HRformer: Hierarchical Regression Transformer for Infrared Small-Target Detection
-
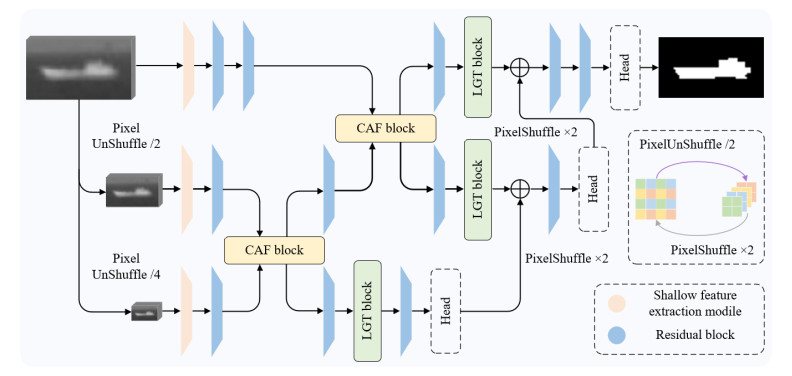
摘要: 红外小目标检测是指从低信噪比、复杂背景的红外图像中对小目标进行检测,在海上救援、交通管理等应用中具有重要实际意义。然而,由于图像分辨率低、目标尺寸小以及特征不突出等因素,导致红外目标很容易淹没在包含噪声和杂波的背景中,如何精确检测红外小目标的外形信息仍然是一个挑战。针对上述问题,构建了一种基于多级回归Transformer(HRformer)网络的红外小目标检测算法。具体来说,首先为了在获得多尺度信息的同时尽可能避免原始图像信息的损失,采用像素逆重组(PixelUnShuffle)操作对原始图像下采样来获取不同层级网络的输入,同时采用一种可学习的像素重组(PixelShuffle)操作对每一层级的输出特征图进行上采样,提升了网络的灵活性;接着,为实现网络中不同层级特征之间的信息交互,本文设计了一种包含空间注意力计算分支以及通道注意力计算分支在内的交叉注意力融合(cross attention fusion, CAF)模块实现特征高效融合以及信息互补;最后,为进一步提升网络的检测性能,结合普通Transformer结构具有较大感受野以及基于窗口的Transformer结构具有较少计算复杂度的优势,提出了一种局部-全局Transformer(LGT)结构,能够在提取局部上下文信息的同时对全局依赖关系进行建模,计算成本也得到节省。实验结果表明,与目前较为先进的一些红外小目标检测算法相比,本文所提出的算法具有更高的检测精度,同时具有较少的参数量,在解决实际问题中更有意义。
-
关键词:
- 红外图像 /
- 弱小目标检测 /
- Transformer /
- 图像分割
Abstract: Infrared small-target detection refers to the detection of small targets in infrared images with low signal-to-noise ratios and complex backgrounds. Infrared small-target detection is essential in applications, such as maritime rescue and traffic management. However, because of factors such as low image resolution, small target size, and inconspicuous features, infrared targets are prone to submergence in a background that contains noise and clutter. The accurate detection of the shape information of small infrared targets remains a challenge. An infrared small-target detection algorithm based on a hierarchical regression transformer (HRformer) network was constructed to address these problems. Specifically, the PixelUnShuffle operation was leveraged to downsample the original image and obtain the input of different network levels to obtain multiscale information while minimizing the loss of the original image information. The PixelShuffle operation upsamples the output feature map of each level, improving the flexibility of the network. Next, a cross-attention fusion module that includes the spatial and channel attention calculation branches realizes efficient feature fusion and information complementarity to realize the information interaction between different levels of features in the network. Finally, combined with the ordinary Transformer structure, which has a large receptive field, and the window-based Transformer, which has the advantage of minimal computational complexity, a local–global transformer structure is proposed to further improve the detection performance of the network and reduce computational costs. The proposed structure can model global dependencies while extracting local context information. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm has a higher detection accuracy and fewer parameters than some advanced infrared small-target detection algorithms. Therefore, the proposed algorithm is suitable for solving practical problems.-
Keywords:
- infrared images /
- small target detection /
- transformer /
- image segmentation
-
-
表 1 消融实验结果
Table 1 Ablation experimental results
Experiment Shuffle CAF LGT IoU nIoU Pd Fa 1 × √ √ 75.00 73.62 97.25 31.14 2 √ × √ 74.36 74.00 98.17 36.59 3 √ √ × 74.85 73.65 97.25 45.51 4 √ × × 70.56 72.47 98.17 61.58 5 × √ × 71.16 72.48 98.17 63.67 6 × × √ 68.74 71.53 97.86 68.67 7 × × × 65.28 68.12 97.25 69.06 8 √ √ √ 76.07 74.43 98.17 24.44 表 2 对比实验结果
Table 2 Experimental results comparison of different algorithms
Method IoU ↑ nIoU ↑ Pd↑ Fa↓ Number of parameters↓ Inference time per image↓/s WSLCM 4.41 33.82 91.74 22593 - - TLLCM 3.51 21.75 92.66 26498 - - IPI 2.62 4.16 84.40 203.07 - - NRAM 45.68 55.49 85.32 161.15 - - PSTNN 51.95 62.66 82.57 394.29 - - MSLSTIPT 20.21 24.74 82.57 259.75 - - MDvsFA 45.28 48.16 76.15 166.07 3.77 M 0.0985 ACM 67.96 71.05 97.25 72.92 387.19K 0.0317 AGPCNet 64.26 70.05 98.16 120.56 12.36M 0.1413 IAANet 75.42 73.53 98.10 24.68 9.09M 0.0704 ALCNet 73.43 71.44 97.84 25.68 384.79k 0.0804 HRformer 76.07 74.43 98.17 24.44 182.46k 0.0304 -
[1] LI Z M, MEI L F, SONG M. A survey on infrared weak small target detection method[C]//Advanced Materials Research, 2014, 945: 1558-1560.
[2] BAI X, ZHOU F. Analysis of new top-hat transformation and the application for infrared dim small target detection[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2010, 43(6): 2145-2156. DOI: 10.1016/j.patcog.2009.12.023
[3] XU Y, ZHANG J. Real-time detection algorithm for small space targets based on max-median filter[J]. Journal of Information & Computational Science, 2014, 11(4): 1047-1055.
[4] CHEN C L P, LI H, WEI Y, et al. A local contrast method for small infrared target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 52(1): 574-581.
[5] HAN J, Moradi S, Faramarzi I, et al. Infrared small target detection based on the weighted strengthened local contrast measure[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 18(9): 1670-1674.
[6] HOU X, ZHANG L. Saliency detection: a spectral residual approach[C]//2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2007: 1-8.
[7] DAI Y, WU Y. Reweighted infrared patch-tensor model with both nonlocal and local priors for single-frame small target detection[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2017, 10(8): 3752-3767. DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2017.2700023
[8] GAO C, MENG D, YANG Y, et al. Infrared patch-image model for small target detection in a single image[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(12): 4996-5009. DOI: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2281420
[9] ZHANG L, PENG L, ZHANG T, et al. Infrared small target detection via non-convex rank approximation minimization joint l 2, 1 norm[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(11): 1821. DOI: 10.3390/rs10111821
[10] ZHANG L, PENG Z. Infrared small target detection based on partial sum of the tensor nuclear norm[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(4): 382. DOI: 10.3390/rs11040382
[11] ZHANG Z, REN J, LI S, et al. Robust subspace discovery by block-diagonal adaptive locality-constrained representation[C]//Proceedings of the 27th ACM international conference on multimedia, 2019: 1569-1577.
[12] GUO J, WU Y, DAI Y. Small target detection based on reweighted infrared patch‐image model[J]. IET Image Processing, 2018, 12(1): 70-79. DOI: 10.1049/iet-ipr.2017.0353
[13] 谷雨, 张宏宇, 孙仕成. 融合多尺度分形注意力的红外小目标检测模型[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44: 332-341. GU Yu, ZHANG Hongyu, SUN Shicheng. Infrared small target detection model with multi-scale fractal attention[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44: 332-341.
[14] 邵斌, 杨华, 朱斌, 等. 基于实时语义分割的红外小目标检测算法[J/OL]. [2023-01-14]. 激光与光电子学进展, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/31.1690.TN.20221031.1649.140.html. SHAO Bin, YANG Hua, ZHU Bin, et al. Infrared small target detection algorithm based on real-time semantic segmentation[J/OL]. [2023-01-14]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/31.1690.TN.20221031.1649.140.html.
[15] DAI Y, WU Y, ZHOU F, et al. Attentional local contrast networks for infrared small target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(11): 9813-9824. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3044958
[16] WANG H, ZHOU L, WANG L. Miss detection vs. false alarm: adversarial learning for small object segmentation in infrared images[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2019: 8509-8518.
[17] CHEN Y, LI L, LIU X, et al. A multi-task framework for infrared small target detection and segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 1-9.
[18] 张传聪, 李范鸣, 饶俊民. 基于特征显著性融合的红外小目标检测[J]. 半导体光电, 2022, 43(4): 828-834. ZHANG Chuancong, LI Fanming, RAO Junmin. Infrared small target detection based on feature saliency fusion[J]. Semiconductor Optoelectronics, 2022, 43(4): 828-834.
[19] 王翔. 一种复杂海空背景下的红外小目标检测跟踪算法[J]. 光学与光电技术, 2022, 20(2): 113-119. WANG Xiang. A detecting and tracking algorithm for the infrared small targets under the complex sea-sky background[J]. Optics & Optoelectronic Technology, 2022, 20(2): 113.
[20] 薛锡瑞, 黄树彩, 马佳顺, 等. 基于局部熵参考预处理的RPCA红外小目标检测[J]. 红外技术, 2021, 43(7): 649-657. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/e8541151-1530-4561-ad38-42349b5da1b8 XUE Xirui, HUANG Shucai, MA Jiashun, et al. RPCA infrared small target detection based on local entropy reference in preprocessing[J]. Infrared Technology, 2021, 43(7): 649-657. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/e8541151-1530-4561-ad38-42349b5da1b8
[21] 朱硕雅, 杨德振, 贾鹏, 等. 时空联合红外小目标检测算法的设计与实现[J]. 激光与红外, 2021, 51(3): 388-392. ZHU Shuoya, YANG Dezhen, JIA Peng, et al. Design and implementation of space-time combined infrared small target detection algorithm[J]. Laser and Infrared, 2021, 51(3): 388-392
[22] CHEN G, WANG W, TAN S. IRSTFormer: a hierarchical vision transformer for infrared small target detection[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(14): 3258. DOI: 10.3390/rs14143258
[23] 高峰, 孟德森, 解正源, 等. 基于Transformer和动态3D卷积的多源遥感图像分类[J/OL] [2023-01-14]. 北京航空航天大学学报, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=uzDkwlsKYf_a0mkJDLhoUifLD_CLUjdAHAXvAIM2Oc2U81D9gbL0OG9MgFUoxoPmlYbrUvlkvxOIE-erLa83gdCWbMK_cSetqEA_ 5TqvJOrbmH9oh0lf U4gQL71 LgQeJUj -SQGWx29E=&uniplatform= NZKPT&language= CHS. GAO Feng, MENG Desen, XIE Zhengyuan, et al. Multi-source remote sensing image joint classification based on transformer and dynamic 3D-convolution[J/OL]. [2023-01-14]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract? v=uzDkwlsKYf_a0mkJDLhoUifLD_CLUjdAHAXvAIM2Oc2U81D9gbL0OG9MgFUoxoPmlYbrUvlkvxOIE-erLa83gdCWbMK_cSetqEA_ 5Tq vJOrbmH9oh0lfU4gQL71LgQeJUj-SQGWx29E=&uniplatform=NZKPT &language=CHS.
[24] Jonnalagadda A, WANG W Y, Manjunath B S, et al. Foveater: Foveated transformer for image classification[J/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2105.14173, 2021.
[25] HAN K, XIAO A, WU E, et al. Transformer in transformer[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2021, 34: 15908-15919.
[26] LIU Z, LIN Y, CAO Y, et al. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2021: 10012-10022.
[27] ZHANG X, ZHOU X, Lin M, et al. Shufflenet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018: 6848-6856.
[28] DAI Y, WU Y, ZHOU F, et al. Asymmetric contextual modulation for infrared small target detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision, 2021: 950-959.
[29] WANG K, DU S, LIU C, et al. Interior attention-aware network for infrared small target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60: 1-13.
[30] ZHANG T, CAO S, PU T, et al. Agpcnet: attention-guided pyramid context networks for infrared small target detection[J/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2111.03580, 2021.
[31] HAN J, Moradi S, Faramarzi I, et al. Infrared small target detection based on the weighted strengthened local contrast measure[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2020, 18(9): 1670-1674.
[32] CHEN C L P, LI H, WEIY, et al. A local contrast method for small infrared target detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2013, 52(1): 574-581.
[33] GAO C, MENG D, YANG Y, et al. Infrared patch-image model for small target detection in a single image[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(12): 4996-5009. DOI: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2281420
[34] ZHANG L, PENG L, ZHANG T, et al. Infrared small target detection via non-convex rank approximation minimization joint l 2, 1 norm[J]. Remote Sensing, 2018, 10(11): 1821. DOI: 10.3390/rs10111821
[35] ZHANG L, PENG Z. Infrared small target detection based on partial sum of the tensor nuclear norm[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(4): 382. DOI: 10.3390/rs11040382
[36] SUN Y, YANG J, AN W. Infrared dim and small target detection via multiple subspace learning and spatial-temporal patch-tensor model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2020, 59(5): 3737-3752.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 张天旭,黄慧,黄丙仓,马燕,徐傲,李晓艳,周孝雯,刘之之. 基于多尺度聚合与高分辨率增强的CTA脑血管分割模型. 计算机工程. 2025(04): 37-46 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 赵欣洋,沈一伟,尹琦云,刘志远,陆洪建,李庆武. 变电站场景下的红外图像鸟类小目标检测方法. 应用科技. 2024(06): 59-67 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)



 下载:
下载: