明涛. 基于多尺度融合与USM的蒙古族家具纹样增强研究. 林产工业. 2024(02): 29-33 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 徐慧琳,赵鑫,于波,韦小牙,胡鹏. 一种多分辨率特征提取红外图像语义分割算法. 红外技术. 2024(05): 556-564 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 杨家全,李邦源,丁贞煜,马文龙,汪航,孙宏滨. 基于多重先验的无监督学习红外图像增强算法. 云南电力技术. 2024(02): 33-40 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 薛峰,陶海峰. 三维虚拟图像中动态特征增强算法设计. 吉林大学学报(信息科学版). 2024(05): 840-846 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)



 下载:
下载: