Hyperspectral Image Classification Based on Feature Importance
-
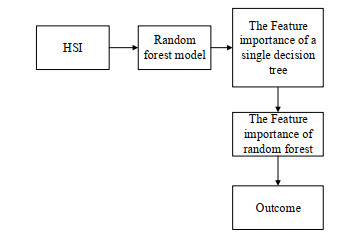
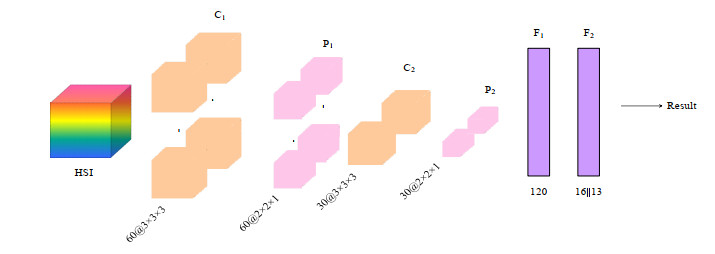
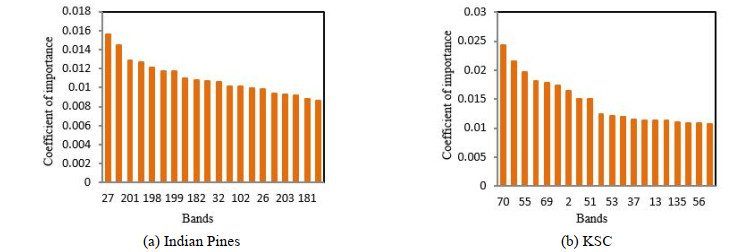
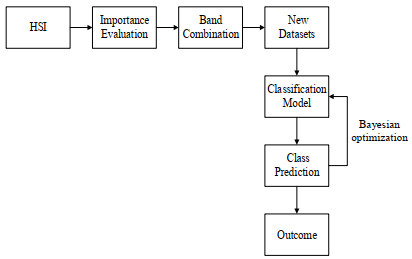
摘要: 为了减少高光谱图像中的冗余以及进一步挖掘潜在的分类信息,本文提出了一种基于特征重要性的卷积神经网络(convolutional neural networks,CNN)分类模型。首先,利用贝叶斯优化训练得到的随机森林模型(random forest,RF)对高光谱遥感图像进行特征重要性评估;其次,依据评估结果选择合适数目的高光谱图像波段,以作为新的训练样本;最后,利用三维卷积神经网络对所得样本进行特征提取并分类。基于两个实测的高光谱遥感图像数据,实验结果均表明:相比原始光谱信息直接采用支持向量机(support vector machine,SVM)和卷积神经网络的分类效果,本文所提基于特征重要性的高光谱分类模型能够在降维的同时有效提高高光谱图像的分类精度。Abstract: To reduce the redundancy in hyperspectral images and further explore their potential classification information, a convolutional neural network(CNN) classification model based on feature importance is proposed. First, the random forest(RF) model obtained by Bayesian optimization training is used to evaluate the importance of hyperspectral images. Second, an appropriate number of hyperspectral image bands are selected as new training samples according to the evaluation results. Finally, the 3D-CNN is used to extract and classify the obtained samples. Based on two sets of measured hyperspectral remote sensing image data, the experimental results demonstrate the following: compared with the original spectral information obtained directly using a support vector machine(SVM) and the CNN classification effect, the proposed hyperspectral classification model based on feature importance can effectively improve the classification accuracy of hyperspectral images while reducing dimensionality.
-
Keywords:
- hyperspectral image /
- feature importance /
- band selection /
- CNN /
- SVM
-
-
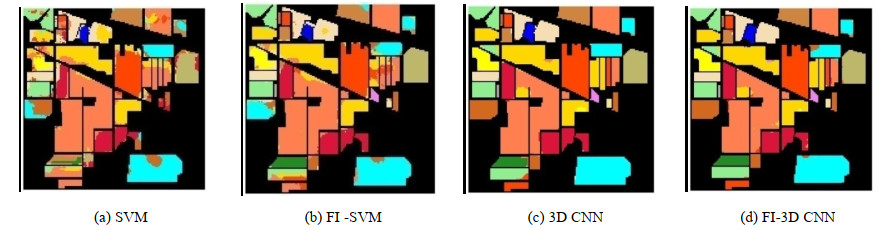
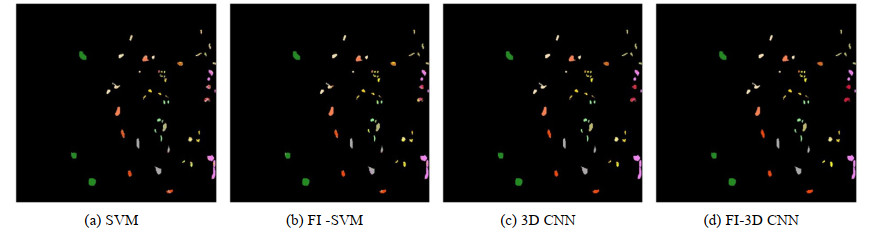
表 1 不同方法在Indian Pines和KSC上分类精度
Table 1 Classification accuracy of different methods in Indian Pines and KSC
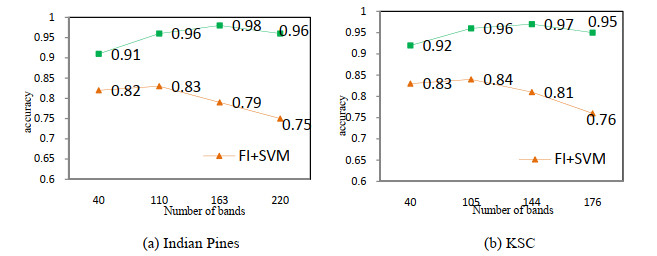
Classification Indian Pines KSC OA$ \pm $SD/(%) Kappa OA$ \pm $SD(%) Kappa SVM 75.86$ \pm $0.38 79.86 76.34$ \pm $0.62 80.59 1D CNN 82.57$ \pm $0.88 83.31 85.50$ \pm $0.73 86.18 3D CNN 96.05$ \pm $0.25 95.25 95.49$ \pm $0.83 95.23 OIF-CNN 84.55$ \pm $0.33 81.92 86.62$ \pm $0.36 88.36 OIF-3D CNN 97.86$ \pm $0.56 96.12 97.13$ \pm $0.15 98.03 FI-SVM 82.34$ \pm $0.29 86.08 85.38$ \pm $0.23 88.01 FI-CNN 85.29$ \pm $0.13 86.18 87.75$ \pm $0.12 89.28 FI-3D CNN 98.03$ \pm $0.16 97.84 97.26$ \pm $0.13 96.98 -
[1] YE M C, JI C X, CHEN H, et al. Residual deep PCA-based feature extraction for hyperspectral image[J/OL]. Neural Computing & Applications, 2020, 32(7): doi: 10.1007/s00521-019-04503-3.
[2] Donoho D L. High-dimensional data analysis: the curses and blessings of dimensionality[J]. AMS Math Challenges Lecture, 2000, 1: 32. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/220049061_High-Di
[3] Marpu G, Chanussot P R J, Benediktsson J A. Linear versus nonlinear PCA for the classification of hyperspectral data based on the extended morphological profiles[J]. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett., 2012, 9(3): 447-451. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2011.2172185
[4] Villa A, Benediktsson J A, Chanussot J, et al. Hyperspectral image classification with independent component discriminant analysis[J]. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., 2011, 49(12): 4865-4876. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2011.2153861
[5] Zabalza J, REN J, WANG Z, et al. Singular spectrum analysis for effective feature extraction in hyperspectral imaging[J]. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett., 2014, 11(11): 1886-1890. DOI: 10.1109/LGRS.2014.2312754
[6] Chacvez P S, Berlin G L, Sowers L B. Statistical method for selecting landsat MSS retio[J]. Jourmal of Applied Photographic Engineering, 1982, 1(8): 23-30. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/80001173869
[7] Charles S. Selecting band combination from multispectral data[J]. Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 1985, 51(6): 681-687. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/80002491091
[8] 张爱武, 杜楠, 康孝岩, 等.非线性变换和信息相邻相关的高光谱自适应波段选择[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2017, 46(5): 05308001. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91846A/20175/672269415.html ZHANG Aiwu, DU Nan, KANG Xiaoyan, et al. Adaptive band selection for nonlinear transform and information adjacent correlation[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2017, 46(5): 05308001. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91846A/20175/672269415.html
[9] HU W, HUANG Y, WEI L, et al. Deep convolutional neural networks for hyperspectral image classification[J]. Journal of Sensors, 2015, 2015: e258619. http://www.tandfonline.com/servlet/linkout?suffix=CIT0026&dbid=16&doi=10.1080%2F15481603.2018.1426091&key=10.1155%2F2015%2F258619
[10] Goodfellow I J, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]//Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2014, 2: 2672-2680.
[11] Haut J, Paoletti M, Plaza J, et al. Cloud implementation of the K-means algorithm for hyperspectral image analysis[J]. J. Supercomput., 2017, 73(1): 514-529. DOI: 10.1007/s11227-016-1896-3
[12] Melgani F, Lorenzo B. Classification of hyperspectral remote sensing images with support vector machines[J]. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., 2004, 42(8): 1778-1790. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2004.831865
[13] Camps-Valls G, Bruzzone L. Kernel-based methods for hyperspectral image classification[J]. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., 2004, 43(6): 1351-1362. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1433032/
[14] Haut J, Paoletti M, Paz-Gallardo A, et al. Cloud implementation of logistic regression for hyperspectral image classification[C]//Comput. Math. Methods Sci. Eng. (CMMSE), 2017, 3: 1063-2321.
[15] Bazi Y, Melgani F. Gaussian process approach to remote sensing image classification[J]. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens., 2010, 48(1): 186-197. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2023983
[16] Breiman L. Bagging predictors[J]. Mach Learn, 1996, 24(2): 123-140. DOI: 10.1007/BF00058655
[17] Cutler A, Cutler D R, Stevens J R. Random Forests[M]//Ensemble Machine Learning, Boston: Springer, 2012: 157-175.
[18] 李贞贵.随机森林改进的若干研究[D].厦门: 厦门大学, 2013. LI Z G. Several Research on Random Forest Improvement[D]. Xiamen: Xiamen University, 2013.
[19] LI Y, ZHANG H, SHEN Q. Spectral-spatial classification of hyper- spectral imagery with 3D convolutional neural network[J]. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(1): 67. DOI: 10.3390/rs9010067
[20] CHEN Y, JIANG H, LI C X, et al. Deep features extraction and classification of hyperspectral images based on convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2016, 54(10): 6232-6251. DOI: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2584107
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 白龙温,贾铭. 一种USB接口的非制冷红外机芯设计. 承德石油高等专科学校学报. 2022(03): 41-46 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(9)



 下载:
下载: