Multiscale Infrared Object Detection Network Based on YOLO-MIR Algorithm
-
摘要: 针对红外图像相对于可见光检测精度低,鲁棒性差的问题,提出了一种基于YOLO的多尺度红外图目标检测网络YOLO-MIR(YOLO for Multi-scale IR image)。首先,为了提高网络对红外图像的适应能力,改进了特征提取以及融合模块,使其保留更多的红外图像细节。其次,为增强对多尺度目标的检测能力,增大了融合网络的尺度,加强红外图像特征的进一步融合。最后,为增加网络的鲁棒性,设计了针对红外图像的数据增广算法。设置消融实验评估不同方法对网络性能的影响,结果表明在红外数据集下网络性能得到明显提升。与主流算法YOLOv7相比在参数量不变的条件下平均检测精度提升了3%,提高了网络对红外图像的适应能力,实现了对各尺度目标的精确检测。Abstract: To address the low detection accuracy and poor robustness of infrared images compared with visible images, a multiscale object detection network YOLO-MIR(YOLO for multiscale IR images) for infrared images is proposed. First, to increase the adaptability of the network to infrared images, the feature extraction and fusion modules were improved to retain more details in the infrared images. Second, the detection ability of multiscale objects is enhanced, the scale of the fusion network is increased, and the fusion of infrared image features is facilitated. Finally, a data augmentation algorithm for infrared images was designed to increase the network robustness. Ablation experiments were conducted to evaluate the impact of different methods on the network performance, and the results show that the network performance was significantly improved using the infrared dataset. Compared with the prevalent algorithm YOLOv7, the average detection accuracy of this algorithm was improved by 3%, the adaptive ability to infrared images was improved, and the accurate detection of targets at various scales was realized.
-
Keywords:
- object detection /
- deep learning /
- infrared image /
- YOLO
-
0. 引言
红外探测器具有全天候成像的特点,在军事侦察领域得到了广泛的应用。其中,红外目标检测是军事侦察领域的关键性技术,为提升自身应对风险能力,无人机设备被大量投入用来定位目标信息。而红外图像具有分辨率低,特征信息弱的特点,在物体不同大小、形状、光照等复杂场景下,如何精确地识别多尺度目标成为研究热点。
随着红外成像技术的发展,目标检测技术被广泛应用于人脸识别、智慧交通、工业检测等领域,是计算机视觉领域的核心问题之一。2014年,Girshick等人[1]提出了一种双阶段目标检测模型R-CNN(Region-Convolutional Neural Network),大大提高了目标检测效果,但是该算法需要重复计算且计算量较大,资源消耗较高,无法满足实时检测的需求。2016~2018年,有研究人员相继提出了YOLO(You Only Look Once)[2]和单阶段目标检测算法(Single Shot MultiBox Detector,SSD)[3],SSD算法为解决小物体定位不精确,检测困难等问题,采用了特征金字塔结构。而YOLO算法可以直接输出不同比例的边界框坐标信息,相对于双阶段目标检测网络,它有更快的检测速度,更小的参数量以及较少的Flops占用,但在小目标或重叠的物体检测中仍有不足。随单阶段目标检测算法的不断改进,在YOLOv3[4]之后衍生出多个版本,如2021年提出的YOLOv5[5],改进了YOLOv4[6]的一些缺陷如IOU损失的问题,且体积小,检测速度更快,检测精度更高,截至目前,YOLOv5以及YOLOv7系列受到了广泛的认可与关注。
YOLOv5以及YOLOv7系列作为目前主流的检测器,具有收敛速度快、检测精度高、可定制性强的优点。但通过迁移式学习将其应用于红外目标检测时,网络检测精度不高。特别是在红外复杂场景或被测物体特征信息较弱的条件下,网络表现出鲁棒性较差的特性,会出现漏检、错检等现象。本文为解决深度学习算法对红外图像适应能力差的问题,对图像的特征提取,融合以及数据处理方法做出了改进,提出了一种基于YOLO-MIR(YOLO for Multi-scale IR image)的红外多尺度目标检测网络。
本算法在特征提取部分借鉴了YOLOv7[7]的MP下采样模块,并将其中的最大池化核替换为更适应红外图像特征的平均池化核。在融合模块中,使用基于PANet[8]的网络结构来增加特征融合的尺度。同时,在数据预处理阶段,设计了针对红外图像的数据增广算法来加速梯度下降以及增加网络的鲁棒性。
1. YOLO-MIR算法分析
1.1 YOLO-MIR网络结构
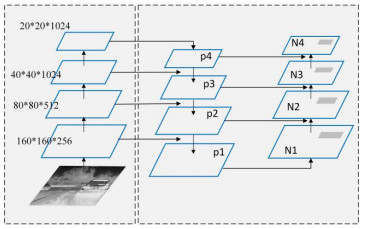
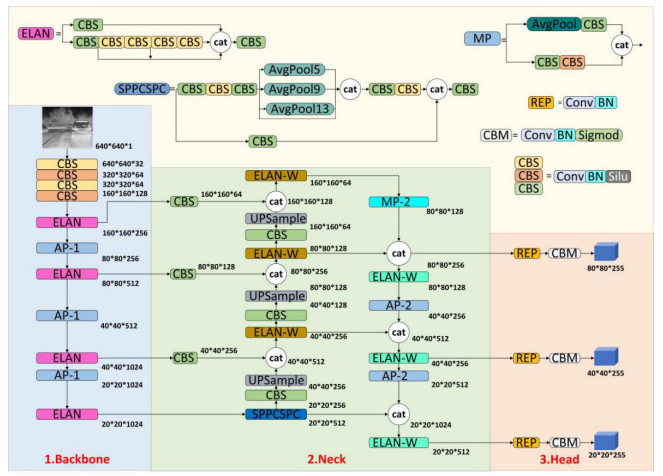
本文以YOLO系列的基本结构和数据处理方法为基础,针对红外图像做出进一步改进,具体为:特征提取模块的改进,多尺度特征融合,以及新的数据处理方法。基于以上改进提出了一种多尺度红外图目标检测网络YOLO-MIR,其网络的结构如图 1所示,主要分为3个部分:Backbone,Neck以及Head。Backbone作为网络的主干对输入图像进行特征提取,Neck部分将主干特征进一步融合,Head负责目标的分类与位置信息的预测。
1.1.1 特征提取
在卷积神经网络中,主干特征提取网络(Backbone)负责从原始输入数据中提取出有意义的特征的部分。这些特征通常是语义化、抽象化的,用来解决分类、检测、分割等问题。特征提取网络通常是由多层卷积模块(CBS)组成,每层通过一系列的卷积(Convolution)、样本标准化(Batch Normalization)和非线性激活函数(Silu)等操作,将输入数据逐渐转换为更高级别的特征表示。在YOLOV7中,引入了ELAN模块(Efficient Layer Aggregation Networks),它使用跨层链接的方式,增加了梯度信息,可以减少网络的计算量。与此同时MP模块由最大池化层(MaxPooling)和CBS(Convolutional+Batch Normalization+Silu)结构并联而成,在下采样的同时保留了图像的空间细节特征。
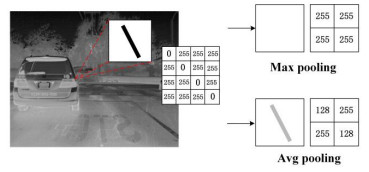
在基于可见光的目标检测算法中,通常使用最大池化算法来提取图像的边缘信息,增加图像锐度。而红外图像有着单通道,热成像的特性,许多基于可见光的算法在红外图像上并不适用。如图 2,当环境温度高而被检测物体温度较低时,目标的灰度值较小,对于卷积神经网络其特征信息不明显,此时用最大池化进行处理会造成特征信息的丢失,从而降低检测精度。
本算法基于YOLOv7的主干特征提取网络(Backbone)做出了改进,将MP模块中的最大池化核替换为平均池化,得到AP模块(AvgPooling+CBS),AP-1与AP-2的结构相同,通道数有所差异。在DarkNet[9]特征提取网络以及Neck层中将AP模块进行应用,相较于主流特征提取方法,改进后的特征提取网络可以有效提取红外图像的低灰度信息,同时保留了更多的图像细节。
1.1.2 特征融合
在卷积神经网络的图像特征中,不同层次的特征代表不同的语义信息。其中,浅特征层的感受野小,空间信息较为丰富,有利于检测小目标的位置信息,而深层特征感受野大,有更多的通道信息,有利于进行特征分类。如何融合不同层次的特征以应对多尺度目标检测是融合网络的首要任务。
相较于双阶段检测网络如Faster R-CNN[10],Mask R-CNN[11],YOLO系列算法为获得更快的检测速度,没有进行建议框的生成,直接在输出特征上进行边界框(bounding box)的回归,这会造成对小目标检测精度低的问题。针对这一问题,本文参考了双阶段检测网络中FPN特征金字塔的思想,并基于PANet网络结构,在Neck部分增加了特征融合的尺度。如图 3,相较于传统YOLO算法,本算法增加了特征分辨率更大的P1特征,不同特征层之间进行上采样或下采样以进行通道的拼接(cat),使不同空间尺度的特征进一步融合。自底向上和自顶向下结合的信息通路结构融合了多分辨率的特征,有助于网络检测不同尺度的目标。
1.1.3 分类与检测
YOLO Head负责将Neck送入的加强特征进行分类与预测,它具体分为3个步骤:①正负样本的判断,②特征图的编码,③解码并进行预测。
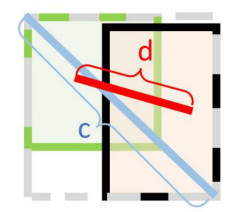
在正负样本判断的过程中,我们借鉴了YOLOv5损失函数的设计,使用CIOU[12]作为判断标准。如图 4,CIOU引入预测框和真实框之间的欧氏距离,解决了IOU对尺度不敏感的问题。其公式如下:
$$ {\text{CIOU}} = {\text{IOU}} - \frac{{{\rho ^2}(b, {b^{{\text{gt}}}})}}{{{c^2}}} - \alpha \upsilon $$ (1) $$ \alpha = \frac{\upsilon }{{1 - {\text{IOU}} + \upsilon }} $$ (2) $$ \upsilon = \frac{4}{{{{\text{π}}^2}}}{(\arctan \frac{{{w^{{\text{gt}}}}}}{{{h^{{\text{gt}}}}}} - \arctan \frac{w}{h})^2} $$ (3) 式中:ρ2(b, bgt)分别代表真实框和预测框中心点间的欧氏距离;c代表的是能够同时包含预测框和真实框的最小闭包区域的对角线距离;IOU代表预测框和真实框的交并比。
在编解码过程中,首先将输入的加强特征进行通道数的调整。以Microsoft COCO数据集[13]为例(80种类别),在基于YOLO的3种不同尺度的Anchor设计中,每一种尺度的Anchor都包含了检测框的坐标和长宽信息(dx, dy, dw, dh)以及物体所属类别(0/1)。为方便进行回归计算,在预测前使用大小为1×1的卷积核进行通道数调整,调整后的通道数为3×(80+4+1)=255。
随着损失函数的降低,预测框与真实框的相似性进一步提高,在检测过程中由于进行多尺度以及多空间位置检测,会产生一系列的预测框。为保证网络检测的准确性,我们使用NMS非极大抑制算法挑选出置信度最高的预测框作为网络的输出。
1.2 数据处理方法
在图像传入神经网络的过程中,通常使用色域变换(HSV)[14],双边模糊(Bilateral Filter)[15]等算法对输入图像进行预处理,增加了图像数据的可变性,有利于损失值的收敛,增加网络的鲁棒性。与可见光不同,红外图像具有通道单一、对比度低、高位宽的特性。在可见光图像上应用的数据处理算法在红外图像上作用不明显甚至有消极作用。如图 5可以看出,原始红外图像经过这些算法处理之后图像质量会进一步下降,不能很好地达成数据增广的目的。针对这一问题,本节提出了一种针对红外图像的数据扩充方法。
红外探测器是根据热辐射的大小进行成像的,其图像灰度有着昼夜翻转的特性。根据这一原理我们将每个像素点的灰度值在一定范围内进行翻转处理,来模拟同一场景下的昼夜成像效果,达到数据增广的目的。其计算如下:
$$ \boldsymbol{F}=\max (\boldsymbol{X})-\boldsymbol{X} $$ (4) 式中:X为输入图像矩阵;max(X)为矩阵中的最大值;F为输出图像矩阵。
经过公式(4)变换前后的图像如图 6所示,(a)表示原始图像,(b)为灰度反转后的图像,经对比可以看出在完成数据扩充的同时图像质量也得到了保证。为验证本方法的有效性,在不同数据集上进行了验证,训练过程中YOLOv7(baseline)采用用随机旋转和镜像翻转作为数据增广方法。结果如表 1所示,在可见光数据集中对每通道的数据进行灰度反转,所提升的精度不明显,在COCO数据集上出现了精度下降的情况,但在红外数据集上使用本算法精度得到了明显提升,在KAIST和FLIR数据集上精度分别上升了2.5%和1.5%。由于可见光与红外图像成像原理不同,所包含的红绿蓝三通道信息不能很好地反应物体与背景间的热度差异,所以使用灰度反转数据扩充方法会导致精度下降的问题,而在红外热图像中,此方法起到了很好的数据扩充作用,对精度的提升也比较明显。
2. 实验及结果分析
2.1 实验设置
实验所用到的数据集为FLIR数据集[18],FLIR数据集共包含14452幅带标签的红外图像,其中10228幅图像取自短视频,4224幅图像取自144 s的连续视频,其中Car标签46692个,Person类别28151个,Bicycle类别4457个,使用Python程序随机划分80%作为训练集,10%作为验证集,余下10%作为测试集。我们使用PyTorch框架来实现本算法,在所有训练中使用的参数如下:训练周期为400,学习率为0.01。使用SGD优化器,其动量和权重衰减参数分别设置为0.9和0.0005。使用单个A6000 GPU进行训练,批次大小设置为32。采用余弦退火算法,初始学习率为0.05。
2.2 消融实验
为了直观地体现各方法对网络性能的影响,以YOLOv7算法作为对比,在FLIR数据集上设置了消融实验。具体分为三步,首先更改网络下采样模块中池化层的种类,其次引入针对红外图像的数据增广方法,最后增加多尺度特征融合模块。通过单步训练与测试,记录各参数变化,分析这些方法网络整体性能的影响。
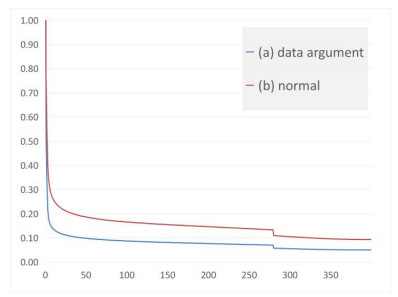
经过300个epoch的训练且当loss稳定后,在FLIR测试集上进行测试。通过表 2可以看出使用多尺度融合模块后mAP提升了1.6%,网络的检测能力得到了提升。并且,将Max pooling替换为Avg pooling后网络的精度也得到了相应提升,证实了在红外图像中使用Avg pooling能获取更多特征信息的假设。如图 7所示,在引入针对红外图像的数据扩充方法后可以有效地帮助网络收敛,加快了梯度下降的速率,同时得到更低的loss值,并且如表 2所示,其检测精度也得到了相应的提高。当同时使用这些方法确定的网络模型进行测试时,检测精度得到了进一步的提升。
表 2 YOLO-MIR在FLIR数据集上的消融实验Table 2. YOLO-MIR ablation experiments on FLIR datasetYOLOv7 Avg pooling Data argument Multi-scale integration mAP50/% √ 90.0 √ √ 90.5 √ √ 90.9 √ √ 91.6 √ √ √ √ 92.7 2.3 对比实验
我们采用平均精度均值(mAP),各类别的平均精度(AP),参数量(Params),权重大小(Weight)等指标对网络性能进行综合评价。通过表 3可以看出与主流的单步检测网络YOLOv4,YOLOv5,SMG-Y和YOLO-ACN相比,YOLO-MIR的性能更高,相对于最新的YOLOv7,在Person,Bicycle,Car各类别的AP上分别高出2.5%,3.8%,4.4%。本算法同时保留了小参数量的优势,可以适应于移动端的部署。相对于硬件要求高,参数量较大的双步检测网络Faster R-CNN和PMBW(A Paced MultiStage BlockWise)相比,本算法体现出明显优势,在参数量远远小于Faster R-CNN和PMBW的条件下Person,Bicycle,Car各类别AP上比Faster R-CNN分别高出14.7%,18.5%,8.8%,比PMBW分别高出9.9%,27%,10.7%,
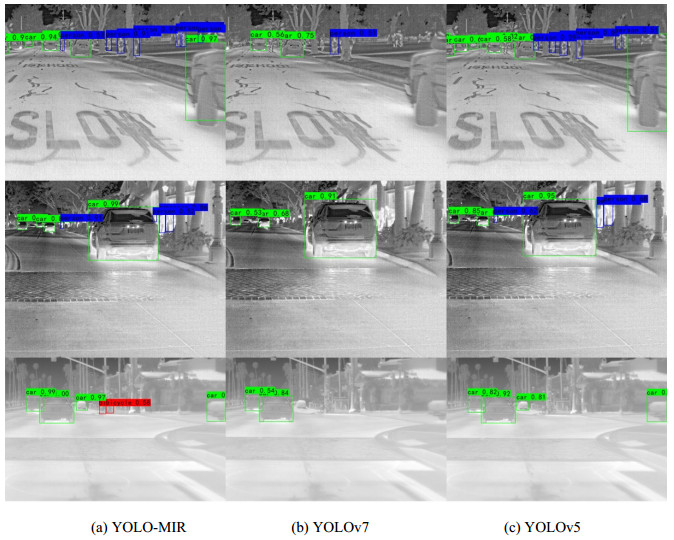
表 3 YOLO-MIR与其他网络在FLIR数据集上的对比实验Table 3. Experiments comparing YOLO-MIR with other networks on FLIR datasetMethods mAP/% Person/% Bicycle/% Car/% Parameters FLOPs/B Faster R-CNN 79.2 76.4 72.5 88.4 41.2M 156.1 YOLOv4 79.3 76.2 75.1 87.3 63.9M 128.3 YOLOv5m 81.6 78.0 78.1 89.2 35.7M 50.2 SMG-Y[19] 77.0 78.5 65.8 86.6 43.8M 54.7 PMBW[20] 77.3 81.2 64.0 86.5 36.0M 120.0 RGBT[21] 82.9 80.1 76.7 91.8 82.7M 130.0 YOLO-ACN 82.1 79.1 57.9 85.1 34.5M 111.5 YOLOv7 89.7 88.6 87.2 92.8 36.9M 104.7 YOLO-MIR 92.7 91.1 91.0 97.2 37.0M 104.8 通过测试结果,我们可以直观地展示网络性能的差异。图 8显示了不同网络的预测结果。通过对比可以看出YOLO-MIR在同一场景下检测到的物体数量更多,且不同尺度目标的置信度明显高于其他网络。通过对比试验可以看出YOLO-MIR具有出色的性能,并且对不同尺度的红外目标都具有更高的检测精度。
3. 结论
为解决主流的目标检测算法对红外图像适应性差、检测精度低的问题,本文提出了一种针对多尺度红外目标的检测算法YOLO-MIR。针对红外图像特征难以提取的问题,本文借鉴了YOLOv7的下采样模块并做出了进一步改进,可以有效地提取红外图像特征。为了适应多尺度目标的检测,在网络的特征融合部分引入PANet特征金字塔结构,增加了高特征分辨率的信息。在数据处理方面,提出了一种针对红外图像的数据增广方法,可以有效加快训练速度的同时提升了网络的鲁棒性。消融实验和对比试验的结果表明,YOLO-MIR比最新的YOLOv7算法在平均检测精度上提高了3%,同时保留了小参数量的优势。在测试过程中,本算法无论是检测速度还是检测精度都有着出色的性能,在日常应用和工业生产中都有很大的应用价值。
-
表 1 YOLOv7数据扩充方法在不同数据集上的对比
Table 1 Comparison of YOLOv7 data expansion methods on different data sets
表 2 YOLO-MIR在FLIR数据集上的消融实验
Table 2 YOLO-MIR ablation experiments on FLIR dataset
YOLOv7 Avg pooling Data argument Multi-scale integration mAP50/% √ 90.0 √ √ 90.5 √ √ 90.9 √ √ 91.6 √ √ √ √ 92.7 表 3 YOLO-MIR与其他网络在FLIR数据集上的对比实验
Table 3 Experiments comparing YOLO-MIR with other networks on FLIR dataset
Methods mAP/% Person/% Bicycle/% Car/% Parameters FLOPs/B Faster R-CNN 79.2 76.4 72.5 88.4 41.2M 156.1 YOLOv4 79.3 76.2 75.1 87.3 63.9M 128.3 YOLOv5m 81.6 78.0 78.1 89.2 35.7M 50.2 SMG-Y[19] 77.0 78.5 65.8 86.6 43.8M 54.7 PMBW[20] 77.3 81.2 64.0 86.5 36.0M 120.0 RGBT[21] 82.9 80.1 76.7 91.8 82.7M 130.0 YOLO-ACN 82.1 79.1 57.9 85.1 34.5M 111.5 YOLOv7 89.7 88.6 87.2 92.8 36.9M 104.7 YOLO-MIR 92.7 91.1 91.0 97.2 37.0M 104.8 -
[1] Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2014: 580-587.
[2] Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2016: 779-788.
[3] LI Z, ZHOU F. FSSD: feature fusion single shot multibox detector[J/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv, 2017, https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.00960.
[4] Redmon J, Farhadi A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement[J/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv, 2018, https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.02767.
[5] Jocher G, Chaurasia A, Stoken A, et al. ultralytics/yolov5: v6.1 - TensorRT, TensorFlow Edge TPU and OpenVINO Export and Inference[Z/OL]. 2022, https://doi.org/10.5281/ZENODO.6222936.
[6] Bochkovskiy A, Wang C Y, Liao H Y M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[J/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv, 2020, https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.10934#:~:text=%EE%80%80YOLOv4%3A%20Optimal%20Speed%20and%20Accuracy%20of%20Object%20Detection%EE%80%81.,features%20operate%20on%20certain%20models%20exclusively%20and%20.
[7] WANG C Y, Bochkovskiy A, LIAO H Y M. YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv, 2022, https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.02696.
[8] LIU S, QI L, QIN H, et al. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2018: 8759-8768.
[9] Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLO9000: Better, Faster, Stronger[C]// Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition. IEEE, 2017: 6517-6525.
[10] REN S, HE K, Girshick R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137-1149. http://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27295650/
[11] He K, Gkioxari G, Dollár P, et al. Mask r-cnn[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2017: 2961-2969.
[12] ZHENG Z, WANG P, REN D, et al. Enhancing geometric factors in model learning and inference for object detection and instance segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 52(8): 8574-8586. http://www.xueshufan.com/publication/3194790201
[13] Veit A, Matera T, Neumann L, et al. Coco-text: Dataset and benchmark for text detection and recognition in natural images[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv, 2016, https://arxiv.org/abs/1601.07140.
[14] Smith A R. Color gamut transform pairs[J]. ACM Siggraph Computer Graphics, 1978, 12(3): 12-19. DOI: 10.1145/965139.807361
[15] Zhou Z, Cao J, Wang H, et al. Image denoising algorithm via doubly bilateral filtering[C]// International Conference on Information Engineering and Computer Science. IEEE, 2009: 1-4.
[16] Hoiem D, Divvala S K, Hays J H. Pascal VOC 2008 challenge[J]. Computer Science, 2009 https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Pascal-VOC-2008-Challenge-Hoiem-Divvala/9c327cf1bb8435a8fba27b6ace50bb907078d8d1.
[17] ZHAO W Y. Discriminant component analysis for face recognition[C]//Proceedings 15th International Conference on Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2000, 2: 818-821.
[18] Venkataraman V, FAN G, FAN X. Target tracking with online feature selection in FLIR imagery[C]// IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, IEEE, 2007: 1-8.
[19] CHEN R, LIU S, MU J, et al. Borrow from source models: efficient infrared object detection with limited examples[J]. Applied Sciences, 2022, 12(4): 1896. DOI: 10.3390/app12041896
[20] Kera S B, Tadepalli A, Ranjani J J. A paced multi-stage block-wise approach for object detection in thermal images[J]. The Visual Computer, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00371-022-02445-x.
[21] Vadidar M, Kariminezhad A, Mayr C, et al. Robust Environment Perception for Automated Driving: A Unified Learning Pipeline for Visual-Infrared Object Detection[C]// IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (Ⅳ). IEEE, 2022: 367-374.
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 李海源,黄俊. 基于YOLOv8的无人机红外航拍目标检测方法. 激光杂志. 2025(02): 73-81 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 饶兴昌,郑盈盈,陆万浩,黄孙港. 基于改进YOLOv7红外海上船舶检测算法. 电光与控制. 2025(04): 23-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杨明,吴轶,申宋彦,王新科,陈鹏. 基于改进YOLOv4的双臂协作分拣目标检测模型构建. 自动化应用. 2025(08): 42-44+49 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李爱华,彭凌西. 基于机器视觉的红外目标抗干扰识别算法. 计算机仿真. 2024(09): 532-537 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)



 下载:
下载: