Infrared and Visible Light Image Fusion Based on Mahalanobis Distance and Guided Filter Weighting
-
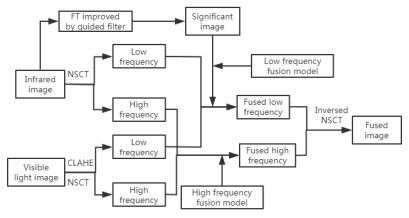
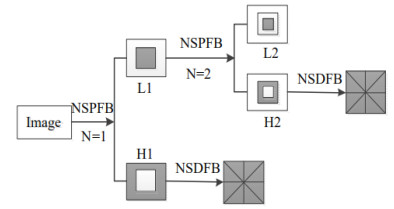
摘要: 为使红外与可见光融合图像获得更好的分辨率和清晰度,提出基于非下采样轮廓波变换(non-subsampled contourlet transform, NSCT)的马氏距离加权拉普拉斯能量和与引导滤波改进(frequency tuned, FT)结合的红外与可见光图像融合算法。首先,对可见光图像进行对比度受限的自适应直方图均衡(contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization, CLAHE),并将红外图像与CLAHE处理后可见光图像进行NSCT变换,分解为低频和高频; 其次,对FT算法使用引导滤波进行改进,利用改进的FT算法提取红外图像显著性图自适应加权融合低频图像,对高频图像使用基于马氏距离加权的拉普拉斯能量和取大融合; 最后,对融合的低频和高频图像进行NSCT逆变换获得融合图像。实验结果表明,该融合方法相较其他传统融合方法,在主观视觉上和客观指标上都有较好的表现。Abstract: To improve the definition of fusion images and obtain better target information during the fusion of infrared and visible light images using the characteristics of non-subsampled contourlet transform(NSCT) coefficients, an Manalanobis distance weighted Laplacian energy combined with guided filtering is proposed to improve the frequency tuned (FT) algorithm. First, the visible light image is subjected to contrast limited adaptive histogram equalization(CLAHE), and the infrared image and the CLAHE processed visible light image are decomposed into a low-frequency approximate image and a high-frequency detail image through a multi-scale and multi-directional NSCT transform. Second, the FT algorithm improved by guided filtering isused to extract the significance graph of infrared images, the adaptive weighted fusion rule based on the significance graph of infrared images is used for low-frequency images, and the fusion rule based on the Laplace energy and maximum weighted by the Manalanobis distance is used for high-frequency images. Finally, the fusion image is obtained by the NSCT inverse transformation of the fused low-frequency and high-frequency images. The experimental results show that this fusion method has better performance in terms of subjective vision and objective indexes than other traditional fusion methods.
-
-
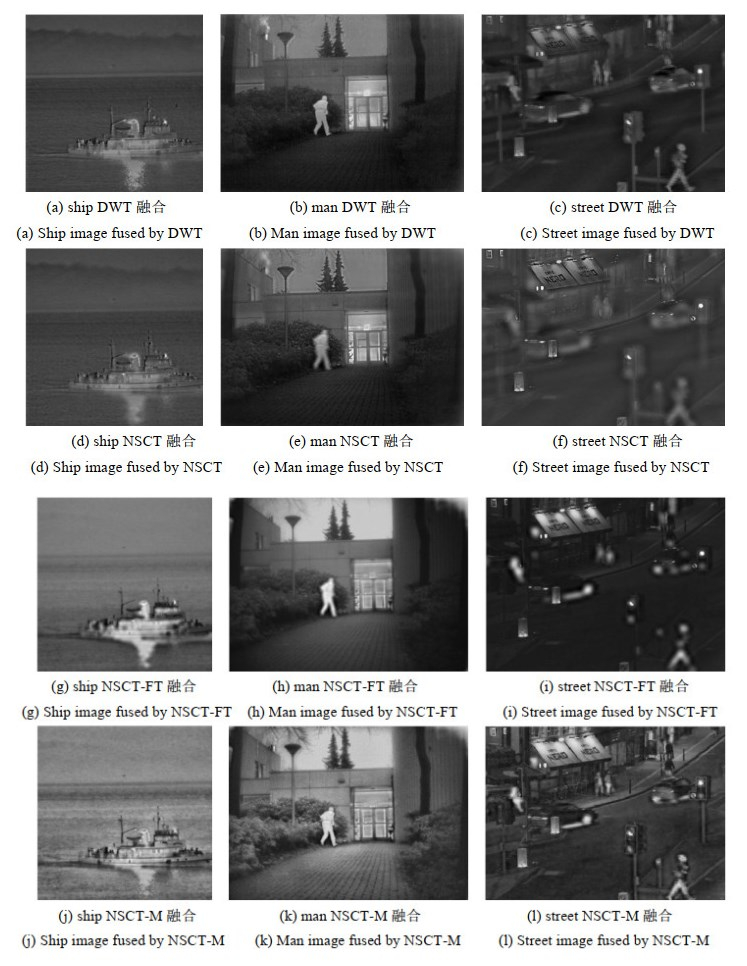
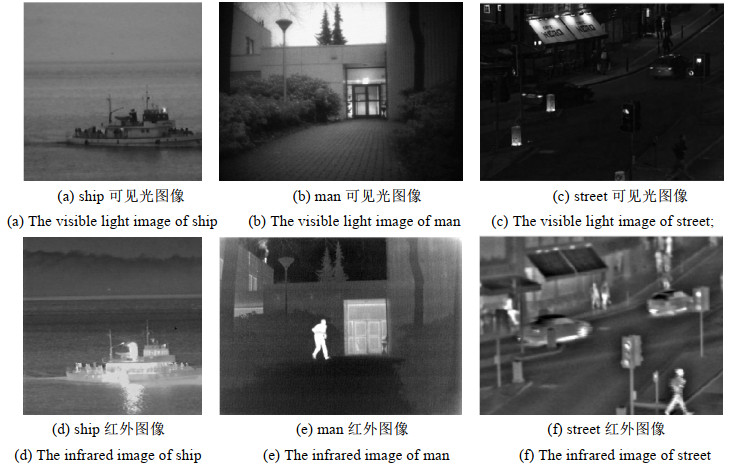
表 1 融合图像客观评价结果
Table 1 Objective evaluation results of fusion image
Image name Fusion method EI SD AG SF Ship DWT 4.9016 10.4666 1.4100 3.1531 NSCT 4.9139 10.4807 1.3980 3.1546 NSCT-FT 5.9540 21.1184 1.6376 3.9024 NSCT-M 6.5735 25.8154 4.7976 10.1821 Man DWT 6.5266 31.5238 2.9829 5.5125 NSCT 6.5491 31.7851 3.2272 6.3206 NSCT-FT 7.1864 61.6516 3.4935 7.1168 NSCT-M 7.6698 58.7864 8.8359 15.5185 Street DWT 5.9299 20.6524 3.1668 7.7725 NSCT 5.9442 21.8888 3.7054 12.7396 NSCT-FT 5.5269 33.4513 4.0396 13.8090 NSCT-M 6.8136 41.2933 8.4553 20.3821 -
[1] LIU Z, CHAI Y, YIN H, et al. A novel multi-focus image fusion approach based on image decomposition[J]. Information Fusion, 2017, 35: 102-116. DOI: 10.1016/j.inffus.2016.09.007
[2] Mauri G, Cova L, Beni S D, et al. Real-time US-CT/MRI image fusion for guidance of thermal ablation of liver tumors undetectable with US: results in 295 cases[J]. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol, 2015, 38(1): 143. DOI: 10.1007/s00270-014-0897-y
[3] Tuia D, Marcos D, Camps-Valls G. Multi-temporal and multi-source remote sensing image classification by nonlinear relative normalization[J]. Isprs Journal of Photogrammetry & Remote Sensing, 2016, 120: 1-12. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0924271616301903
[4] Baviskar J, Mulla A, Kudu N, et al. Sub-band exchange DWT based image fusion algorithm for enhanced security[C]//International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics of IEEE, 2014: 534-539.
[5] ZHAO Cheng, HUANG Yongdong, QIU Shi. Infrared and visible image fusion algorithm based on saliency detection and adaptive double-channel spiking cortical model[J]. Infrared Physics and Technology, 2019: 102: 102976. DOI: 10.1016/j.infrared.2019.102976
[6] SONG Minghui, LIU Lu, PENG Yuanxi, et al. Infrared & visible images fusion based on redundant directional lifting-based wavelet and saliency detection[J]. Infrared Physics and Technology, 2019, 101: 45-55. DOI: 10.1016/j.infrared.2019.05.017
[7] 甄媚, 王书朋. 可见光与红外图像自适应加权平均融合方法[J]. 红外技术, 2019, 41(4): 341-346. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/hwjs201904008 ZHEN Mei, WANG Shupeng. An adaptive weight average fusion method for visible and infrared images[J]. Infrared Technology, 2019, 41(4): 341-346. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/hwjs201904008
[8] 甘玲, 张倩雯. 结合NSCT与引导滤波的图像融合方法[J]. 红外技术, 2018, 40(5): 444-448, 454. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/hwjs201805007 GAN Ling, ZHANG Qianwen. Image fusion method combining non-subsampled contourlet transform and guide filtering[J]. Infrared Technology, 2018, 40(5): 444-448, 454. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/hwjs201805007
[9] 刘智嘉, 贾鹏, 夏寅辉, 等. 基于红外与可见光图像融合技术发展与性能评价[J]. 激光与红外, 2019, 49(5): 633-640. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2019.05.021 LIU Zhijia, JIA Peng, XIA Yinhui, et al. Development and performance evaluation of infrared and visual image fusion technology[J]. Laser and Infrared, 2019, 49(5): 633-640. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2019.05.021
[10] 肖儿良, 刘雯雯. 多尺度梯度域可见光与红外热图像融合方法研究[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2015, 32(10): 3160-3163, 3167. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2015.10.065 XIAO Erliang, LIU Wenwen. Research of multi-scale gradient domain visible and thermal image fusion method[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2015, 32(10): 3160-3163, 3167. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2015.10.065
[11] WANG Shiying, SHEN Yan. Multi-modal image fusion based on saliency guided in NSCT domain[J]. IET Image Processing, 2020, 14(13): 3188-3201. DOI: 10.1049/iet-ipr.2019.1319
[12] 刘斌, 辛迦楠, 谌文江, 等. 不可分拉普拉斯金字塔构造及其在多光谱图像融合中的应用[J]. 计算机应用, 2019, 39(2): 564-570. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJY201902045.htm LIU Bin, XIN Jianan, CHEN Wenjiang, et al. Construction of non-separable Laplacian pyramid and its application in multi-spectral image fusion[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2019, 39(2): 564-570. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJY201902045.htm
[13] Baviskar J, Mulla A, Kudu N, et al. Sub-band exchange DWT based image fusion algorithm for enhanced security[C]//International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communications and Informatics of IEEE, 2014: 534-539.
[14] 郭全民, 王言, 李翰山. 改进IHS-Curvelet变换融合可见光与红外图像抗晕光方法[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2018, 47(11): 440-448. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYJ201811060.htm GUO Quanmin, WANG Yan, LI Hanshan. Anti-halation method of visible and infrared image fusion based on improved IHS-curvelet transform[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2018, 47(11): 440-448. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYJ201811060.htm
[15] Do Minh N, Vetterli Martin. The contourlet transform: an efficient directional multiresolution image representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing: a Publication of the IEEE Signal Processing Society, 2005, 14(12): 2091-2107. DOI: 10.1109/TIP.2005.859376
[16] 胡顺石, 丁琳, 秦建新, 等. 基于Iαβ色彩空间和Contourlet变换相结合的融合方法[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2010, 27(4): 1521-1523. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSYJ201004089.htm HU Shunshi, DING Lin, QIN Jianxin. Image fusion technique based on combination of Iαβ color space and contourlet transform[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2010, 27(4): 1521-1523. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSYJ201004089.htm
[17] HOU Yingkun, ZHAO Chunxia, LIU Mingxia. The nonsubsampled contourlet transform: theory, design, and applications[J]. International Conference on Computer Science and Software Engineering of IEEE, 2008, DOI: 10.1109/CSSE.2008.806.
[18] 刘卷舒, 蒋伟. 改进的基于非下采样的Contourlet变换的图像融合算法[J]. 计算机应用, 2018, 38(S1): 194-197. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJY2018S1046.htm LIU Juanshu, JIANG Wei. Improved image fusion algorithm based on nonsubsampled Contourlet transform[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2018, 38(S1): 194-197. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJY2018S1046.htm
[19] 常诚, 黄国荣, 常雅男, 等. 基于非下采样Contourlet变换的无人机景象匹配算法[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2014, 14(2): 137-140, 171. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2014.02.032 CHANG Cheng, HUANG Guorong, CHANG Yanan, et al. Scene matching algorithm for unmanned aerial vehicle based on nonsubsampled contourlet transform[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2014, 14(2): 137-140, 171. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2014.02.032
[20] 林子慧, 魏宇星, 张建林, 等. 基于显著性图的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 红外技术, 2019, 41(7): 640-645. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/hwjs201907008 LIN Zihui, WEI Yuxing, ZHANG Jianlin, et al. Image fusion of infrared and visible image based on saliency map[J]. Infrared Technology, 2019, 41(7): 640-645. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/hwjs201907008
[21] 刘玉婷, 陈峥, 付占方, 等. 基于CLAHE的红外图像增强算法[J]. 激光与红外, 2016, 46(10): 1290-1294. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2016.10.023 LIU Yuting, CHEN Zheng, FU Zhanfang, et al. Infrared image enhancement algorithm based on CLAHE[J]. Laser and Infrared, 2016, 46(10): 1290-1294. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2016.10.023
[22] Achanta R, Hemami S, Estrada F. Frequency-tuned salient region detection[C]//Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition of IEEE, 2009: DOI: 10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206596.
[23] 谢伟, 王莉明, 胡欢君, 等. 结合引导滤波的自适应多曝光图像融合[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2019, 55(4): 193-199. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSGG201904029.htm XIE Wei, WANG Liming, HU Huanjun, et al. Adaptive multi-exposure image fusion with guided filtering[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2019, 55(4): 193-199. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSGG201904029.htm
[24] 孙晓龙, 王正勇, 符耀庆, 等. 基于改进拉普拉斯能量和的快速图像融合[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2015, 51(5): 193-197. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSGG201505037.htm SUN Xiaolong, WANG Zhengyong, FU Yaoqing, et al. Fast image fusion based on sum of modified Laplacian[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2015, 51(5): 193-197. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSGG201505037.htm
[25] 刘光宇, 庞永杰. 基于阿尔法均值算法和马氏距离的图像自适应滤波[J]. 吉林大学学报: 工学版, 2015, 45(2): 670-674. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLGY201502050.htm LIU Guangyu, PANG Yongjie. Filter of the optical image based on alpha-trimmed mean filter and Mahalanobis distance[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Engineering and Technology Edition, 2015, 45(2): 670-674. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JLGY201502050.htm
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 胡敏,郭强,习向东,陈磊,刘杰,赵飞. 玻璃钢管材无损检测方法综述. 材料导报. 2023(S2): 594-598 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(10)



 下载:
下载: