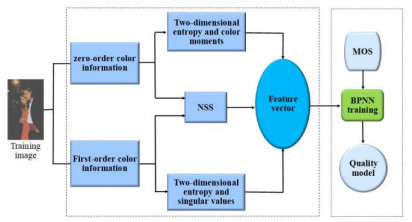
No-reference Quality Evaluation Algorithm for Color Gamut Mapped Images Based on Double-Order Color Information
-
摘要:
色域映射是用于在不同设备之间实现彩色图像高保真传输的一种技术。但通过色域映射得到的图像不可避免因颜色信息的损失产生严重的伪影和失真,从而导致纹理结构失真和色彩自然度失真。基于颜色信息损失严重的事实,本文提出了一种基于双阶颜色表示的无参考质量评价方法。传统图像质量评价方法大多基于灰度域提取质量感知特征,少数考虑颜色信息的方法也仅从色调、饱和度等颜色分量中提取特征。色调、饱和度均是通过R、G、B三个颜色分量线性计算而得,忽略了颜色的导数信息。因此本文算法从零阶颜色信息(R、G、B颜色分量)和一阶颜色信息(即导数信息)中进行特征提取,并将所提特征进行回归训练得到质量预测模型。实验证明,该模型对色域映射图像质量的预测性能优于现有的无参考质量评价方法。
Abstract:Gamut mapping is a technology used to achieve high-fidelity transmission of color images between different devices. However, an image obtained through gamut mapping inevitably produces serious artifacts and distortions because of color information loss, which leads to distortions in texture and color naturalness. Since color information loss is serious in gamut mapped images (GMIs), a no-reference quality evaluation method based on double-order color representation is proposed. Many traditional image quality assessment (IQA) methods extract quality-aware features (QAFs) in the gray domain, and a few IQA methods extract QAFs from color components, such as hue and saturation. Hue and saturation were calculated linearly using the R, G, and B color components while ignoring the derivative information of the color. Therefore, this study extracted features from zero-order (R, G, and B components) and first-order (derivative) color information. These features were then used for regression training to obtain a quality prediction model. Experimental results show that the model is superior to existing no-reference quality evaluation methods in predicting the quality of GMIs.
-
-
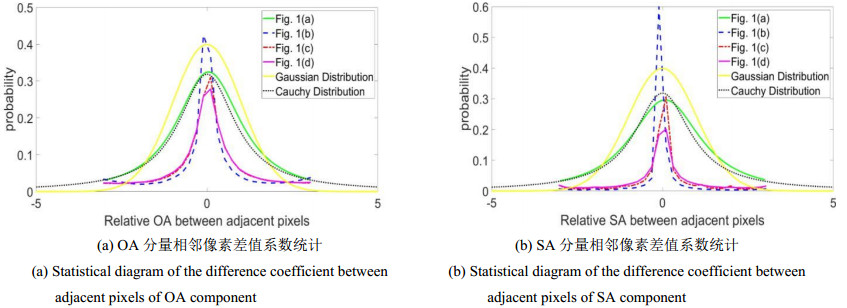
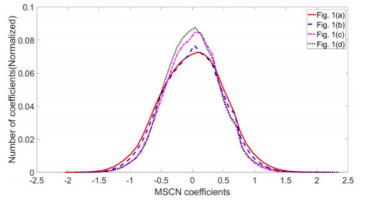
图 2 原始高清图像和色域映射图像在零阶和一阶的颜色分量图。(a) 原始图像;(b)-(f)分别为(a)的OA、SA、R、G、B分量图;(g) 色域映射图像;(h)-(l)分别为(g)的OA、SA、R、G、B分量图
Figure 2. Zero-order and first-order color component of original image and GMI. (a) is the original image; (b)-(f) are OA、SA、R、G、B component of (a) respectively; (g) is the GMI; (h)-(l) are OA、SA、R、G、B component of (g) respectively
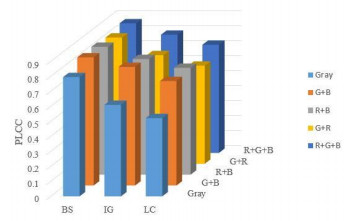
表 1 三个数据库中算法性能比较
Table 1 Comparative evaluation on the three gamut mapping databases
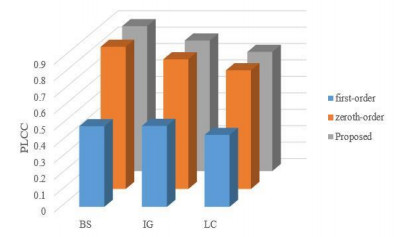
Method BS database IG database LC database PLCC SRCC KRCC PLCC SRCC KRCC PLCC SRCC KRCC BRISQUE 0.7633 0.5678 0.4126 0.5153 0.4654 0.3345 0.5026 0.5274 0.3802 DESIQUE 0.8213 0.5941 0.4354 0.5987 0.5666 0.4211 0.5692 0.5973 0.4429 NFERM 0.7441 0.5566 0.4072 0.4399 0.4510 0.2968 0.4934 0.4985 0.3617 IDEAL 0.7859 0.6652 0.4994 0.6195 0.6139 0.4550 0.5780 0.5989 0.4417 GMNSS 0.8170 0.6774 0.5100 0.7369 0.7086 0.5526 0.6256 0.6154 0.4630 GMCSD 0.8374 0.7028 0.5402 0.7508 0.7273 0.5633 0.6778 0.6848 0.5152 BLGS 0.7865 0.7275 0.5116 0.7464 0.7165 0.5147 0.7573 0.7074 0.5033 GMLCH 0.8385 0.7069 0.5337 0.6302 0.6039 0.4523 0.6565 0.6498 0.4876 BOSS 0.4830 0.4826 0.3531 0.4573 0.4318 0.3167 0.7035 0.6021 0.4490 VQGC 0.8315 0.7016 0.5334 0.5732 0.5442 0.4057 0.6298 0.6332 0.4675 Proposed 0.8816 0.7394 0.5735 0.7944 0.7586 0.5929 0.7252 0.7360 0.5655 表 2 NSS特征与非NSS统计特征的性能对比
Table 2 Performance comparison of NSS features with NON-NSS statistical features
BS IG LC PLCC SRCC KRCC PCC SRCC KRCC PCC SRCC KRCC NSS 0.8098 0.6799 0.5171 0.5891 0.5721 0.4175 0.6550 0.6634 0.4928 NO NSS 0.7038 0.4725 0.3394 0.5645 0.5241 0.3912 0.4713 0.3620 0.2677 Proposed 0.8816 0.7394 0.5735 0.7944 0.7586 0.5929 0.7252 0.7360 0.5655 -
[1] LI H L, ZHAO H X, LIU M N, et al. Research on spatial gamut mapping from source device to destination device[C]//2023 IEEE 18th Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications. 2023: 1909-1914.
[2] Zamir S W, Vazquez Corral J, Bertalmio M. Vision models for wide color gamut imaging in cinema[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(5): 1777-1790. DOI: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2938499
[3] Takeuchi M, Sakamoto Y, Yokoyama R. Gamut-extension methods considering color information restoration[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 80146-80158. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2923400
[4] Prashanth N, Dattathreya, Manjunath P, et al. High Dynamic Range (HDR) Imaging using Color Gamut Mapping[C]//2018 4th International Conference on Applied and Theoretical Computing and Communication Technology (iCATccT), 2018: 2104-2112.
[5] KIM J O, LEE K, KIM J, et al. Ambient light robust color gamut mapping for optical see-through displays[J]. Optics Express, 2020, 28(10): 15392-15405. DOI: 10.1364/OE.391447
[6] ZHOU W, WANG Z. Blind omnidirectional image quality assessment: integrating local statistics and global semantics[C]//2023 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, 2023: 1405-1409.
[7] 李佳, 郑元林, 廖开阳, 等. 基于显著性深层特征的无参考图像质量评价算法[J]. 计算机应用, 2022, 42(6): 1957-1964. LI Jia, ZHENG Yuanlin, LIAO Kaiyang, et al. No-reference image quality assessment algorithm based on saliency deep features[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2022, 42(6): 1957-1964.
[8] CAI H, LI L D, YI Z L, et al. Towards a blind image quality evaluator using multi-scale second-order statistics[J]. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2019, 71: 88-99. DOI: 10.1016/j.image.2018.11.003
[9] 杨国梁, 苏俊宏, 薛鹏翔, 等. 基于深度学习网络的可见光图像重构质量评价研究[J]. 激光杂志, 2022, 43(1): 95-100. YANG Guoliang, SU Junhong, XUE Pengxiang, et al. Evaluation of visible image reconstruction quality based on deep learning network[J]. Laser Journal, 2022, 43(1): 95-100.
[10] 柴改霞, 郭全民, 孙晓娟. 可见光与红外融合的汽车抗晕光图像评价方法[J]. 红外技术, 2020, 42(4): 378-384. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/hwjs202004011 CHAI Gaixia, GUO Quanmin, SUN Xiaojuan. Vehicle anti-halation image evaluation method based on visible and infrared fusion[J]. Infrared Technology, 2020, 42(4): 378-384. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/hwjs202004011
[11] Mittal A, Moorthy A K, Bovik A C. No-reference image quality assessment in the spatial domain[J]. IEEE Transactions Image Processing, 2012, 21(12): 4695-4708. DOI: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2214050
[12] ZHANG Y, Chandler D M. No-reference image quality assessment based on log-derivative statistics of natural scenes[J]. Journal of Electronic Imaging, 2013, 22(4): 043025. DOI: 10.1117/1.JEI.22.4.043025
[13] WANG Z, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R, et al. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600-612. DOI: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861
[14] 余伟, 徐晶晶, 刘玉英, 等. 基于自然场景统计的色域映射图像无参考质量评价[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2020, 57(14): 61-70. YU Wei, XU Jingjing, LIU Yuying, et al. No-reference quality evaluation for gamut mapping images based on natural scene statistics[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(14): 61-70.
[15] CAI H, LI L D, YI Z L, et al. Blind quality assessment of gamut-mapped images via local and global statistical analysis[J]. Journal of Visual Communication & Image Representation, 2019, 61(5): 250-259.
[16] 余伟, 康凯, 袁连海. 基于颜色与结构失真的色域映射图像无参考质量评价算法[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2021, 38(8): 2549-2555. YU Wei, KANG Kai, YUAN Lianhai. No-reference quality evaluation algorithm for gamut mapping images based on color and structural distortions[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2021, 38(8): 2549-2555.
[17] JAMES F P. 计算机视觉基础[M]. 章毓晋, 译. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2019: 21-27. JAMES F P. Foundations of Computer Vision[M]. ZHANG YuJin, translated. Beijing: TsingHua University Press, 2019: 21-27.
[18] LEE D, Plataniotis K N. Toward a no-reference image quality assessment using statistics of perceptual color descriptors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(8): 3875-3889.
[19] TAN M T, Ryu S. Particle number fluctuations, Rényi entropy, and symmetry-resolved entanglement entropy in a two-dimensional Fermi gas from multidimensional bosonization[J]. Physical Review B, 2020, 101(23): 2469-2450.
[20] Estanon C R, Aquino N, Puertas-Centeno D, et al. Two-dimensional confined hydrogen: An entropy and complexity approach[J]. International Journal of Quantum Chemistry, 2020, 120(11): 1596-1605.
[21] ZHOU Y, LI L D, WU J J, et al. Blind quality index for multiply distorted images using biorder structure degradation and nonlocal statistics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2018, 20(11): 3019-3032. DOI: 10.1109/TMM.2018.2829607
[22] 吴圳桦, 唐文艳, 吕文阁, 等. 基于ISSA何积分图的二维熵图像多阈值分割快速算法[J]. 广东工业大学学报, 2023, 40(5): 47-55. WU Zhenhua, TANG Wenyan, LYU Wenge, et al, Fast image segmentation with multilevel threshold of twodimensional entropy based on issa and integral graph[J]. Journal of Guangdong University of Technology, 2023, 40(5): 47-55.
[23] 胡涛. 基于图像二维熵的路面纹理边缘分布均匀性检测方法研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉科技大学, 2023: 15-17. HU Tao. Research on Detection Method of Pavement Texture Edge Distribution Uniformity Based on Two-Dimensional Image Entropy[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2023: 15-17.
[24] FANG Y M, MA K D, WANG Z, et al. No-reference quality assessment of contrast-distorted images based on natural scene statistics[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2015, 22(7): 838-842.
[25] ZHOU Y, LI L D, ZHU H C, et al, No-reference quality assessment for contrast-distorted images based on multifaceted statistical representation of structure[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and image Representation, 2019, 60: 158-169.
[26] WANG W, LIANG R, QI Y, et al, Prediction model of spontaneous combustion risk of extraction borehole based on PSO-BPNN and its application[J]. Scientific Reports, 2024, 14(1): 577-581.
[27] Baranczuk Z, Zolliker P, Image-Individualized Gamut Mapping Algorithms[J]. Journal of Imaging Science & Technology, 2010, 54(3): 0302011-0302017.
[28] 余伟. 色域映射图像客观质量评价方法研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2020: 17-29. YU Wei. Study on Objective Quality Evaluation Method of Gamut Mapped Images[D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2020: 17-29.
[29] GU K, ZHAI G T, YANG X K, et al. Using free energy principle for blind image quality assessment[J]. IEEE Transaction on Multimedia, 2015, 11(1): 50-63.
[30] FANG Y M, YAN J B, DU R G et al. Blind quality assessment for tone-mapped images by analysis of gradient and chromatic statistics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2021, 23: 955-966.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 刘文强,姜迈,乔顺利,李宏达. 面向双模态夜视图像的混合尺度融合算法. 兵器装备工程学报. 2024(05): 291-298 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王金生,周元元,陈珺. 基于残差Swin Transformer模块的红外与可见光图像融合研究. 苏州市职业大学学报. 2024(02): 55-62 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 陈彦林,王志社,邵文禹,杨帆,孙婧. 红外与可见光图像多尺度Transformer融合方法. 红外技术. 2023(03): 266-275 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: