A Lightweight Infrared Target Detection Algorithm for Multi-scale Targets
-
摘要: 针对现有基于深度学习的红外目标检测算法参数量大、复杂度较高、对多尺度目标检测性能较差等问题,提出了一种针对多尺度目标的轻量级红外目标检测算法。算法以YOLOv3为基础,采用MobileNet V2轻量级骨干网络、设计改进的简化空间金字塔结构(simSPP)、Anchor Free机制、解耦头和简化正负样本分配策略(SimOTA)分别对Backbone、Neck和Head进行优化,最终得到模型大小为6.25 M,浮点运算量2.14 GFLOPs的LMD-YOLOv3轻量级检测算法。在构建的MTS-UAV数据集上mAP达到90.5%,在RTX2080Ti显卡上FPS达到99,与YOLOv3相比mAP提升了2.60%,模型大小为YOLOv3的1/10。Abstract: To solve the problems of large parameters, high complexity, and poor detection performance of multiscale targets in the existing infrared target detection algorithms based on deep learning, a lightweight infrared target detection algorithm for multiscale targets is proposed. Based on YOLOv3, the algorithm uses the MobileNet V2 backbone network, simplified spatial pyramid structure (simSPP), anchor-free mechanism, decoupling head, and simplified positive and negative sample allocation strategies (SimOTA) to optimize the backbone, neck, and head, respectively. Finally, LMD-YOLOv3 with the model size of 6.25 M and floating-point computation of 2.14 GFLOPs was obtained. Based on the MTS-UAV data set, the mAP reached 90.5%, and on the RTX2080Ti dataset, the FPS reached 99. Compared with YOLOv3, mAP increased by 11.7%, and the model size was only 1/10 of YOLOv3.
-
Keywords:
- object detection /
- multi-scale /
- lightweight algorithm
-
0. 引言
随着红外成像设备的发展,红外探测凭借其隐蔽性强、成本低廉和可全天候作业等优势,在智能监控、精确制导等多个领域得到了广泛应用。作为目标检测中的一个重要分支,红外目标检测已经成为当前研究热点之一。由于红外图像不具备颜色和纹理等外观信息,目标检测中的可用特征少,且红外成像效果还受大气热辐射的不均匀、不稳定性制约,因此研究适用于复杂背景下的检测算法是红外目标检测研究中的重点和难点。
基于手工固定滑动窗口、步长和固定超参数的传统检测方法对于环境多样性不具有很好的鲁棒性能,通常只对特定背景有效,没有办法获取准确的语义信息,检测的精度不高。基于深度卷积神经网络的方法凭借强大的特征提取和学习能力,能够从复杂图像中提取特征并进行分层表示,这些特性使得设计基于深度卷积神经网络的目标检测算法成为当前复杂背景下红外目标检测的有效突破口。近年来,随着计算机硬件的发展以及红外数据集的扩充,越来越多的基于深度学习的红外目标检测算法问世。以Faster RCNN系列[1-3]为代表的两阶段目标检测算法具有较高的检测精度,以SSD系列[4]、YOLO系列[5-7]为代表的单阶段目标检测算法在实时目标检测的应用中扮演着重要角色。Liu等人[8]率先将基于深度学习的目标检测算法应用到红外目标检测中,但由于图像尺寸小、只有灰度信息、特征不明显,致使机器视觉领域现有的基于深度学习的目标检测算法不适合于红外小目标检测[9]。为解决红外目标淹没在背景杂波中时,虚警率高、检测率低的问题,Zhao等人[10]利用卷积神经网络巧妙地将检测问题转化为模式分类问题,提出了一种天空复杂云背景下红外小目标检测算法;文献[11]利用回归型的深度卷积神经网络进行背景成分抑制,通过阈值分割提取出候选目标区域;Fan等人[12]在分析红外图像特点的基础上,通过角点检测提取潜在目标区域以保证检测率,再将潜在目标区域输入基于卷积神经网络的分类器中,进行非目标区域的剔除,成功降低了检测的虚警率。对于目标遮挡、形变、目标部位未完全暴露态势下的目标检测问题,Zhang等人[13]在空中飞机目标结构、红外特性分析的基础上,定义带有约束条件的损失函数,构建用于空中目标要害部位识别的深度卷积网络模型,提出一种基于关键点检测卷积网络的空中红外目标要害部位检测算法,在抗噪性、鲁棒性上表现出优越的性能。
目前的目标检测算法大多是基于anchor box设定,能够检测到的目标大小取决于anchor box的大小,在anchor box数量一定的情况下,算法能够检测到目标的大小跨度是有限的,而增加anchor box数量会带来更多计算量。在实际场景中,待检测的目标可能从各个方位以不同尺度出现,因此研究红外多尺度目标的检测是充满挑战且具有重要意义的工作。针对上述问题,本文从降低模型复杂度、强化红外特征、提高多尺度目标检测性能3个角度出发,对YOLOv3算法进行优化。在特征提取阶段,采用轻量级的MobileNet V2网络代替Darknet-53作为骨干网络进行特征提取;在特征融合阶段,改进SPP空间金字塔结构,通过实验证明改进后的SimSPP能够以更小的参数量达到相同的性能;在检测阶段取消anchor机制,采用解耦头分别完成分类和回归任务,采用简化的正负样本分配策略作为样本匹配方案,提出了针对多尺度目标的轻量级红外目标检测算法。
1. LMD-YOLOv3算法介绍
1.1 YOLOv3算法介绍
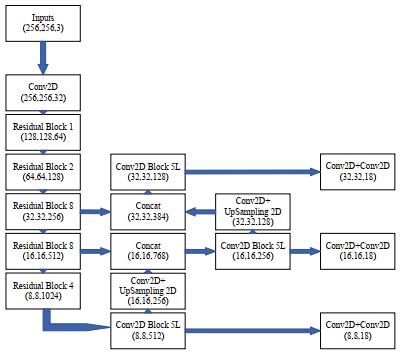
YOLOv3(You Only Look Once)是2018年Joseph Redmon等人提出的一种端到端的目标检测算法[14],在Darknet-19的基础上,借鉴了ResNet的残差结构,使用跳跃连接缓解深层网络中出现的梯度消失问题,形成Darknet-53特征提取网络;特征融合阶段,采用FPN特征金字塔进行加强特征提取,在提取多特征图的基础上,将不同大小的特征图进行融合,用小尺寸特征图检测大尺寸目标,用大尺寸特征图检测小尺寸目标,对小目标检测的效果有了明显提升;采用全卷积结构,通过3×3和1×1卷积进行特征整合和通道数调整,完成目标预测,最终形成“Darknet53+FPN+YOLOHead”的模型结构,网络结构如图 1所示。
如图 1所示,首先在输入端调整图像尺寸为256×256,利用DBL卷积模块和多个Residual Block残差模块组成的Darknet-53特征提取网络得到8倍、16倍和32倍下采样特征图;在网络颈部进行浅层特征与高层语义特征的融合,32倍下采样特征经过卷积生成小尺寸特征图,中间尺寸特征图由上采样后的32倍特征与输出的16倍特征Concat后生成,大尺寸特征图则由16倍和8倍特征融合生成;检测头对3个不同尺度特征图分别划分不同大小的栅格图,对边界框的4个偏移量、目标置信度和类别进行预测,产生多个Bounding Box,最后通过非极大值抑制和IoU交并比计算,得到预测结果。与其他目标检测算法相比,YOLOv3模型结构简单,检测速度快,且具备一定的多尺度目标检测能力。
1.2 LMD-YOLOv3算法
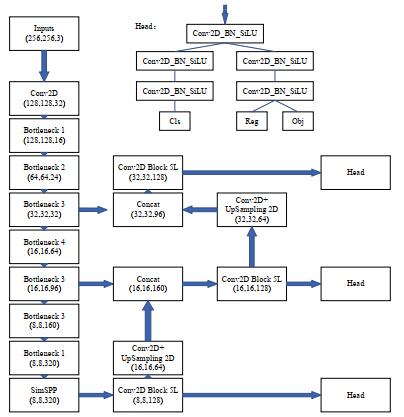
为提升算法对多尺度红外目标的检测性能,本文基于YOLOv3算法进行改进,提出了模型大小仅6.26 M,浮点运算量仅2.15 GFLOPs的Lightweight Multiscale infrared target Detection- You Only Look Once(LMD-YOLOv3),具体结构如图 2所示。本文分别从Backbone、Neck、Head三个方面对改进进行说明。
1.2.1 Backbone改进
为尽可能地减少模型运算量,提高算法检测速度,改善Darknet-53特征提取网络带来大量参数的问题,节省计算资源,本文对MobileNet V2[15]骨干网络进行优化。MobileNet V2是Andrew G. Howard等于2018年在MobileNet V1[16]的基础上提出的改进版本,是目前轻量级神经网络中最具代表性的网络之一。
MobileNet系列网络的主要思想是采用深度可分离卷积来减少运算量及参数量。深度可分离卷积将标准卷积拆分为深度卷积和逐点卷积,首先使用单通道卷积核对每个输入通道进行卷积,然后使用多通道的1×1卷积核将每个通道的卷积结果进行线性组合,构建新的特征。假设输入为DF×DF×M尺寸特征图,输出为DF×DF×N尺寸特征图,采用标准卷积核大小为DK×DK,则使用标准卷积计算量为DK×DK×M×DF×DF×N,第一阶段的深度卷积计算量为DK×DK×M×DF×DF,第二阶段逐点卷积计算量为M×N×DF×DF,采用深度可分离卷积的总计算量为DK×DK×M×DF×DF+M×N×DF×DF,即当标准卷积核为3×3时,深度可分离卷积运算量与标准卷积相比降低了9倍。
与MobileNet V1相比,MobileNet V2的核心模块是Inverted resblock,在3×3深度卷积之前对通道数进行扩张,使网络能够获得更多特征;在1×1卷积进行通道降维后,用线性变换代替非线性的ReLU,防止滤除有用信息对特征造成破坏。因此,MobileNet V2在大幅减少模型参数量的同时,也能一定程度上保证模型的检测性能不受影响。
1.2.2 Neck改进
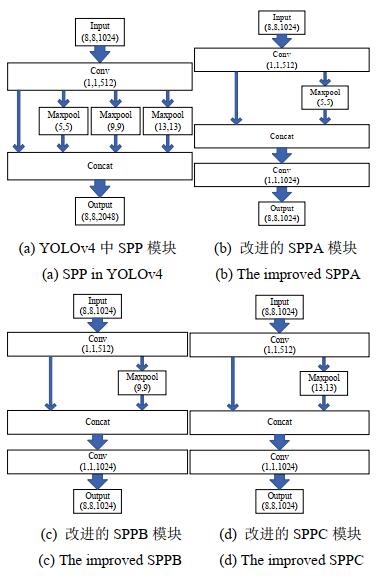
受SPPNet网络[17]的启发,我们注意到在YOLOv3骨干网后加入SPP模块可能有助于提升模型的检测精度。SPP通过多个不同尺寸内核的最大池化操作,再将所有输出特征图进行concat通道拼接实现局部特征和全局特征在特征图级别上的融合,丰富特征图的表达能力。因此,我们在参考YOLOv4[5]网络中SPP模块结构的基础上对其进行改进,结构如图 3所示,其中图 3(a)为YOLOv4中SPP模块结构,图 3(b)为改进的SPPA模块,图 3(c)为改进的SPPB模块,图 3(d)为改进的SPPC模块。
当数据集图片尺寸为256×256时,32倍下采样后进入SPP模块时宽高为8,通道数为1024。由于SPP的本质是融合不同尺度感受野信息,空间金字塔池化结构的最大池化核大小决定了该结构能够得到特征图感受野的大小。我们猜想:最大池化核大小越接近需要池化的特征图尺寸,空间金字塔池化结构能够得到越接近特征图全局的感受野信息,特征融合后对于检测性能的提升效果越好。同时,为减少计算复杂度,在新的SPP模块中,仅保留最接近需要池化的特征图尺寸的Maxpool操作。最后加入卷积模块完成通道数的调整,保持SPP模块输入输出图片的宽高和通道数不变,使改进后的SPP模块能够即插即用到其他检测算法中。
1.2.3 Head改进
受YOLOX[7]目标检测算法的启发,我们对YOLOv3检测Head部分做了3点改进:
1)采用Anchor Free机制
为解决目前Anchor Base算法检测头复杂度高,且训练前聚类分析生成的Anchor集合对数据集依赖性强,导致算法泛化性能较差的问题,我们采用Anchor Free的方法,将YOLOv3中对每个位置进行3个预测调整为进行一个预测,每次仅预测网格左上角的宽、高偏移量及预测框的宽、高,有效降低了检测器参数量和浮点运算量。另一方面Anchor Free的引入使LMD-YOLOv3算法能够检测到的目标尺度不再受预设的Anchor Box大小限制,大大提升了算法对多尺度目标的检测性能。
2)采用解耦头(Decoupled Head)
由于分类与回归任务之间存在冲突,采用耦合的检测头会对模型性能造成影响,而分离的头部又会带来运算复杂度的增加。为平衡模型检测精度和检测速度,我们首先采用1×1卷积进行降维,再通过两个3×3卷积分别进行分类和回归,以增加少量参数为代价实现了检测性能的大幅提升。
3)采用简化的正负样本分配策略
YOLO Head中仅将采样中心点作为正样本,导致周围高质量样本被忽略,正负样本分配(Optimal Transport Assignment, OTA)策略考虑全局最优,具有更强的高质量样本搜索能力。为兼顾算法性能和训练时长,我们采用简化的正负样本分配策略,首先计算预测gtgi的成本表示,然后选择固定区域内成本最低的前K个预测作为正样本。SimOTA比YOLO Head计算方法更靠近全局最优,较OTA又减少了25%的训练耗时。SimOTA中gtgi和pj预测之间成本计算公式如下:
$$ {C_{ij}} = L_{ij}^{{\text{cls}}} + qL_{ij}^{{\text{reg}}} $$ (1) 式中:q为平衡系数;Lijcls和qLijreg是gtgi和预测pj之间的分类损失和回归损失。
2. 实验结果分析
2.1 MTS-UAV数据集
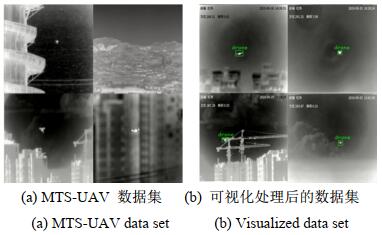
由于目前缺乏相关公开可用的空中红外多尺度目标数据集,本实验在“The 1st Anti-UAV Workshop & Challenge”比赛提供的红外无人机视频数据集的基础上构建MTS-UAV数据集涵盖多种不同复杂场景,如图 4(a)所示。我们在提供的红外无人机数据集中筛选出符合要求的36个红外视频段,使用FFmpeg以fps=5的速率将视频提取成帧,调整图像大小为256×256,编写python程序进行对应标签的提取,将标签格式由json转化成xml,最终得到由9214张图片和9214个对应的标签文件组成的VOC数据集。MTS-UAV数据集为验证数据集标签的准确性,对数据集进行可视化处理,如图 4(b)所示。
MTS-UAV数据集采用xml标签文件,其中包含图片大小“256×256”、标签类别“drone”,以及目标位置坐标“xmin”、“ymin”、“xmax”和“ymax”等信息。我们通过提取标签文件中每个目标的上述信息,对数据集中无人机目标的先验框大小及相关特性进行了统计分析,得到目标的平均宽高分别为17.0、11.5,目标与图片的宽高比分别为0.0646和0.0450。数据集无人机目标大小分布由1×1到64×64,目标尺度差异较大,适用于复杂场景下对空中多尺度目标检测算法的研究。
2.2 实验细节和评估指标
本实验模型训练测试使用硬件平台为11th Gen Intel ® CoreTM i9-11900F CPU,GeForce RTX 2080 Ti 11G GPU;软件使用Ubuntu 20.04系统,python 3.8,Pytorch 1.7.0深度学习框架;目标检测算法框架使用商汤科技联合香港中文大学开发的基于PyTorch的深度学习目标检测框架MMDetection。在MTS-UAV数据集的基础上,按照8:2的比例划分为训练数据集和测试数据集。实验共进行epoch为100次的迭代训练,使用Adam梯度下降算法,训练初始化学习率为0.0001,采用马赛克数据增强。
在检测实时性方面,本实验采用Parameters、FLOPs、FPS,即模型参数量、浮点运算量和每秒处理帧数3项指标评估模型的大小、复杂程度和检测速度。在检测精度方面,采用准确率(Precision,P)、召回率(Recall,R)、阈值IOU为0.5的平均精度(Average Precision,AP)三项指标评判算法模型的检测性能[27],其中P、R和AP值分别表示为:
$$ P = \frac{{{X_{{\text{TP}}}}}}{{{X_{{\text{TP}}}} + {X_{{\text{FP}}}}}} $$ (2) $$ R = \frac{{{X_{{\text{TP}}}}}}{{{X_{{\text{TP}}}} + {X_{{\text{FN}}}}}} $$ (3) $$ {\text{AP}} = \int\limits_0^1 {P(R){\text{d}}R} $$ (4) 式(2)和式(3)中:XTP表示正确检测的目标数;XFP表示被检错的目标数;XFN表示未被检出的目标数。
2.3 SimSPP模块实验与结果分析
本节对文章提出的SimSPP模块设计的有效性进行验证,实验首先对比了在YOLOv3模型特征融合阶段在顶层特征图的处理上加入一个不同的SPP模块后,算法对多尺度目标检测性能的变化。我们在MTS-UAV数据集上对算法进行训练,并在测试集上进行验证,结果如表 1所示。
表 1 SimSPP模块在YOLOv3算法上实验结果对比Table 1. Comparison of experimental results of SimSPP module on YOLOv3 algorithmModel Recall mAP FPS FLOPs Params YOLOV3 90.70% 87.90% 74 12.41G 61.52M YOLOV3+
SPP90.90% 88.60% 71 12.57G 64.15M YOLOV3+
SPPA90.20% 88.00% 73 12.51G 63.10M YOLOV3+
SPPB90.60% 88.50% 72 12.51G 63.10M YOLOV3+
SPPC90.90% 88.30% 72 12.51G 63.10M 由于分类与回归任务之间存在冲突,采用耦合的检测头会对模型性能造成影响,而分离的头部又会带来运算复杂度的增加。为平衡模型检测精度和检测速度,我们首先采用1×1卷积进行降维,再通过两个3×3卷积分别进行分类和回归,以增加少量参数为代价实现了检测性能的大幅提升。表中从目标平均召回率、检测精度、每秒检测帧数、浮点运算量和模型参数量等5个指标对比分析SimSPP模块对网络性能的影响。其中,SPP表示传统具有3个不同尺度池化核的特征金字塔模块,SPPA表示剔除两个较大池化核后,仅保留5×5池化核的特征金字塔模块,SPPB、SPPC分别表示仅有9×9池化核以及13×13池化核的特征金字塔模块。从表 1可以看出对于8×8大小的顶层特征图,采用9×9池化核的特征金字塔模块效果最佳。与不使用SPP模块的YOLOv3相比以极小的运算代价,获得了mAP提升,与采用传统3个池化核的特征金字塔模块算法相比,在保持检测精度的同时,实现了模型参数和运算量的优化,提升了算法检测速度。
同时,为检验SimSPP模块在其他算法中的适用性,我们在MTS-UAV数据集上对YOLOX-s算法进行实验,具体结果如表 2所示。
表 2 SimSPP模块在YOLOX-s算法上实验结果对比Table 2. Comparison of experimental results of SimSPP module on YOLOX-s algorithmYOLOX-S YOLOX-SA YOLOX-SB YOLOX-SC mAP 80.90% 80.70% 80.90% 80.60% FPS 84 90 91 91 YOLOX算法在特征提取的最后阶段有一个SPP模块,我们选取YOLOX中较小的YOLOX-S模型进行训练,表中YOLOX-SA代表特征金字塔模块中仅有5×5池化核,YOLOX-SB、YOLOX-SC分别表示特征金字塔模块中仅有9×9池化核、13×13池化核。由表 2可以看出,将SimSPP模块应用到YOLOX-S算法中,能够在保证检测精度的同时,实现检测速度的提升。对YOLOX算法进一步分析发现,该SPP模块作用的特征图尺寸也是8×8,因此,结合前两组实验,我们发现,在MTS-UAV数据集上,特征金字塔结构是有效的,且当池化核大小设置为最接近这一层特征图的大小时SimSPP模块性能达到最佳,能够更好地实现检测速度与检测精度的均衡。
2.4 LMD-YOLOv3模型实验与结果分析
2.4.1 消融实验与结果分析
本节通过LMD-YOLOv3中不同模块间的消融实验,对比算法中不同模块设计,验证算法中各个模块在空中多尺度红外目标检测问题上的有效性。实验共设4组,现将具体实验设置做如下说明:
实验1:实验使用以Darknet53为骨干网Backbone、以FPN为颈部Neck、以网络第3次、第4次和第5次下采样特征图通过3个YOLO Head进行预测的YOLOv3作为消融实验的基准Baseline。
实验2:在实验1的基础上,在Neck部分顶层添加simSPP模块。
实验3:在实验2的基础上,在Head部分采用Anchor Free机制、Decoupled Head以及简化的正负样本分配策略。
实验4:在实验3的基础上,在Backbone部分用MobileNet V2代替Darknet53为骨干网进行特征提取。
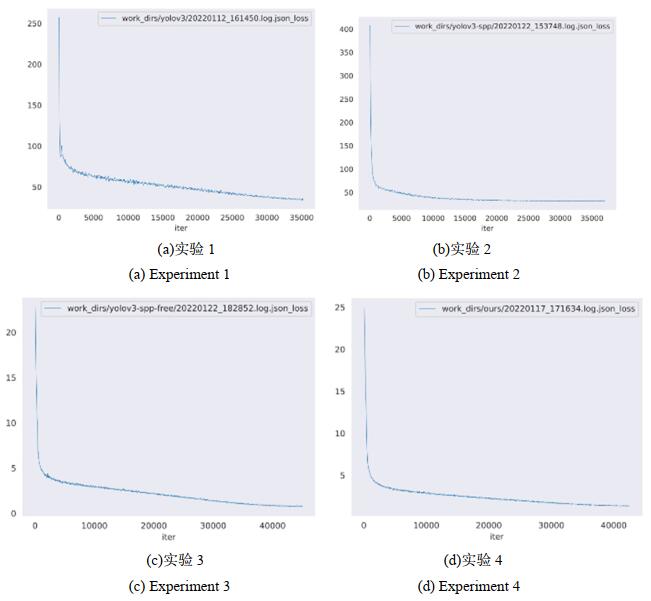
将完成100个epoch训练后的模型在测试数据集上进行评估测试,损失函数如图 5,具体结果如表 3所示。
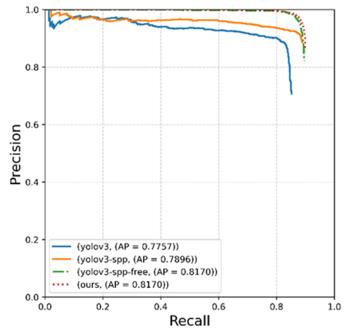
表 3 LMD-YOLOv3消融实验结果对比Table 3. LMD-YOLOv3 comparison of ablation experiment resultsRecall mAP FPS FLOPs Params Experiment 1 90.70% 87.90% 74 12.41G 61.52M Experiment 2 90.60% 88.50% 72 12.51G 63.10M Experiment 3 91.20% 90.40% 74 11.19G 46.20M Experiment 4 91.20% 90.50% 99 2.14G 6.25M 如表 3所示,随着组件的增加,算法性能逐步提升。Baseline的实验结果如实验1所示,YOLOv3算法在数据集上达到了87.90%的检测精度和每秒74帧的检测速度,在目前主流检测算法中占据优势地位。表中实验2在FPN的基础上添加了SimSPP模块,对比实验1和实验2,我们发现改进的简化SPP结构仅用0.1 G的运算量为代价,增强了特征图的表达能力,使算法精度提升了0.6%。对比实验2和实验3,证明了Head部分的改进使算法检测精度和速度都有所提升,有助于提高算法对多尺度目标的检测性能。此外,由图 5中(b)、(c)对比发现,Decoupled Head将分类与回归任务分离,使其能够加速模型训练收敛。实验4在实验3的基础上采用MobileNet V2轻量级网络,将模型压缩为YOLOv3的1/10,使算法的检测速度有了大幅提升。实验P-R(precision-recall)曲线如图 6。
2.4.2 横向对比实验与结果分析
本节在MTS-UAV数据集上对LMD-YOLOv3算法与其他常规目标检测算法的综合性能进行比较,主要以召回率、检测精度、每秒检测帧数、浮点运算量和模型参数量等5个指标进行衡量,结果如表 4所示。
表 4 横向实验结果对比Table 4. Comparison of horizontal experimental resultsRecall/% mAP/% FPS FLOPs/G Params/M YOLOv3 90.70 87.90 74 12.41 61.52 YOLOv4 85.57 86.99 70 11.30 63.9 YOLOX-s 88.20 80.90 84 2.13 8.94 Faster-RCNN 81.60 81.30 49 26.24 41.12 LMD-YOLOv3 (Ours) 91.20 90.50 99 2.14 6.25 从实验结果可见,本文所提的算法凭借90.50%的检测精度,与其他常规目标检测算法相比具有更好的表现。与YOLOv3相比,LMD-YOLOv3算法在提升了2.60%目标检测精度和99帧/s检测速度的同时,将召回率由90.70%提升至91.20%。在目标检测算法中,准确率越高则产生虚警概率越低,召回率越高则发生漏检概率越低。对于空中红外目标的检测而言,召回率指标与准确率同样重要,尤其是在检测入侵目标时,我们可以接受一定范围内的虚警,但是不希望产生过多的漏检。而许多算法研究中只关注检测精度、速度的提升,忽略了召回率的大幅下降,这是不符合实际应用需求的。
2.5 检测结果可视化
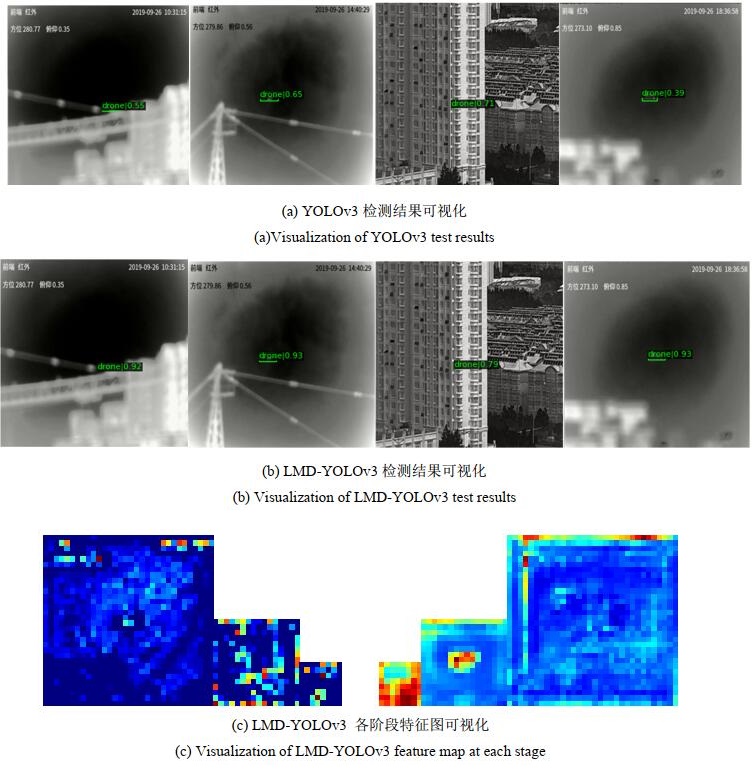
为验证LMD-YOLOv3算法在实际检测场景中的有效性,我们抽取测试集中部分图像,对算法检测结果进行评估与可视化分析。图 7展示了YOLOv3算法和改进后的LMD-YOLOv3算法在MTS-UAV数据集的部分测试集上的检测结果以及LMD-YOLOv3算法各阶段特征图。
由图 7中(a)、(b)对比可以直观地看出LMD- YOLOv3算法与YOLOv3算法相比具有更好的检测性能。图 7(c)分别为3层backbone和3层neck的输出,可以发现第二层neck的输出最能反映出真实目标位置,在下一步研究中我们将重点利用第二层特征进行目标检测。
3. 结语
本文对红外多尺度目标检测问题进行研究,提出了一种针对多尺度目标的轻量级红外目标检测算法。在完成数据集构建的基础上,对传统SPP结构进行改进,仅保留一个Maxpool操作,将改进后的SimSPP模块添加至模型颈部位置,通过调整池化核大小进行多组实验并发现:当池化核大小设置为最接近这一层特征图的大小时SimSPP模块性能达到最佳。在此基础上,结合Anchor Free机制、解耦头和简化正负样本分配策略等最新算法优化方法,采用轻量级提取网络完成空中红外目标检测算法设计。通过实验表明,在RTX2080Ti设备上LMD-YOLOv3检测速度达到99帧/s,mAP达到90.5%,其他算法相比,本文所提算法对空中红外多尺度目标的检测能力有明显的提升。
-
表 1 SimSPP模块在YOLOv3算法上实验结果对比
Table 1 Comparison of experimental results of SimSPP module on YOLOv3 algorithm
Model Recall mAP FPS FLOPs Params YOLOV3 90.70% 87.90% 74 12.41G 61.52M YOLOV3+
SPP90.90% 88.60% 71 12.57G 64.15M YOLOV3+
SPPA90.20% 88.00% 73 12.51G 63.10M YOLOV3+
SPPB90.60% 88.50% 72 12.51G 63.10M YOLOV3+
SPPC90.90% 88.30% 72 12.51G 63.10M 表 2 SimSPP模块在YOLOX-s算法上实验结果对比
Table 2 Comparison of experimental results of SimSPP module on YOLOX-s algorithm
YOLOX-S YOLOX-SA YOLOX-SB YOLOX-SC mAP 80.90% 80.70% 80.90% 80.60% FPS 84 90 91 91 表 3 LMD-YOLOv3消融实验结果对比
Table 3 LMD-YOLOv3 comparison of ablation experiment results
Recall mAP FPS FLOPs Params Experiment 1 90.70% 87.90% 74 12.41G 61.52M Experiment 2 90.60% 88.50% 72 12.51G 63.10M Experiment 3 91.20% 90.40% 74 11.19G 46.20M Experiment 4 91.20% 90.50% 99 2.14G 6.25M 表 4 横向实验结果对比
Table 4 Comparison of horizontal experimental results
Recall/% mAP/% FPS FLOPs/G Params/M YOLOv3 90.70 87.90 74 12.41 61.52 YOLOv4 85.57 86.99 70 11.30 63.9 YOLOX-s 88.20 80.90 84 2.13 8.94 Faster-RCNN 81.60 81.30 49 26.24 41.12 LMD-YOLOv3 (Ours) 91.20 90.50 99 2.14 6.25 -
[1] Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2014: 580-587.
[2] Girshick R. Fast R-CNN[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2015: 1440-1448.
[3] Ren S, He K, Girshick R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. Advances in neural Information Processing Systems, 2015, 28: 91-99.
[4] LIU W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, et al. SSD: Single shot multibox detector[C]//European conference on computer vision., 2016: 21-37.
[5] Bochkovskiy A, WANG C Y, LIAO H Y M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[J/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv, 2020, https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.10934
[6] WANG C Y, Yeh I H, LIAO H Y M. You Only Learn One Representation: Unified Network for Multiple Tasks[J/OL]. arXiv pre-print arXiv, 2021, https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.04206.
[7] GE Z, LIU S, WANG F, et al. Yolox: Exceeding yolo series in 2021[J/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv, 2021, https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.08430.
[8] LIU M, DU H, ZHAO Y, et al. Image small target detection based on deep learning with SNR controlled sample generation[M]//Current Trends in Computer Science and Mechanical Automation, 2018: 211-220.
[9] LIN Liangkui, WANG Shaoyou, TANG Zhongxing. Using deep learning to detect small targets in infrared oversampling images[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 29(5): 947-952. DOI: 10.21629/JSEE.2018.05.07
[10] ZHAO D, ZHOU H, RANG S, et al. An adaptation of CNN for small target detection in the infrared[C]//IGARSS 2018-2018 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, 2018: 669-672.
[11] 谢江荣. 基于深度学习的空中红外目标检测关键技术研究[D]. 上海: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院上海技术物理研究所), 2019. XIE Jiangrong. Research on Key Technologies of Air Infrared Target Detection Based on Deep Learning[D] Shanghai: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2019.
[12] FAN M, TIAN S, LIU K, et al. Infrared small target detection based on region proposal and CNN classifier[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2021, 15: 1927-1936. DOI: 10.1007/s11760-021-01936-z
[13] 张凯, 刘昊, 杨曦, 等. 基于关键点检测网络的空中红外目标要害部位识别算法[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2020, 38(6): 1154-1162. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2020.06.003 ZHANG K, LIU H, YANG X, et al. Key position recognition algorithm of aerial infrared target based on key point detection net-work [J]. Journal of Northwest University of Technology, 2020, 38(6): 1154-1162 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2020.06.003
[14] Redmon J, Farhadi A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement[J/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv, 2018, https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.02767.
[15] Howard A, Zhmoginov A, CHEN L C, et al. Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks: Mobile networks for classification, detection and segmentation[J/OL]. Computer Science, 2018, https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.04381v2.
[16] Howard A G, ZHU M, CHEN B, et al. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[J/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv, 2017, https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861.
[17] HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904-1916. DOI: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 朱文轩. 多尺度目标检测算法在复杂场景下的性能评估与改进. 信息与电脑. 2025(06): 5-7 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: