Infrared Pedestrian Action Recognition Based on Improved Spatial-temporal Two-stream Convolution Network
-
摘要: 为了提升复杂背景下红外序列的行人动作识别精度,本文提出了一种改进的空时双流网络,该网络首先采用深度差分网络代替时间信息网络,提高时空特征的表征能力与提取效率;然后,采用基于决策级特征融合机制的代价函数对模型进行训练,可以更大限度地保留不同网络帧间图像的时空特征,更加真实地反映行人的动作类别。仿真结果表明,本文提出的改进网络在自建的红外视频数据集上获得了81%的识别精度,且计算效率也提升了25%,具有较高的工程应用价值。Abstract: This study proposes an improved spatial-temporal two-stream network to improve the pedestrian action recognition accuracy of infrared sequences in complex backgrounds. First, a deep differential network replaces the temporal stream network to improve the representation ability and extraction efficiency of spatio-temporal features. Then, the improved softmax loss function based on the decision-making level feature fusion mechanism is used to train the model, which can retain the spatio-temporal characteristics of images between different network frames to a greater extent and reflect the action category of pedestrians more realistically. Simulation results show that the proposed improved network achieves 87% recognition accuracy on the self-built infrared dataset, and the computational efficiency is improved by 25%, which has a high engineering application value.
-
0. 引言
行人动作识别是计算机视觉领域重要的研究方向,其在视频监控、智能交通、运动分析、导航制导等军事和民用领域都具有重要的研究意义和应用价值[1-3]。由于红外图像只依赖于目标本身的热辐射强度,不受复杂环境下的颜色干扰,因此基于红外图像的动作识别技术的性能不依赖于天气的影响,可以全天候全天时进行检测[4]。然而,正因为红外图像缺乏纹理颜色特征值信息,也加大了行人检测与行为识别的难度[5]。
为了提升红外行人动作识别的效果,国内外学者也提出了许多动作识别算法[6-12]。南航的丁萌教授提出了一种基于似物性和稀疏编码及空间金字塔特征提取的动作识别方法[6]。Fernando等人提出基于双密度双树复小波变换的动作识别,通过利用支持向量机(Support Vector Machines, SVM)对样本的小波熵进行动作分类和识别[7]。为了充分利用红外与可见光不同模态下互补特征,Varol提出了一种基于多模态特征融合动作识别模型,提高了低对比度目标的识别性能[8]。随着近年来硬件技术的发展,深度学习在图像处理领域得到了广泛的应用[9-12]。目前行人检测及其动作识别算法通常是基于深度学习网络,主要利用三维卷积网络、长短期记忆网络(Long Short-Term Memory, LSTM)和双流网络来自主学习高维时空特征并自动进行分类识别[10]。Kuehne[11]设计了一种基于卷积神经网络的动作识别算法,以满足辅助驾驶的需求。Ioffe等人[12]提出了一种基于多级分割模型的动作识别网络,通过对疑似区域进行深度特征提取,提取红外复杂背景下行为动作的检测精度。基于深度网络的红外行人动作识别中大多是对检测到的行人进行分析,以实现不同简单动作的识别,如站立、行走、蹲、跑等。然而,人体动作是一个序列动作,只要引入时域特征,才有助于提升识别的精度。Wang等人[13]将原始的二维卷积核扩展为三维卷积核,提出了基于三维卷积的异常行为模型,但此类方法参数设置复杂且参数量巨大。LSTM是利用卷积网络逐帧提取红外行人特征,并充分利用了行人的空时特征,提升了行为动作的表征能力,但其多尺度高维处理模式制约了网络运行速度。
众所周知,视觉皮层主要负责大脑皮层中处理视觉信息,其存在背侧流(Dorsal Stream)和腹侧流(Ventral Stream)两条信息输出通道,分别对应空间通路与内容通路[14]。受此启发,Simonyan等人[15]创造性地提出了基于双流卷积网络的动作识别。双流卷积神经网络是一种融合了空间信息网络与时间信息网络的处理结果,通过使用光流图作为网络输入来补偿空间网络无法捕获的时间维度信息,并对不同模型得到的结果进行融合,提升了行人行为的识别精度,但光流的提取过程耗时较长,不满足工程研制的实时性要求。
为了提升复杂背景下红外视频序列的行人检测与动作识别的精度与效率,本文在双流卷积网络的基础上,提出了快速且有效的动作识别模型,并在公共基准数据集与自建数据集基础上进行对比实验,验证本文设计算法的实用性和有效性。
1. 双流卷积网络与长短记忆神经网络
1.1 双流卷积网络
双流网络结构由两个独立的空间流网络和时间流网络组成,分别用来学习视频帧间的空间位置信息与光流数据中的时间运动特征,如图 1所示。这两个网络具有相同的结构,每个结构均由3个池化层和3个卷积层组成,并且在每个卷积层后面增加一个非线性层。尽管两个独立网络具有相同的结构,但它们在双流网络中扮演的角色不同。空间流网络的输入是原始图像序列,而时间流网络则是相邻数据间的光流。为了更好地表征视频序列间的时空特征,双流网络结构设计了两个融合层,其目的是在空间位置融合空间和运动特性,以使相同像素位置处的通道响应相一致。
双流网络结构的输出结果采用级联融合。假定两个网络的输出特征分别表示xA∈RH×W×D和xB∈RH×W×D,其中H,D和W是特征图的高度、通道数和宽度。该融合操作将两个特征图堆叠在整个特征通道d的相同空间位置(i, j)上,即得到yi, j, d=xi, j, dA与yi, j, 2d=xi, j, dB。双流网络极大地提高了行为识别的精度,但也存在一定的局限性。双流网络的时间特征存在于相邻帧之间的光流,对时间维的利用信息有限,其光流的计算复杂度较高。双流网络不能对时空特征的像素级关系进行建模。
1.2 长短记忆神经网络
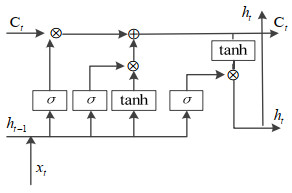
长短记忆神经网络是一种特殊的递归神经网络,能够解决递归神经网络长时依赖与梯度消失的问题[16]。LSTM网络采用“门结构”传递当前时刻处理的信息给下一时刻使用,能够充分挖掘海量数据中蕴含的有效信息,其网络结构如图 2所示。所谓的门结构由一个sigmoid网络层σ与一个按位乘操作构成。
众所周知,已发生的历史数据有助于提升下一刻事件的发生概率。当前的递归网络大都采用最后一帧的状态进行特征表示,显然会丢失大多数动态信息。相比于从局部帧提取特征信息,全序列的整体特征可以更好地呈现全局表示。
2. 基于改进的双流网络行为识别
2.1 空时特征传播
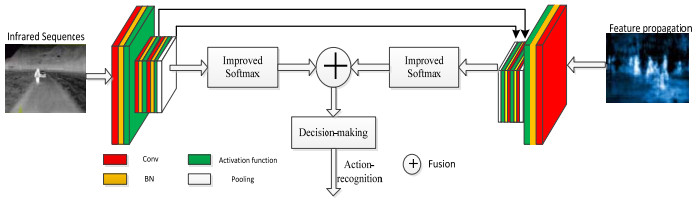
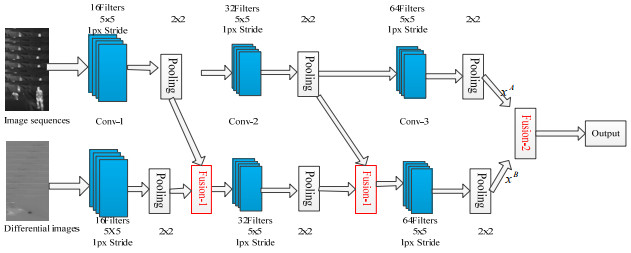
众所周知,双流网络结构由两个独立的空间流网络和时间流网络组成,分别输入图像序列与光流图,其中光流的计算复杂,且需要大量的硬件资源,导致其工程应用实时性不强。在摄像机固定的情形下,前景的光流为零。也就是说,图像间的差分与光流结果是类似的。因此,本文提出了基于深度差分的双流网络模型,该模型采用深度差分网络代替时间网络以获取红外序列中的帧间关系和时间关系。深度差分是一种基于深度特征传播的网络结构[12],获得基于关键帧的特征传播差分图,可以用来代替光流图作为时间流网络的输入,可降低计算复杂度,且增强了特征传播图对人体动作的姿势表达和类别识别能力。改进的双流网络结构如图 3所示,其中卷积核大小分别为7×7和3×3。
视场与视角固定的热像仪输出的相邻红外序列具有高度相似性,其获取的光流特征很微弱。也就是说,大量的逐帧光流计算获得的光流特征不明显。文献[17]提出的差分关键帧能快速获得图像间的差异,提高图像压缩性能。差分关键帧包含了视频中相邻帧间时间关系,具有光流图相似的性能,但其具有生成速度快、计算运算量小等优点。由于红外序列存在帧间冗余大和复杂度高的问题,本文首先根据多时间尺度抽帧,利用差分特征传播获得序列的关键帧。假设一段由t帧序列组成的输入视频记为X,每个片段首先被分成每段时间相等的T段,然后再从每段中抽取关键帧xi,则整个视频记为X={x1, x2, …, xT};这些关键帧经过相邻帧差计算得到的差分关键帧,记为Y={y1, y2, …, yT};最后,将关键帧和差分关键帧分别输入到差分卷积网络,得到对应的高维空时特征向量{S1, S2, …, Si, …, ST},其中Si∈Rd, i=1, 2, …, T,d是关键帧特征维数。
本文所设计的双流网络结构可以快速地提取红外序列的高维空时特征,并在已检测到行人区域的基础上得到对应差分特征。每一个卷积核紧跟一个池化操作,本文采用的池化操作包含平均池化与最大池化,其计算公式如式(1)所示:
$$ {\mathit{P}_{\mathit{i} \to \mathit{j}}}= \frac{{({\mathit{S}_1} \oplus {\mathit{S}_{\mathit{i}{\rm{ + 1}}}} \oplus \ldots \oplus {\mathit{S}_\mathit{j})}}}{({\mathit{j} - \mathit{i} + 1})} $$ (1) 式中:Pi→j表示关键帧i~j之间的平均池化特征。关键帧经过卷积池化和全连接计算后,深度差分网络最终输出结果是一个d维的特征向量,最终得到整段序列的高维时空信息。每一张关键帧通过全局平均池化操作后形成一个1×1×1024维的向量,再通过最后一个卷积层提取最终时空特征。
2.2 改进损失函数的决策级融合机制
双流网络的空时双通道分支分别对同一红外序列不同模态图进行特征提取,获得空间位置信息与时间运动信息,这两类特征在融合模块的作用下提升了动作的表征能力,但原始的双流网络只采用了特征级联进行融合。同时,红外序列人体动作识别问题本身的复杂性,其性能往往容易受到环境噪声的干扰,最终做出错误的决策而影响整个模型的输出。为了提升识别模型的精度,本文提出了一种决策级融合机制,该融合机制借鉴了LSTM网络的记忆特性,通过对先前输出数据进行建模,并采用耦合机制将不同维度下的信息进行关联,其在高维空间中具有特征不变性。本文设计了一个基于改进Softmax逻辑回归的强分类器,并对融合后的特征进行分类,其获得的最高分类概率作为行人动作识别概率,能够更有效地提升动作识别的精度。在文献[15]中,假定当前给定的样本序列x(i)有k个类别,则输出y(i)∈{1, 2, …, k},其训练集{(x(i), y(i))}, i∈{1, 2, …, k}。对于给定的样本特征x,其对类别j的估算条件概率为p(y=j|x),该概率等式可以表示为如下等式:
$$\mathit{p}\left( {{y^{(i)}} = j\mid {x^{(i)}};\theta } \right) = \frac{{{{\rm{e}}^{\mathit{\boldsymbol{\theta }}_j^{\rm{T}}{\mathit{x}^{(i)}}}}}}{{\sum\nolimits_{l = 1}^{\rm{k}} {{{\rm{e}}^{\mathit{\boldsymbol{\theta }}_l^{\rm{T}}{x^{(i)}}}}} }}$$ (2) 因此,Softmax逻辑回归中的每个类别分类概率为:
$${h_\theta }({x^{(i)}}) = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {p({y^{(i)}} = 1\left| {{x^{(i)}}} \right.;\boldsymbol{\theta} )} \\ {p({y^{(i)}} = 2\left| {{x^{(i)}}} \right.;\boldsymbol{\theta} )} \\ \vdots \\ {p({y^{(i)}} = k\left| {{x^{(i)}}} \right.;\boldsymbol{\theta} )} \end{array}} \right]$$ (3) 由于每一类的概率满足指数族分布[18],若将等式(3)获得的识别概率hθ(x(i))进行级数展开,我们可以得到:
$${h_\theta }({x^{(i)}}) = \frac{1}{{\sum\limits_{j = 1}^k {{{\rm{e}}^{\boldsymbol{\theta} _j^{\rm{T}}}}{x^{(j)}}} }}\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{{\rm{e}}^{\boldsymbol{\theta} _1^{\rm{T}}}}{x^{(l)}}} \\ {{{\rm{e}}^{\boldsymbol{\theta} _2^{\rm{T}}}}{x^{(l)}}} \\ \vdots \\ {{{\rm{e}}^{\boldsymbol{\theta} _k^{\rm{T}}}}{x^{(l)}}} \end{array}} \right]$$ (4) 模型参数θ是一个k行矩阵,其每一行表征了对应类别的参数,因此模型参数矩阵θ可以写成θ=[θ1T, θ2T, …, θkT]。式(4)中$1/\sum\nolimits_{l = 1}^{\rm{k}} {{{\rm{e}}^{\mathit{\boldsymbol{\theta }}_l^{\rm{T}}{x^{(i)}}}}} $是对概率分布的归一化操作,以便对输出概率进行量化分析。通过对整体样本结果进行对数似然推导,其损失函数如下所示:
$$J(\boldsymbol{\theta} ) = - \frac{1}{m}\sum\limits_{i = 1}^m {\sum\limits_{j = 1}^k {I({y^{(i)}} = j)\log \frac{{{\rm{e}}_j^{\rm{T}}{x^{(l)}}}}{{\sum\limits_{l = 1}^k {{\rm{e}}_j^{\rm{T}}{x^{(l)}}} }}} } $$ (5) 式中:I(y(i)=j)是一个示性函数,当出现正例时取值为1,反之为0。为了使模型参数矩阵θ最小化,参见文献[16],将式(4)带入式(5)中得到概率值表示为:
$$ J(\boldsymbol{\theta} ) = - \frac{1}{m}\sum\limits_{i = 1}^m {\sum\limits_{j = 1}^k {{y^{(i)}}\log {h_\theta }({x^{(i)}}) + (1 - {y^{(i)}})\log (1 - \log {h_\theta }({x^{(i)}}))} } $$ (6) 为了对等式(6)所示损失函数进行最小化优化计算,一般采用梯度下降法进行优化,其偏导数如下所示:
$${\nabla _{{\mathit{\theta }_\mathit{j}}}}\mathit{J}(\mathit{\boldsymbol{\theta }})= - \frac{1}{m}\sum\limits_{i = 1}^m {{x^{(i)}}I{\rm{(}}{y^{(i)}} = j{\rm{)}} - p{\rm{(}}{y^{(i)}} = j\left| {{y^{(i)}}{\rm{;}}\boldsymbol{\theta} } \right.))} $$ (7) 式中:概率向量${\nabla _{{\mathit{\theta }_\mathit{j}}}}\mathit{J}(\mathit{\boldsymbol{\theta }})$的第l个偏导∂J(θ)/∂θjl表示损失函数对j个类别的l个参数求偏导。对式(8)进行梯度下降迭代进行更新来确定最小化损失函数,其迭代更新等式如下所示:
$${\theta _j}\mathit{ = }{\theta _j} - \alpha {\nabla _{{\mathit{\theta }_\mathit{j}}}}\mathit{J}(\mathit{\boldsymbol{\theta }})$$ (8) 然而,Softmax逻辑回归时采用等式(8)的更新策略会影响到参数的更新效果。因此,本文采用文献[16]提出的多目标分类网络进行优化,等式(2)的概率可以改写为${{\rm{e}}^{{{{\rm{(}}{\mathit{\theta }_j}{\rm{ - }}\phi {\rm{)}}}^{\rm{T}}}{x^{(i)}}}}/\sum\nolimits_{l = 1}^{\rm{k}} {{{\rm{e}}^{{{{\rm{(}}{\mathit{\theta }_j}{\rm{ - }}\phi {\rm{)}}}^{\rm{T}}}{x^{(i)}}}}} $,该等式展开得到$\mathit{p}({\mathit{y}^{(\mathit{i})}} = j|{x^{(i)}};\mathit{\theta }) = {{\rm{e}}^{\mathit{\theta }_l^{\rm{T}}{x^{(i)}}/\sum\nolimits_{l = 1}^{\rm{k}} {{{\rm{e}}^{\mathit{\theta }_l^{\rm{T}}{x^{(i)}}}}} }}$。也就是说,将超参数θ的每一项全部减掉${{\rm{e}}^{{\phi ^{\rm{T}}}{x^{(i)}}}}$时,其得到的损失函数概率值不发生变化,这表明Softmax在对不同样本进行分类时,其结果不受初值影响,但这可能导致最优解不唯一。为了解决这个问题,本文在损失函数中引入正则权值衰减项λ,对其最优解进行约束,加快收敛过程。因此,本文改进的损失函数可改写为如下等式:
$$ J(\theta ) = - \frac{1}{m}\sum\limits_{i = 1}^m {\sum\limits_{j = 1}^k {I({y^{(i)}} = j)\log \frac{{{\rm{e}}_j^{\rm{T}}{x^{(l)}}}}{{\sum\limits_{j = 1}^k {{\rm{e}}_j^{\rm{T}}{x^{(l)}}} }}} } + \frac{\lambda }{2}\sum\limits_{j = 1}^k {\sum\limits_{j = 0}^n {\theta _{ij}^2} } $$ (9) 当λ大于0,等式(9)的偏导数是:
$$ {\nabla _{{\theta _j}}}J(\theta ) = - \frac{1}{m}\sum\limits_{i = 1}^m {[{x^{(i)}}I{\rm{(}}{y^{(i)}} = j{\rm{)}} - p{\rm{(}}{y^{(i)}} = j\left| {{y^{(i)}}{\rm{;}}\theta } \right.))]} + \lambda {\theta _j} $$ (10) 为了求解以上改进Softmax逻辑回归等式的解,获得行人动作的分类概率wi。本文构造一个决策级融合机制,该机制分别对不同样本下的类别概率wic和wid进行决策。对于不同动作类别,采用乘法原理可以得到输入图像的识别概率pk:
$${p_k} = \frac{{{p_{k,{w^{\rm{d}}}}} \times {p_{k,{w^{\rm{c}}}}}}}{{\sum\limits_{k = 1}^K {{p_{k,{w^{\rm{d}}}}} \times {p_{k,{w^{\rm{c}}}}}} }}$$ (11) 最后对红外视频中多个序列段进行处理,找到最大化的输出结果,即为当前序列的最终识别概率值u:
$$u = \arg \mathop {\max }\limits_{k,i} {p_{k,i}}\;\;k = 1,2, \ldots ,\mathit{K}$$ (12) 式中:i是每种类型动作所包含的视频数量;k为动作类型总数。
本文提出一种基于决策级特征融合机制的代价函数,可以更大尺度地保留不同网络帧间图像的空间及时间信息,并采用多数表决原则提高不同关键帧序列下动作类别识别概率,从而提高了红外人体运动识别的性能。
3. 实验结果与分析
3.1 红外行人数据集
红外图像是一种探测目标物发射的热辐射而形成的图像,没有明显的纹理细节特征,很难通过红外图像获得打球、吸烟等精细行为动作。对于红外行人检测及动作识别任务,现有的模型大都是采用了OTCBVS、KAIST、FLIR三个数据集[5]进行行人检测,但对于行人动作分析难度较大。主要归咎这些图像并不是连续的序列,其运动时间跨度大,很难进行关联分析。InfAR数据集[18]是目前红外行为识别领域公开的基准数据集,包含走路、打架、拍手、握手、慢跑、拥抱等12种日常行为,其中每种行为类型具有50个视频序列,每段序列均由单人或多人交互完成,但数据量有限。大多数算法都是在可见光数据集上进行迁移学习,提升红外序列的识别效果。
本文提出的模型是中科院自动化所的横向课题,主要针对监控区域的单个行人的行为特征进行分析,因此项目组采集了大量的行人运动视频,有助于提升模型性能。为了便于性能对比,本文也建立了一个自建数据集,并对图像中行人及其行为动作进行了标注,包含站立、蹲着、躺着、跑步等动作类别,所有类别的数量比较均衡,总共3115个红外视频片段。表 1展示了不同类别的序列数量,其中前12类是单人行为动作,后4类多人交互动作。
表 1 数据集类别及其数量Table 1. Classes and quantities of data-setsNO Categories Total 1 Walk 152 2 Stand 203 3 climb 186 4 Jog 265 5 Jump 174 5 Punch 128 7 Lying 295 8 Wave1 168 9 Wave2 177 10 Crouch 312 11 Sitting 268 12 Handclapping 208 13 Push 158 14 Fight 119 15 Handshake 134 16 Hug 168 3.2 参数设置
本文所有的红外图像的分辨率为640×512,采用5倍交叉验证所提模型的性能。本文所选用的网络都是基于Tensor Flow框架实现,采用随机梯度下降法学习网络参数,其中批尺寸为128,动量值和权重衰减分别设为0.9和0.0005。学习率的初始值为0.01,前50轮的训练过程中保持学习率0.001不变,然后每训练10轮将学习率衰减10%,用来防止过拟合。本文设置的实验环境如下所示:CPU I7-8700k @ 2.80 GHz,64GB (DDR3 1600 MHz),Nvidia Tesla P40,Ubuntul 6.04,64位操作系统。
为客观分析有效性,本文选用了精确率(precision rate,Pr)、漏检率(miss rate,Mr)、召回率(recall rate,Rr)指标来量化分析检测性能,所有的指标可以通过真阳性(true positive,TP)、假阳性(false positive,FP)、假阴性(false negative,FN)、真阴性(true negative,TN)进行计算,并得到混淆矩阵。
3.3 消融分析
本文所提模型采用深度差分网络代替时间网络获得基于关键帧的特征传播差分图,可降低计算复杂度,且增强了特征传播图对人体动作的姿势表达能力。同时,采用基于改进Softmax逻辑回归的强分类器进行行人动作类别决策,提升类别识别能力。为了分析不同改进措施的效果,本节将进行消融分析。表 2展示了深度差分网络(deep differential network,DDN),改进Softmax(improved softmax,IS)与决策融合(decision fusion, DF)对红外行人运行序列的识别效果,其中方框表明基准网络中替换掉的模块。
表 2 不同模块性能分析Table 2. Performance analysis of different modulesDDN IS DF Pr/% FPS 77.12 13.9 ☑ 77.83 18.1 ☑ 79.91 13.8 ☑ 79.78 12.7 ☑ ☑ 81.79 17.8 ☑ ☑ 82.09 18.5 ☑ ☑ 81.83 11.6 ☑ ☑ ☑ 83.01 17.7 表 2中第一行不替换任何模块,是原始的双流网络,其获得的识别精度与帧率分别为77.12%与13.9。消融分析中,分别替换掉不同的模块,其性能也将相应的变换。第三行是特征传播差分图代替复杂的光流计算,其处理效率大大提高,帧率提升了17.1%,精度也有一点提升。IS与DF的改进对性能也有相应的提升,分别增加了3%的识别精度。若同时在原始双流网络中替换两个模块,可以看出采用任意模块的性能要优于仅采用一个模块的性能。值得注意的是本文的改进模块主要针对效率与精度进行了改进,只要替换成深度差分网络,最终的识别效率将大大提升,主要是由于特征传播差分图具有生成速度快、计算运算量小等优点。最终,3个模块从不同的角度对双流网络进行改进,最终对自建的红外运动序列获得了82.01%的识别精度与17.7的处理帧率。
3.4 定性定量分析
为了对本文提出的红外行人动作识别算法的性能进行分析,本文选用了常见的行为识别算法进行性能对比,分别是IDT(improved dense trajectories)[19],C3D(Convolutional 3D)[20],SCNN-3G[21](Spatio- temporal Convolutional Neural Network based on 3D-gradients),L-LSTM[22](Lattice Long Short-Term Memory),Ts-3D[23](two-stream inflated 3D convolutional)和OFGF[24](optical flow guided feature),其中IDT是行为识别领域中非常经典传统的算法,通过引入背景光流消除方法,并沿着轨迹提取特征,使获得的特征更适合人体运动的描述;C3D是对连续帧构建三维多通道卷积特征,通过先验知识提取多维特征,增强反向传播训练速度与特征表征能力;L-LSTM是一种基于栅格化长短期记忆的行为识别模型,以卷积方式将循环网络作用于视频序列,并假定视频中的运动在不同的空间位置是静止的;Ts-3D是一种基于改进双流网络的行为识别算法,由2DCNN Inception-V1扩张而来,可以使用预训练的参数增强训练的效率;OFGF是一种快速稳健的视频动作识别运动表示方法,通过计算时空梯度获取人体的运动趋势。所有的对比算法都是采用作者的源码进行测试。由于部分原始代码主要针对3维自然图像进行分析,而本文的研究对象是二维灰度图像。为了算法模型的一致性,所有输入图像都是将灰度图扩展成3通道图。同时,本文所有试验都采用相同的测试集与训练集进行对比。
由于红外热像仪输出的Cameralink数字视频达到了100帧,其相邻帧之间的内容变化相当缓慢。为了使输入序列能有效表征序列动作信息,本文采用多尺度抽帧策略获取输入数据集,确保固定维度的前提下获得更丰富的时序信息。因此,部分关键帧之间的数据非常冗余,只需要少量的信息就可以表征人体的运动趋势。也就是说,利用差分关键帧就可以获得与持续时间无关的趋势信息,确保获得的特征信息沿着时间维度均匀分布。可以看出,本文改进的策略具有光流图相似的性能,能够充分地表征人体的时序动作信息,但计算复杂度更小。
图 4展示了差分关键帧与对应的光流图。原始数据序列与差分图分别从不同角度得到互补的特征信息,可以明显看出序列中大多数背景噪声已被删除,并且成功保留了人体动作目标。另外,本文获取的差分信息与原始图像的光流信息类似,这种操作不仅可以降低计算复杂度,还可以使模型更加鲁棒。
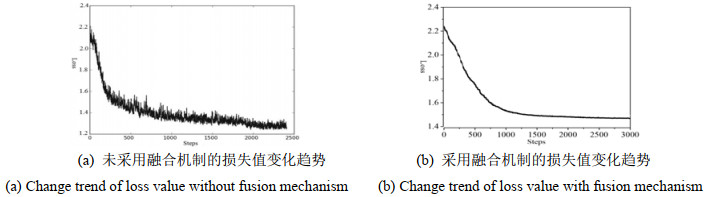
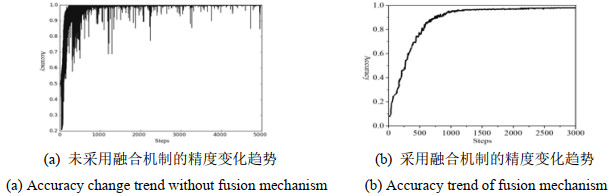
图 5与图 6分别展示了本文所提模型训练过程中的损失值及其识别精度。训练过程中,损失函数的学习率是随着训练轮数变化而动态更新,防止训练过程过拟合。从图 5结果可以看出,采用决策级融合机制后的损失收敛较为迅速且稳定,而未采用融合的训练损失较为抖动。图 6中融合后的双流网络训练精度可以迅速上升并接近99%,说明决策级融合机制可以将空间-时间信息进行有效地融合,通过互补的特征信息,提升人体动作的表征能力。
由于人体的行为动作千差万别,细分所有的类别是非常困难的事情。本文主要对所提算法的性能进行验证。因此,实验选用了站立、行走、跑步、跳跃等16种运动进行识别。人体检测模型采用Yolo-v3进行,本文获得的差分图在行人检测结果的基础上进行细化,缩小处理的范围,有助于提升人体运动趋势的表征能力。表 3展示了所有对比算法在相同测试集下的定量结果。可以看出虽然部分数据集下IDT的结果不如基于深度学习的行为识别算法,但整体上与IDT的结果融合可以提升一点性能,尤其是在站立序列上,其结果与深度学习算法差距不大。C3D与Ts-3D(two-stream 3D)是目前做行为识别的两大主流方法,其识别精度达到了75.2%,但这两种方案严重依赖于相邻时序的变化差异,一旦其关键帧之间的帧序列较少,其性能将大大降低,例如大幅度运动导致相邻两帧变化较大,最终识别精度不足,例如序列2的结果只有57%。L-LSTM往往依赖卷积网络的最后一层特征作为输入,不能够捕捉到低层次运动特征,而且对于遍历整个视频也很难去训练。为了提高长时间的行为识别,密集采样是常用的方法,但这需要庞大的计算开销。OFGF的平均精确率(%)、漏检率(%)与召回率(%)分别是73.8%,19.2%与78.4%。虽然这是对比算法的最优算法,仅需要少量时间成本,就可以嵌入任何现有的深度网络框架中,其处理帧频达到69.7。本文提出的模型将其输入深度差分网络中提取时间维度特征,在保证精度的同时可以大幅减少运算耗时,最终得到了78%的识别精度。可以看出,本模型对比L-LSTM的识别精度提高了6.7%,比使用了68层的C3D有1.8%的精度提升,充分说明了本文提出模型可以更为有效地进行红外人体动作识别。
表 3 不同对比算法的性能分析Table 3. Performance analysis of different comparison modelsCategories IDT C3D SCNN-3G L-LSTM Ts-3D OFGF Our Pr Mr Rr Pr Mr Rr Pr Mr Rr Pr Mr Rr Pr Mr Rr Pr Mr Rr Pr Mr Rr Walk 64 27 70 66 21 72 68 23 72 74 19 77 76 27 74 79 16 80 78 10 80 Stand 72 20 75 76 19 77 76 19 74 82 19 87 84 20 75 84 16 85 85 20 86 climb 50 36 61 53 31 63 61 34 66 66 25 67 71 36 61 76 24 81 78 16 81 Jog 66 28 70 68 23 75 70 23 70 67 28 76 71 28 70 76 19 78 86 8 90 Jump 60 32 65 61 31 68 67 34 67 60 32 74 72 32 65 72 22 77 71 16 80 Punch 41 50 44 41 40 43 46 51 48 51 40 58 60 50 64 61 30 64 67 22 69 Lying 56 36 60 57 31 66 59 33 65 56 36 67 70 30 67 66 22 69 67 16 70 Wave1 65 31 65 68 29 68 68 30 68 65 31 76 72 23 75 75 11 80 82 11 85 Wave2 68 28 69 70 30 71 71 23 76 68 28 87 78 28 79 81 17 86 88 8 88 Crouch 41 29 41 43 34 45 44 23 46 41 29 58 53 20 50 60 22 61 68 26 71 Sitting 70 24 78 73 28 80 72 28 79 71 24 81 78 19 81 80 15 88 82 14 87 Handclap 37 33 38 38 34 42 38 30 33 37 33 50 45 23 58 67 22 68 72 23 76 Push 41 46 44 44 47 46 42 42 47 41 46 57 66 30 64 71 23 74 71 16 79 Fight 53 35 57 58 30 58 56 31 58 53 35 67 67 29 67 63 15 77 80 13 80 Handshake 62 29 67 65 31 70 66 26 70 62 29 76 71 20 77 75 19 87 76 22 81 Hug 67 26 69 66 27 72 61 28 74 76 28 74 74 26 78 78 25 79 81 14 85 Mixed dataset 57 31 60 59 30 63 60 29 63 60 30 70 69 27 69 72 18 77 77 15 80 4. 结语
本文提出了一种改进空时双流网络的红外行人动作识别模型,可以更大限度地保留不同网络帧间图像的时空特征,更加真实地反映行人的动作类别。仿真实验也从不同角度验证了本文模型的有效性。下一步工作考虑细化红外动作类别,建立更加丰富的训练样本集,提高模型的识别精度与泛化能力,并在AI嵌入式平台基础上移植模型,以实现复杂红外监控环境下的行为识别。同时,项目组也将在机载平台上改进所提算法,以实现航拍图像的行人动作识别。
致谢: 本文所有数据来自中国科学院沈阳自动化研究所提供的光电跟踪取证系统;本文研究得到了北京工商大学吴晓波副教授的帮助,在此一并表示感谢。 -
表 1 数据集类别及其数量
Table 1 Classes and quantities of data-sets
NO Categories Total 1 Walk 152 2 Stand 203 3 climb 186 4 Jog 265 5 Jump 174 5 Punch 128 7 Lying 295 8 Wave1 168 9 Wave2 177 10 Crouch 312 11 Sitting 268 12 Handclapping 208 13 Push 158 14 Fight 119 15 Handshake 134 16 Hug 168 表 2 不同模块性能分析
Table 2 Performance analysis of different modules
DDN IS DF Pr/% FPS 77.12 13.9 ☑ 77.83 18.1 ☑ 79.91 13.8 ☑ 79.78 12.7 ☑ ☑ 81.79 17.8 ☑ ☑ 82.09 18.5 ☑ ☑ 81.83 11.6 ☑ ☑ ☑ 83.01 17.7 表 3 不同对比算法的性能分析
Table 3 Performance analysis of different comparison models
Categories IDT C3D SCNN-3G L-LSTM Ts-3D OFGF Our Pr Mr Rr Pr Mr Rr Pr Mr Rr Pr Mr Rr Pr Mr Rr Pr Mr Rr Pr Mr Rr Walk 64 27 70 66 21 72 68 23 72 74 19 77 76 27 74 79 16 80 78 10 80 Stand 72 20 75 76 19 77 76 19 74 82 19 87 84 20 75 84 16 85 85 20 86 climb 50 36 61 53 31 63 61 34 66 66 25 67 71 36 61 76 24 81 78 16 81 Jog 66 28 70 68 23 75 70 23 70 67 28 76 71 28 70 76 19 78 86 8 90 Jump 60 32 65 61 31 68 67 34 67 60 32 74 72 32 65 72 22 77 71 16 80 Punch 41 50 44 41 40 43 46 51 48 51 40 58 60 50 64 61 30 64 67 22 69 Lying 56 36 60 57 31 66 59 33 65 56 36 67 70 30 67 66 22 69 67 16 70 Wave1 65 31 65 68 29 68 68 30 68 65 31 76 72 23 75 75 11 80 82 11 85 Wave2 68 28 69 70 30 71 71 23 76 68 28 87 78 28 79 81 17 86 88 8 88 Crouch 41 29 41 43 34 45 44 23 46 41 29 58 53 20 50 60 22 61 68 26 71 Sitting 70 24 78 73 28 80 72 28 79 71 24 81 78 19 81 80 15 88 82 14 87 Handclap 37 33 38 38 34 42 38 30 33 37 33 50 45 23 58 67 22 68 72 23 76 Push 41 46 44 44 47 46 42 42 47 41 46 57 66 30 64 71 23 74 71 16 79 Fight 53 35 57 58 30 58 56 31 58 53 35 67 67 29 67 63 15 77 80 13 80 Handshake 62 29 67 65 31 70 66 26 70 62 29 76 71 20 77 75 19 87 76 22 81 Hug 67 26 69 66 27 72 61 28 74 76 28 74 74 26 78 78 25 79 81 14 85 Mixed dataset 57 31 60 59 30 63 60 29 63 60 30 70 69 27 69 72 18 77 77 15 80 -
[1] Karpathy A, Toderici G, Shetty S, et al. Large- scale video classification with convolutional neural networks[C]// CVPR, 2014: 1725-1732.
[2] Tran D, Bourdev L D, Fergus R, et al. Learning spatiotem-poral features with 3d convolutional networks[C]//ICCV, 2015: 4489-4497.
[3] ZHANG B, WANG L, WANG Z, et al. Real-time action recognition with enhanced motion vector CNNs[C]//CVPR, 2016: 2718-2726.
[4] Niebles J C, CHEN C W, LI F F. Modeling temporal structure of decomposable motion segments for activity classification[C]// ECCV, 2010: 392-405.
[5] Tumas P, Nowosielski A, Serackis A. Pedestrian detection in severe weather conditions[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 62775-62784. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2982539
[6] 魏丽, 丁萌, 曾丽君. 红外图像中基于似物性与稀疏编码的行人检测[J]. 红外技术, 2016, 38(9): 752-757. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/hwjs201609007 WEI Li, DING Meng, ZENG Lijun. Pedestrian Detection Based on Objectness and Sparse Coding in a Single Infrared Image[J]. Infrared Technology, 2016, 38(9): 752-757. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/hwjs201609007
[7] Fernando B, Gavves E M, Ghodrati J O, et al. Modeling video evolution for action recognition[C]//CVPR, 2015: 5378-5387.
[8] Varol G, Laptev I, Schmid C. Long-term temporal convolutions for action recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 40(6): 1510-1517.
[9] Donahue J, Anne Hendricks L, Guadarrama S, et al. Long-term Recurrent Convolutional Networks for Visual Recognition and Description[M]. Elsevier, 2015: 2625-2634.
[10] Soomro K, Zamir A R, Shah M. A dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in the wild[J/OL]. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, arXiv: 1212.0402, 2012.
[11] Kuehne H, Jhuang H, Garrote E, et al. HMDB: A large video database for human motion recognition[C]//ICCV, 2011: 2556-2563.
[12] Ioffe S, Szegedy C. Batch normalization: Accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift[C]//ICML, 2015: 448-456.
[13] WANG L, QIAO Y, TANG X. Video action detection with relational dynamic- poselets[C]//ECCV, 2014: 565-580.
[14] GAN C, YAO T, YANG K, et a. You lead, we exceed: Labor-free video concept learning by jointly exploiting web videos and images[C]//CVPR, 2016: 923-932.
[15] Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Two-Stream Convolutional Networks for Action Recognition in Videos[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2014, 150: 109-125. http://de.arxiv.org/pdf/1406.2199
[16] 冉鹏, 王灵, 李昕, 等. 改进Softmax分类器的深度卷积神经网络及其在人脸识别中的应用[J]. 上海大学学报: 自然科学版, 2018, 24(3): 352-366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDXZ201803004.htm RAN Peng, WANG Ling, LI Xin, et al. Deep convolution neural network based on improved softmax classifier and its application in face recognition[J]. Journal of Shanghai University: Natural Science Edition, 2018, 24(3): 352-366. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDXZ201803004.htm
[17] Yasin H, Hussain M, Weber A. Keys for Action: An Efficient Keyframe-Based Approach for 3D Action Recognition Using a Deep Neural Network[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(8): 2226. DOI: 10.3390/s20082226
[18] GAO Chenqiang, DU Yinhe, LIU Jiang, et al. InfAR dataset: Infrared action recognition at different times[J]. Neurcomputing, 2016, 212: 36-47. DOI: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.05.094
[19] WANG H, SCHMID C. Action recognition with improved trajectories[C]//Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE, 2013: 3551-3558.
[20] Du Tran, Lubomir Bourdev, Rob Fergus, et al. Learning spatiotemporal features with 3D convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE, International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE, 2015: 4489-4497.
[21] 杨天明, 陈志, 岳文静. 基于视频深度学习的时空双流人物动作识别模型[J]. 计算机应用, 2018, 38(3): 895-899. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJY201803050.htm YANG T M, CHENG Z, YU, W J, et al. Spatio-temporal two-stream human action recognition model based on video deep learning[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2018, 38(3): 895-899, 915. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJY201803050.htm
[22] LIN S, JIA K, CHEN K, et al. Lattice long short-term memory for human action recognition[C]// Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE, 2017: 2166-2175.
[23] Carrlira J, Gisslrman A. Quo vadis. action recognition? A new model and the kinetics dataset[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE, Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE, 2017: 4724-4733.
[24] SUN S, KUANG Z, SHENG L, et al. Optical Flow Guided Feature: A Fast and Robust Motion Representation for Video Action Recognition[C]//The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2018: 20118-20132.



 下载:
下载: