Study on Corrosion Behavior of Aspergillus niger on Ge Antireflection Coating
-
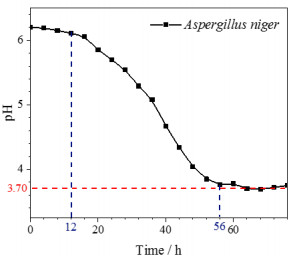
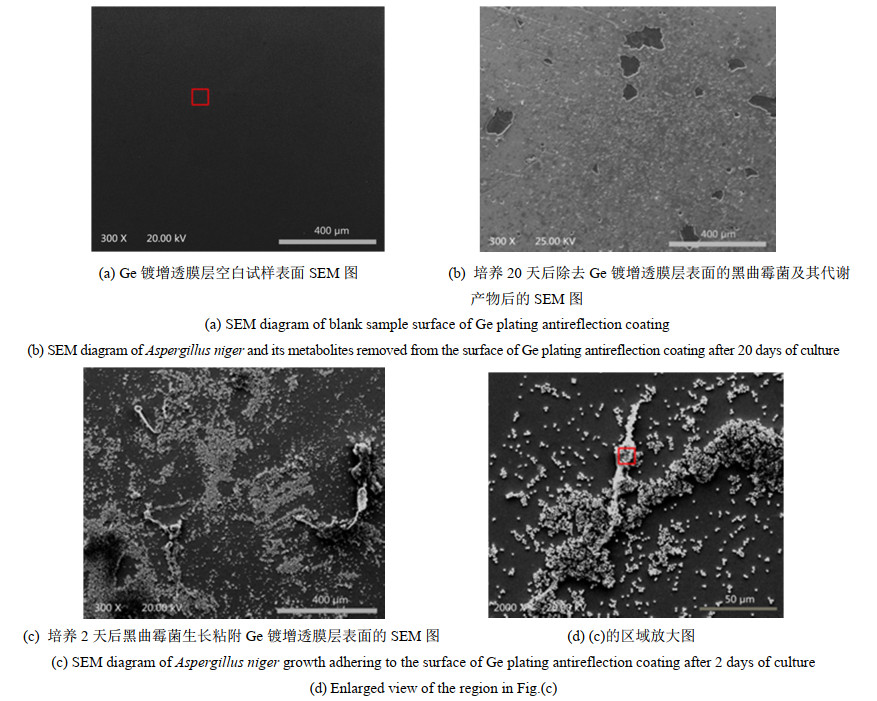
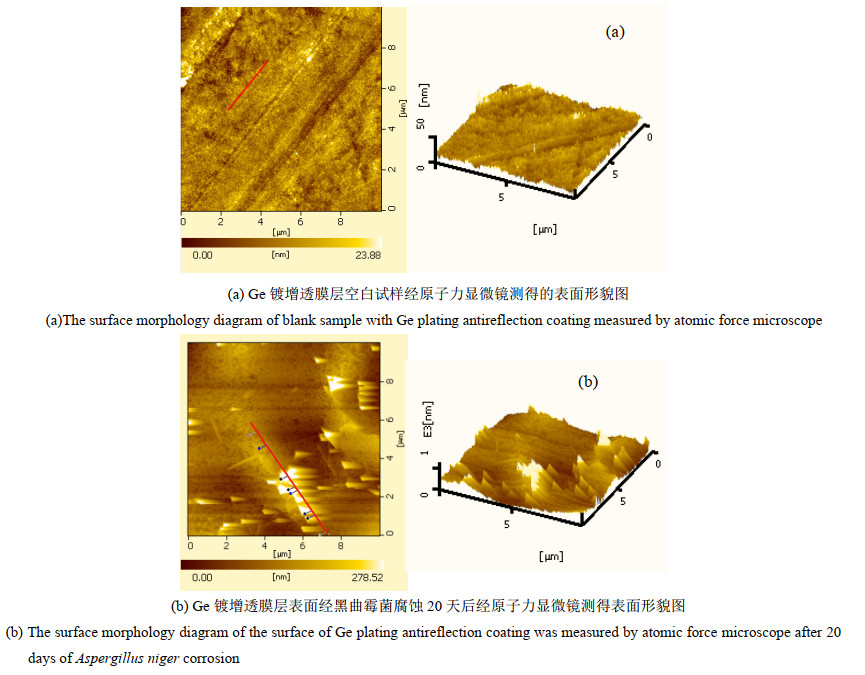
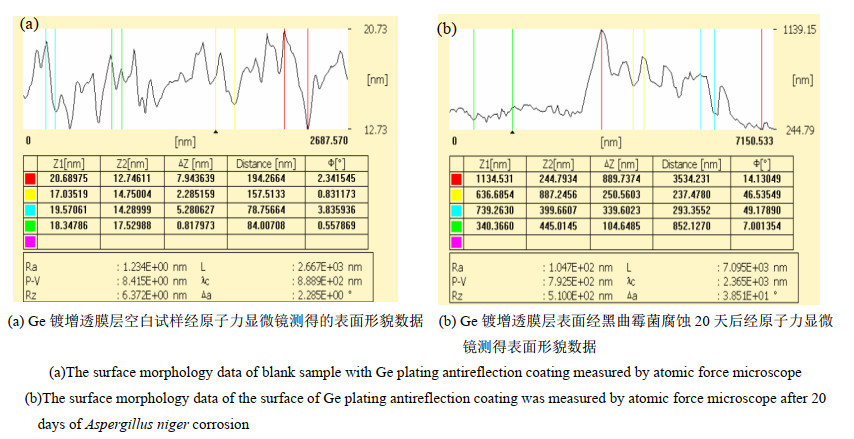
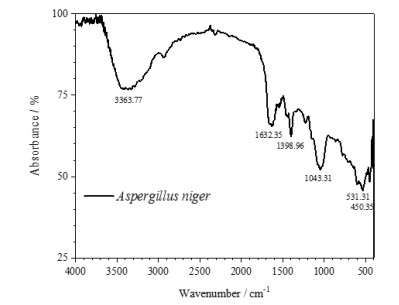
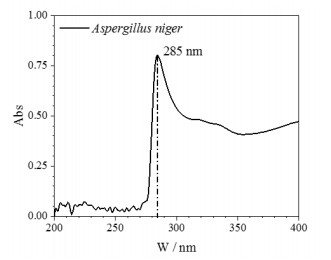
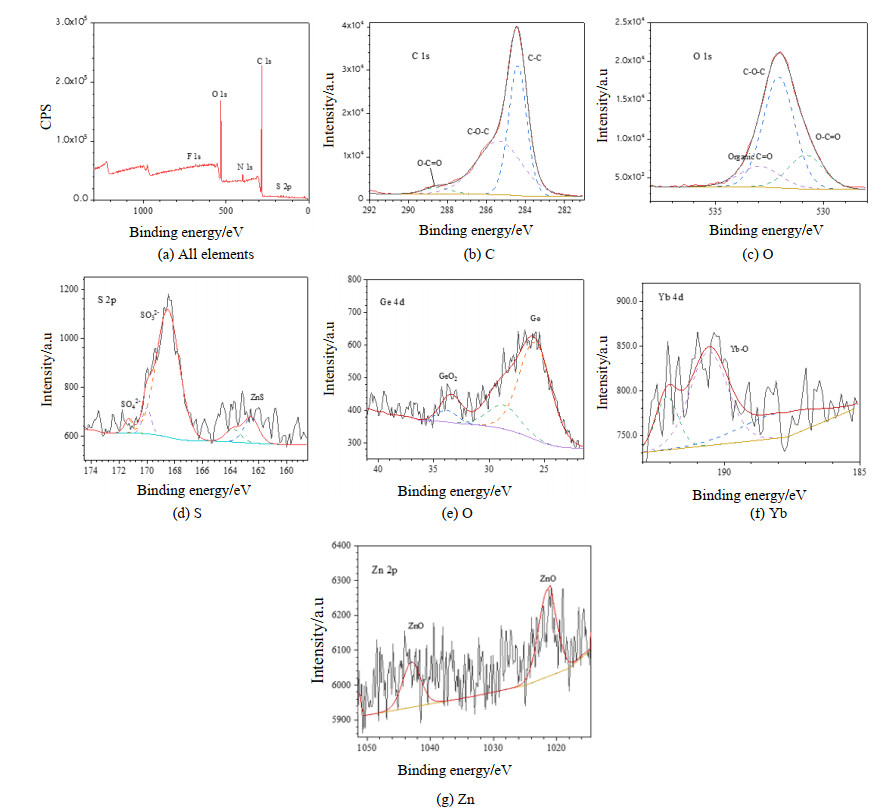
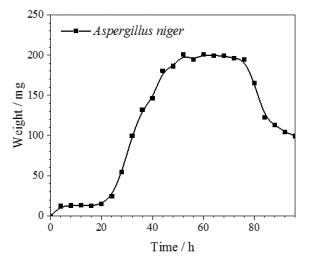
摘要: 为开发新型保护膜系和光学系统的防霉设计提供数据支撑,了解Ge镀增透膜层在黑曲霉环境下的腐蚀行为,有助于提高红外窗口材料的环境适应性。通过霉菌加速试验,采用荧光显微镜、扫描电镜、X射线光电子能谱等,研究黑曲霉菌对Ge镀增透膜层样品的腐蚀行为及影响规律。黑曲霉菌为产酸型微生物,在稳定期时,它的生物量最高,细胞代谢产物的积累达到高峰,在对数生长阶段,由其引起的生长环境pH值变化显著,增加了环境的酸度;黑曲霉菌初始以Ge镀增透膜层样品表层吸附的碳元素为营养粘附于样品表面,并在样品表面大量繁殖,消耗样品表层的碳含量,随着黑曲霉菌的大量繁殖,样品表面的pH值也随之降低,样品表面的金属元素被氧化,开始逐步溶解,Ge镀增透膜层样品表层的锗元素、锌元素相继被剥离,参与反应后,样品的表层形貌被破坏严重,形成了大量的腐蚀坑。黑曲霉菌对Ge镀增透膜层的腐蚀行为以点蚀方式为主,它的生长代谢作用促进Ge镀增透膜层的腐蚀。Abstract: The objective was to understand the corrosion behavior of the Ge antireflection coating in Aspergillus niger, provide data support for the development of novel protective film systems and the anti-mold design of optical systems, and improve the environmental adaptability of infrared materials. The method was to study the corrosion behavior and influence law of Aspergillus niger on the Ge antireflection coating samples via fungus-accelerated tests using fluorescence microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The results demonstrated that Aspergillus niger is an acid-producing microorganism; in the stable phase, its biomass was the highest, and the accumulation of cell metabolites peaked. In the logarithmic growth phase, it caused significant changes in the pH value of the growth environment, which increased environmental acidity. Carbon was adsorbed on the surface layer of the Ge antireflection coating, then the Aspergillus niger used it as nutrition to adhere to the surface of the sample, and multiply on its surface, thereby consuming the carbon content of the surface. With the proliferation of Aspergillus niger, the pH of the sample surface also decreased, and the metal elements on the sample surface were oxidized and gradually dissolved. The Ge and Zn on the surface of the Ge antireflection coating sample were successively peeled off. After participating in the reaction, the surface morphology of the sample was severely damaged and a large number of corrosion pits were formed. It was inferred that the corrosion behavior of Aspergillus niger on the Ge antireflection coating samples was mainly pitting corrosion, and that growth metabolism promoted the corrosion of antireflective coatings.
-
Keywords:
- Aspergillus niger /
- Ge antireflection coating /
- corrosion behavior
-
-
表 1 能谱元素分析结果
Table 1 Results of energy spectrum element analysis
Element/wt% C O F S Yb Zn Ge Others Control 8.77 1.59 7.44 13.19 45.69 18.26 5.06 <0.001 Aspergillus niger 46.77 9.07 4.21 6.68 20.65 10.52 2.10 <0.001 -
[1] 余怀之. 红外光学材料[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2007: 149-150. YU Huaizhi. Infrared Optical Material[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2017: 149-150.
[2] 杨玉萍, 字正华, 钟辉, 等. 霉菌对Ge、ZnS和ZnSe膜层的影响[J]. 红外技术, 2016, 38(12): 1078-1081. DOI: 10.11846/j.issn.1001_8891.201612013 YANG Yuping, ZI Zhenghua, ZHONG Hui, et al. Impact of fungus on films on Ge, ZnS and ZnSe[J]. Infrared Technology, 2016, 38(12): 1078-1081. DOI: 10.11846/j.issn.1001_8891.201612013
[3] 张旭, 许宁, 张徽, 等. ZnS/金刚石薄膜复合窗口材料的研究现状[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2010, 29(5): 1109-1113. DOI: 10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.2010.05.037 ZHANG Xu, XU Ning, ZHANG Hui, et al. Research progress on ZnS/diamond composite window materials[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2010, 29(5): 1109-1113. DOI: 10.16552/j.cnki.issn1001-1625.2010.05.037
[4] Eimutis Juzeliūnas, Rimantas Ramanauskas, Albinas Lugauskas, et al. Microbially influenced corrosion of zinc and aluminium –Two-year subjection to influence of Aspergillusniger [J]. Corrosion Science, 2007, 49(11): 4098-4112. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2007.05.004
[5] Eimutis Juzeliūnas, Rimantas Ramanauskas, Albinas Lugauskas, et al. Microbially influenced corrosion acceleration and inhibition. EIS study of Zn and Al subjected for two years to influence of Penicillium frequentans, Aspergillusniger and Bacillus mycoides[J]. Electrochemistry Communications, 2005, 7(3): 305-311. DOI: 10.1016/j.elecom.2005.01.012
[6] 王蕾. 两株典型真菌对AZ31B镁合金的腐蚀行为影响研究[D]. 昆明: 云南大学, 2015. WANG Lei. The Study on the Influence of Two Typical Fungi on the Corrosion Behavior of AZ31B Magnesium Alloy[D]. Kunming: Yunnan University, 2015.
[7] 陈丹明, 李明, 郑兴明. 霉菌对A04-60氨基烘干磁漆的侵蚀作用研究[J]. 腐蚀科学与防护技术, 2014, 26(1): 19-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSFJ201401004.htm CHEN Danming, LI Ming, ZHENG Xingming. Study on the erosion effect of mold on A04-60 amino baking enamel[J]. Corrosion Science and Protection Technology, 2014, 26(1): 19-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FSFJ201401004.htm
[8] 熊福平. 湿热海洋环境中铝合金7075-T6霉菌腐蚀机理研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2018. XIONG Fuping. Study on Mold Corrosion Mechanism of Aluminum Alloy 7075-T6 in Hot and Humid Marine Environment[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2018.
[9] 邹士文, 肖葵, 董超芳, 等. 霉菌环境下喷锡处理印制电路板的腐蚀行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(3): 809-815. DOI: 10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2013.03.030 ZOU Shiwen, XIAO Kui, DONG Chaofang, et al. Corrosion behavior of printed circuit boards treated with tin spraying in mold environment[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2013, 23(3): 809-815. DOI: 10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2013.03.030
[10] DAI Xinyan, WANG Hua, JU Lukwang, et al. Corrosion of aluminum alloy 2024 caused by Aspergillus niger [J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2016, 115: 1-10.
[11] GUO Zhangwei, LIU Tao, CHENG Y Frank, et al. Adhesion of Bacillus subtilis and Pseudoalteromonaslipolytica to steel in a seawater environment and their effects on corrosion[J]. Colloids Surf. B, 2017, 157: 157-165. DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.05.045
[12] DUAN Jizhou, WU Suru, ZHANG Xiaojun, et al. Corrosion of carbon steel influenced by anaerobic biofilm in natural seawater[J]. Electrochim. Acta, 2008, 54: 22-28. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2008.04.085
[13] Batmanghelich F, LI L, Seo Y. Influence of multispecies biofilms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Desulfovibrio vulgaris on the corrosion of cast iron[J]. Corros. Sci. , 2017, 121: 94-104. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2017.03.008
[14] Abriouel H, Franz C M, Ben Omar, et al. Diversity and applications of Bacillus bacteriocins[J]. Fems Microbiol. Rev., 2011, 35: 201-232. DOI: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00244.x
[15] Miranda C A, Martins O B, Clementino M M. Specieslevel identification of Bacillus strains isolates from marine sediments by conventional biochemical, 16S rRNA gene sequencing and inter-tRNA gene sequence lengths analysis[J]. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 2008, 93: 297-304. DOI: 10.1007/s10482-007-9204-0
[16] QU Qing, HE Yue, WANG Lei, et al. Corrosion behavior of cold rolled steel in artificial seawater in the presence of Bacillus subtilisC2[J]. Corros. Sci., 2015, 91: 321-329. DOI: 10.1016/j.corsci.2014.11.032
[17] Flemming H C, Neu T R, Wozniak D J. The EPS matrix: the "house of biofilm cells"[J]. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189: 7945-7947. DOI: 10.1128/JB.00858-07
[18] Masoumeh Moradi, SONG Zhenlun, TAO Xiao. Introducing a novel bacterium Vibrio neocaledonicus sp., with the highest corrosion inhibition efficiency[J]. Electrochem. Commun. , 2015, 51: 64-68. DOI: 10.1016/j.elecom.2014.12.007
[19] Dutta A, Bhattacharyya S, Kundu A, et al. Macroscopic amyloid fiber formation by Staphylococcal biofilm associated SuhBprotein[J]. Biophys. Chem. , 2016, 217: 32-41. DOI: 10.1016/j.bpc.2016.07.006
[20] San N O, Nazır H, Donmez G. The effect of Aeromonaseucrenophila on microbiologically induced corrosion of nickel-zinc alloy[J]. Int. Biodeter. Biodegr. , 2013, 80: 34-40. DOI: 10.1016/j.ibiod.2012.09.014
[21] Naik U C, Srivastava S, Thakur I S. Isolation and characterization of Bacillus cereus IST105 from electroplating effluent for detoxification of hexavalent chromium[J]. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. , 2012, 19: 3005-3014. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-012-0811-6
[22] Peron M, Torgersen J, Berto F. Mg and its alloys for biomedical applications: exploring corrosion and its interplay with mechanical failure[J]. Metals, 2017, 7: 252. DOI: 10.3390/met7070252
[23] Pestova E, Millichap J J, Noskin G A, et al. Intracellular targets of moxifloxacin: a comparison with other fluoroquinolones[J]. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. , 2000, 45: 583-590. DOI: 10.1093/jac/45.5.583
[24] 周丹, 李立平, 罗彬, 等. 金色南洋珠与染色金珠的谱学特征对比[J]. 宝石和宝石学杂志, 2015, 17: 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BSHB201503001.htm ZHOU Dan, LI Liping, LUO Bin, et al. A characteristic of spectroscopy comparative study golden seawater cultured pearl from south sea and seawater cultured pearl dyed[J]. Journal of Gems and Gemmology, 2015, 17: 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BSHB201503001.htm
[25] 王箴. 化工词典[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2000. WANG Zhen. Chemical Dictionary[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2000.
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: