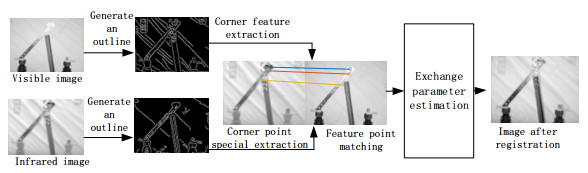
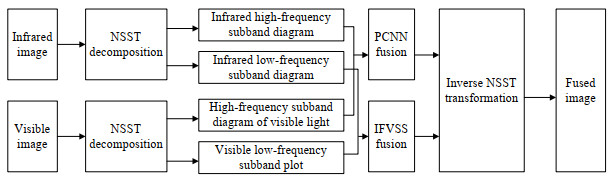
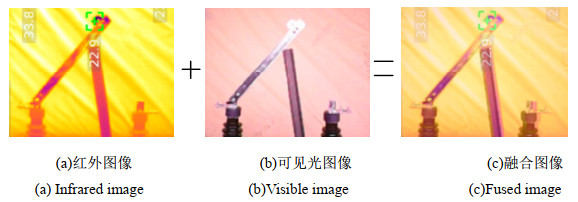
Recognition of High-Voltage Isolation Switch Opening and Closing State Based on Image Fusion
-
摘要:
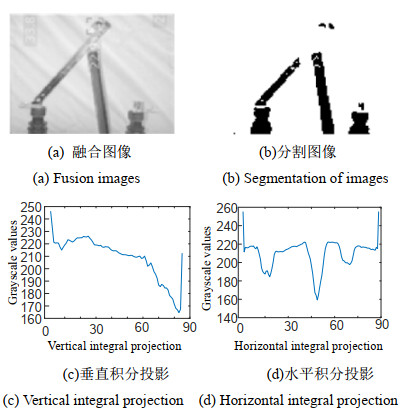
为了解决现有隔离开关分合闸状态识别率较低的问题,提出了一种基于NSST-PCNN-IFVSS的图像融合方法。在对红外和可见光图像的预处理阶段进行图像配准,再采用像素级融合来实现两图像的融合。在融合阶段采用非下采样剪切波变换将红外和可见光图像分解为高频子带图和低频子带图,在高频子带图部分采用脉冲耦合神经网络进行融合,在低频子带图部分采用基于视觉显著特性分割的图像融合方法进行融合,通过非下采样剪切波变换的逆变换将两个子带图像结合起来得到融合后的图。建立融合质量指标评价方案来对比本方案与常见的图像融合方案的效果。对融合后的图像进行像素积分投影算法进行处理,进而实现对高压隔离开关分合闸状态进行识别。通过实验仿真验证了NSST-PCNN-IFVSS(Non Subsampled Shearlet Transform-Pulse Coupled Neural Network-Image Fusion based on Visual Salience Segmentation)的图像融合效果优于常见的6种融合方法,且图像融合后的识别结果优于单一的可见光图像和红外图像。
-
关键词:
- 高压隔离开关 /
- 图像融合 /
- NSST-PCNN-IFVSS /
- 图像配准 /
- 像素积分投影
Abstract:To solve the low recognition rate problem of the existing isolation switch state identification, a method of image fusion based on NSST-PCNN-IFVSS is proposed. Image registration is performed in the preprocessing stage of infrared and visible light images; subsequently, pixels and fusion are used to achieve the fusion of the two images. In the fusion stage, the non-subsampled shearlet transform is used to decompose the infrared and visible light images into high- and low-frequency sub-band images. In the high-frequency sub-band image part, a pulse coupled neural network is used for fusion, whereas the image fusion method based on visual saliency segmentation is used for fusion in the low-frequency sub-band image part. The two sub-band images are combined by the inverse transform of the non-subsampled shearlet transform to obtain the fused image. A fusion quality index evaluation scheme is established to compare the effect of this method with common image fusion methods. The fused image is processed by a pixel integration projection algorithm to determine the state of the high-voltage isolation switch. Experimental simulation verifies that the image fusion effect of the non-subsampled shearlet transform-pulse coupled neural network-image fusion based on visual salience segmentation is better than six common fusion methods, and the recognition result after image fusion is better than that of the single visible light image and infrared image.
-
0. 引言
在沿海机场往往会面临机场跑道方向上时有货轮经过附近海域或大型海上平台在航线方向海上作业影响飞机起飞降安全的情况,由于机场位于开阔水域,往来船舶等频繁,发生跑道入侵事件的风险很大[1];在内陆江河或沿海航道上同样会面临过往船只过高对跨江或跨海大桥产生安全威胁的情况,需要预防桥梁受到船舶撞击[2]。为此这些地方往往需要对过往船只的高度乃至位置进行监测,实时掌握目标航向和目标高度以便评估其威胁程度。
在船舶移动的过程中由于多普勒效应影响,同时雷达引导上传目标数据周期性长、实时性差,单纯的雷达探测只能获取滞后的目标绝对位置信息,不可避免会产生一定的误差[3-4],无法掌握目标准确的高度,且随着水位的涨落,同一型船只在不同的时间经过同一位置也难以保证船只最高点的高程保持不变,为此需要一种高精度目标定位系统能够实时解算出目标的绝对位置和高程信息。
为此,本文设计了一种集成有高清可见光相机、红外热像仪、高精度激光测距机、倾角仪、光电编码器于一体的光电船只目标定位系统。
1. 测量原理
光电船只目标定位系统安装于陆地基座上,依靠内部集成的高清可见光相机、红外热像仪及激光测距机可实现昼夜对目标船只位置和高程信息的监测,下文图中云台均以PTZ代表,系统工作示意图如图 1所示。
通过北斗定位装置获取云台自身的经纬度高程坐标信息(本文中经纬度高程坐标信息均基于2000国家大地坐标系),通过激光测距机和云台编码器获取目标相对于云台的相对坐标信息,通过倾角仪获取云台安装基座姿态变化信息以对目标解算位置进行实时修正。以上信息经云台内部目标定位解算模块解算,给出目标的绝对位置信息,如图 2所示。
由于系统设备安装方式为陆基安装,故只需在系统安装完毕后,利用北斗定位装置对光电系统安装位置进行一次自身坐标位置标定,以获取光电系统的经纬度坐标和高程信息。同时利用云台内部的水平向和高低向光电编码器获取目标相对于云台的角度信息,通过激光测距机获取目标相对于云台的测量距离,由此可解算出目标对于光电系统的相对位置和高程信息,再结合光电系统自身的大地坐标位置即可解算出目标的绝对位置和高程信息,目标与云台坐标系关系如图 3所示。
目标相对于云台坐标系的相对位置信息为:
$$ \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{x_1}} \\ {{y_1}} \\ {{z_1}} \end{array}} \right] = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {d\cos a\sin b} \\ {d\cos a\cos b} \\ {d\sin a} \end{array}} \right] $$ (1) 式中:x1、y1、z1为目标在云台坐标系内的坐标信息;d为目标相对云台的直线距离;a为目标相对于云台的俯仰角;b为目标相对于云台的方位角。
实际应用中,云台所处的安装基座一般要高出地面或者建筑物一定高度,长期受到大风或者振动影响后基座面相对于初始安装时往往会发生一定的姿态改变,这会造成目标相对于云台自身的相对位置也会发生轻微变化,进而一定程度上会影响对目标的定位解算精度。因此引入云台内倾角仪输出的姿态信息对云台姿态进行校正。目标与发生偏移后云台坐标系关系如图 4所示。
目标在偏移后的云台坐标系的绝对位置信息为:
$$ \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{x_2}} \\ {{y_2}} \\ {{z_2}} \end{array}} \right] = {\mathit{\boldsymbol{C}}}\left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{x_1}} \\ {{y_1}} \\ {{z_1}} \end{array}} \right] + \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{x_0}} \\ {{y_0}} \\ {{z_0}} \end{array}} \right] $$ (2) 式中:x0、y0、z0为在大地坐标系下三轴的坐标;x2、y2、z2为在大地坐标系下三轴的坐标;α、β、δ分别为偏移后的云台坐标系各轴相对于原坐标系各轴的姿态变化角度,矩阵C为:
$$ {\mathit{\boldsymbol{C}}} = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {\cos \delta \cos \beta }&{\sin \alpha \sin \delta \cos \beta - \cos \alpha \sin \beta }&{\cos \alpha \sin \delta \cos \beta + \sin \alpha \sin \beta } \\ {\cos \beta }&{\sin \alpha \sin \delta \sin \beta + \cos \alpha \sin \beta }&{\cos \alpha \sin \delta \cos \beta - \sin \alpha \cos \beta } \\ { - \sin \delta }&{\sin \alpha \cos \delta }&{\cos \alpha \cos \delta } \end{array}} \right] $$ (3) 2. 云台伺服系统设计
云台伺服系统采用经典的位置环、速度环、电流环三环设计,通过位置环结合速度环和电流环实现云台根据雷达系统引导信息调转到指定位置,由于雷达引导坐标位置精确性较差且具有滞后性,需要进一步优化工作流程才能锁定测量目标。因此云台在接收雷达引导信息调转到位后,转入识别跟踪流程,识别并锁定跟踪目标船只最高点,并对其进行目标定位测量解算。伺服系统控制方案如图 5所示。
其中位置环和电流环采用Proportional integral比例积分控制器,速度环采用Linear active disturbance rejection control线性自抗扰控制器。
自抗扰控制由韩京清教授最早提出,通过跟踪-微分器、反馈控制律、扩张状态观测器组成的控制器不依赖于系统的精确数学模型具有良好的鲁棒性和适应性[5]。针对自抗扰控制中非线性结构多、待调控制参数多的不便于工程化使用情况,高志强教授进一步提出了待调参数数量简化的线性自抗扰控制算法即LADRC,使整定参数和带宽相关,整定难度简化,更适合应用于工程领域[6]。
云台采用表贴式永磁同步电机,电机转矩和运动方程为:
$$ \left\{ \begin{array}{l} {T_{\rm{e}}} = {T_{\rm{L}}} + B\omega + J\frac{{{\rm{d}}\omega }}{{{\rm{d}}t}} \hfill \\ {T_{\rm{e}}} = {C_{\rm{t}}}{i_{\rm{q}}} \hfill \end{array} \right. $$ (4) 式中:Te为电磁转矩;TL为负载转矩;B为阻尼系数;ω为电机机械角速度;J为转动惯量;Ct为转矩系数;iq为转矩电流分量。
根据电机转矩和运动方程可见,速度环适宜使用一阶LADRC速度控制器,首先设计扩张状态观测器部分。
由式(4)可以进一步得到状态方程:
$$ \left\{ \begin{array}{l} {{\dot x}_1} = {x_2} + {l_0}{i_{\rm{q}}} \hfill \\ {x_2} = f \hfill \end{array} \right. $$ (5) 式中:x1=ω为电机机械角速度;x2为$ f = \frac{1}{J}({C_t}{i_{\rm{q}}} - {T_{\rm{L}}} - B\omega ) - l{}_0{i_{\rm{q}}} $,为未知待观测量;l0为速度环LADRC控制器待调参数。
采用的线性状态观测器方程为:
$$ \left\{ \begin{array}{l} \dot z = {\mathit{\boldsymbol{A}}}z + {\mathit{\boldsymbol{B}}}u + {\mathit{\boldsymbol{L}}}({x_1} - {z_1}) \hfill \\ {\mathit{\boldsymbol{A}}} = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} 0&1 \\ 0&0 \end{array}} \right] \hfill \\ {\mathit{\boldsymbol{B}}} = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{l_0}} \\ 0 \end{array}} \right] \hfill \\ {\mathit{\boldsymbol{L}}} = \left[ {\begin{array}{*{20}{c}} {{l_1}} \\ {{l_2}} \end{array}} \right] \hfill \end{array} \right. $$ (6) 式中:z为系统观测的状态量;x为系统实际的状态量;u为系统输入量。
由式(5)、式(6)可以得到:
$$ \left\{ \begin{array}{l} \dot {\hat \omega} = \hat f + {l_0}{i_{\rm{q}}} + {l_1}(\omega - \hat \omega ) \hfill \\ \hat f = {l_2}(\omega - \hat \omega ) \hfill \end{array} \right. $$ (7) 式中:$ \hat \omega $为电机角速度观测值;$ \hat f $为待观测量f的观测值。
取$ {l_0}{i_q} = {u_0} - \hat f $,当$ \hat f $无限接近于f时,则由式(5)有:
$$ \dot \omega = f + ({u_0} - \hat f) = {u_0} $$ (8) 式中:u0为控制律输出量。
电机速度环经过控制器可等效为一阶积分环节,故LADRC控制律环节可简化设计为比例控制器[7],取$ {u_0} = {K_{\rm{p}}}({\omega _{{\rm{ref}}}} - \hat \omega ) $,ωref为速度环给定转速。云台采用的力矩电机为低速电机且长期工作于低速运行状态,故省去LADRC中的跟踪-微分器环节设计,由此可以得到速度环LADRC控制器结构如图 6所示。
系统中俯仰向采用J180LWX005型无刷力矩电机和EAC90F-0M21S型光电编码器,采用的电机和编码器参数如表 1所示。
表 1 电机和编码器参数Table 1. Motor and encoder parameterJ180LWX005 motor Value EAC90F-0M21S encoder Value Rated torque/(N⋅m) 8 Resolution 21 bits Rated current/A 4 Accuracy < 30″ No-load speed/rpm 110 Maximum speed/rpm 6000 Torque coefficient/(N⋅m/A) 2 Phase resistor/Ω 1.6 Phase inductance/mH 4.5 速度环给定转速ωref=3.66°/s,分别测试速度环采用PI控制器和LADRC控制器速度响应情况,并在速度达到稳定后突加一固定干扰力矩,速度环响应曲线如图 7所示。
由图 7、图 8可见采用LADRC控制器后,云台速度环可更快抑制扰动,转速控制波动量小更加平稳,位置调转响应更快。
位置闭环响应曲线如图 8所示,电机初始位置为30°,测试时先回到0°位置,再调转至50°位置。
3. 系统软件设计
该目标定位系统工作流程如图 9所示。云台根据雷达引导信息调转至指定位置,由于雷达引导位置存在一定误差,加上目标船只处于移动状态因此雷达引导信息具有滞后性,且雷达不能获取到目标最高点位置,因此云台调转到位后不能立刻进行目标船只定位测高,需要先识别选定视场内目标船只最高点,然后再开启跟踪锁定目标船只最高点进行定位测高。
在得到目标船只测距值后,通过依次读取云台倾角仪获取云台相对大地坐标系姿态角、云台编码器值获取目标船只相对云台坐标系极坐标,结合云台所处的经纬度高程信息,即可解算出目标船只准确的经纬度和高程信息。
4. 测试结果
随机选取了4个不同方向不同距离的目标点对系统的测量精度进行测试,目标点经纬度测试情况如表 2所示。
表 2 目标经纬度测量对照Table 2. Target longitude and latitude measurement comparisonActual value of target longitude and latitude/° Measurement value of target longitude and latitude/° Distance/m Deviation/m Longitude: 118.7693622; Latitude: 31.87598539 Longitude: 118.7693379; Latitude: 31.8759465 2638 4.77 Longitude: 118.7841865; Latitude: 31.896963 Longitude: 118.7841426; Latitude: 31.8969342 3825 4.86 Longitude: 118.7775752; Latitude: 31.9166531 Longitude: 118.777571; Latitude: 31.9166863 6025 3.71 Longitude: 118.86845383; Latitude: 31.89987727 Longitude: 118.868425; Latitude: 31.8998692 8224 2.84 目标点高程测试情况,如表 3所示。综合表 2和表 3可见,该系统对目标点在经纬度测量上误差不超过5 m,高程测量上误差不超过2 m,可实现较高的测量精度。
表 3 目标高程测量对照Table 3. Target height measurement comparisonActual value of target height/m Measurement value/m Distance/m Deviation/m 87.944 88.2 2638 0.256 113.346 112.4 3825 -0.946 116.26 115.2 6025 -1.06 230.2 228.7 8224 -1.5 5. 结束语
文中提出了一种光电式高精度目标船只定位系统,利用该系统可获取较高精度的目标位置和高程信息,有效提高了目标定位测算的准确度和效率。
试验表明了该设计的合理性。试验结果证明该系统可给出目标位置较高精度的定位数据,投入使用后工作稳定可靠,具有良好的性能,在无人值守监控定位领域具有广泛的应用前景。
-
表 1 不同融合方法得到的图像质量评价指标
Table 1 Image quality evaluation indicators obtained by different fusion methods
Fusion methods QAB/F IE MI VSI STD SSIM LAB 9.9351 5.8204 -6.37e-12 9945 27.3467 1 IHS 11.3684 6.1834 -8.00e-12 10030 32.3809 1 Weighted average fusion 9.1370 6.1181 -1.00e-11 9945 33.6583 1 Brovey 12.1616 5.3541 -6.10e-12 9944 38.2942 1 Wavelet transform fusion 8.1644 6.5108 -1.65e-11 9945 33.0885 1 PCA 8.7515 5.3947 -7.02e-12 10030 26.4476 1 NSST-PCNN-IFVSS 14.3917 6.5260 -1.03e-11 10030 38.5471 1 表 2 不同类型图像识别准确率对比表
Table 2 Different types of image recognition accuracy comparison
Image type Opening accuracy Closing accuracy Infrared image 88% 87% Visible image 91% 89% Fused images 95% 94% -
[1] XU J, LI Q, LUO Y, et al. State measurement of isolating switch using cost fusion and smoothness prior based stereo matching[J]. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 2020, 17(3): 172988142092529. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDHB202405016.htm [2] LI Y, DONG X, LIU Z, et al. Design of grinding tool for isolating switch with multiple operating conditions in substation[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2020, 1601(4): 042015-042019. DOI: 10.1088/1742-6596/1601/4/042015
[3] 曾小松, 罗菁, 姚强, 等. 500 kV GIS隔离开关触头温度监测及外壳温度传感器优化布置[J]. 高压电器, 2021, 57(10): 111-119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYDQ202401004.htm ZENG Xiaosong, LUO Jing, YAO Qiang, et al. Temperature monitoring of 500 kv GIS isolation switch contacts and optimal placement of shell temperature sensor[J]. High Voltage Electrical Apparatus, 2021, 57(10): 111-119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYDQ202401004.htm
[4] 陈富国, 蔡杰, 李中旗. 基于机器视觉的高压隔离开关设备状态判别与故障诊断技术[J]. 微型电脑应用, 2022, 38(2): 191-194. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-757X.2022.02.055 CHEN Fuguo, CAI Jie, LI Zhongqi. State identification and Fault diagnosis of High voltage isolation Switchgear based on machine vision [J]. Microcomputer Applications, 2022, 38(2): 191-194. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-757X.2022.02.055
[5] 腾云, 雷丞, 李洪涛, 等. 基于HOG和SVM的高压隔离开关分合闸状态自动识别技术研究[J]. 高压电器, 2020, 56(9): 246-252. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYDQ202009036.htm TENG Yun, LEI Cheng, LI Hongtao, et al. Research on automatic state recognition of high voltage isolation switch based on HOG and SVM [J]. High Voltage Electrical Apparatus, 2020, 56(9): 246-252. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYDQ202009036.htm
[6] 刘子英, 张靖, 邓芳明. 基于BP神经网络的高压隔离开关分合闸监测识别[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2020, 48(5): 134-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDQW202005018.htm LIU Ziying, ZHANG Jing, DENG Fangming. On-off monitoring and identification of high voltage isolation switch based on BP neural network [J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48(5): 134-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDQW202005018.htm
[7] 刘春来, 周涛涛, 马宏明, 等. 基于力矩与转角检测的GW4-126型隔离开关典型机械故障诊断[J]. 高压电器, 2020, 56(2): 232-239. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYDQ202002037.htm LIU Chunlai, ZHOU Taotao, MA Hongming, et al. Typical mechanical fault diagnosis of GW4-126 isolation switch based on torque and angle detection [J]. High Voltage Electrical Apparatus, 2020, 56(2): 232-239. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYDQ202002037.htm
[8] 于力, 曹双鹏, 荆澜涛, 等. 550 kV GIS内隔离开关机械故障仿真研究[J]. 高压电器, 2021, 57(10): 127-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYDQ202405001.htm YU Li, CAO Shuangpeng, JING Lantao, et al. Mechanical fault simulation of isolation switch in 550 kV GIS[J]. High Voltage Electrical Apparatus, 2021, 57(10): 127-133. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYDQ202405001.htm
[9] 刘仕兵, 宋陵灿, 郭文璟, 等. 基于定子电流特征与SVM高压隔离开关机构故障诊断[J]. 高压电器, 2020, 56(6): 289-295. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYDQ202006043.htm LIU Shibing, SONG Lingcan, GUO Wenjing, et al. Fault diagnosis of high voltage isolation switch based on stator current characteristics and SVM[J]. High Voltage Electrical Apparatus, 2020, 56(6): 289-295. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYDQ202006043.htm
[10] CAO Y, TANG L, JIN R, et al. Grayscale image for broadband linear polarization measurement by an ultracompact metasurface[J]. Optics Letters, 2021, 46(5): 1117-1120. DOI: 10.1364/OL.415844
[11] Ehsan S M, Imran M, Ullah A, et al. A single image dehazing technique using the dual transmission maps strategy and gradient-domain guided image filtering[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 89055-89063. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3090078
[12] 谢文昕, 马伟, 杜雪雪, 等. 起重机械金属结构缺陷的热成像技术研究[J]. 红外技术, 2022, 44(7): 741-749. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/cn/article/id/ef131bfa-8ddb-49e8-827f-f1ea324eb408 XIE Wenxin, MA Wei, DU Xuexue, et al. Thermal imaging of metal structure defects in lifting machinery[J]. Infrared Technology, 2022, 44(7): 741-749. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/cn/article/id/ef131bfa-8ddb-49e8-827f-f1ea324eb408
[13] Jhan J P, Rau J Y. A generalized tool for accurate and efficient image registration of UAV multi-lens multispectral cameras by n-surf matching[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14: 6353-6362. DOI: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3079404
[14] 何凯, 刘坤, 沈成南, 等. 基于相似图像配准的图像修复算法[J]. 电子科技大学学报, 2021, 50(2): 207-213. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKDX202102008.htm HE Kai, LIU Kun, SHEN Chengnan, et al. Image restoration algorithm based on similar image registration[J]. Journal of University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2021, 50(2): 207-213. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKDX202102008.htm
[15] Dinesh K P, Jeetha B R. Canny edge detection and contrast stretching for facial expression detection and recognition using machine learning[J]. Far East Journal of Electronics and Communications, 2021, 24(1): 35-66. DOI: 10.17654/EC024010035
[16] Radha R, Pushpa M. A comparative analysis of SIFT, SURF and ORB on sketch and paint based images[J]. International Journal of Forensic Engineering, 2021(8): 102-110.
[17] Amir A, Mokhtar K. A deeper Newton descent direction with generalized Hessian matrix for SVMs: an application to face detection[J]. International Journal of Mathematical Modelling and Numerical Optimization, 2021, 11(2): 196-208. DOI: 10.1504/IJMMNO.2021.114485
[18] Levenberg K A. A method for the solution of certain non-linear problems in least squares[J]. Quarterly of Applied Mathematics, 2018, 2(4): 436-438.
[19] HU Peng, WANG Chenjun, LI Dequan, et al. An improved hybrid multiscale fusion algorithm based on NSST for infrared–visible images[J]. The Visual Computer, 2024, 40: 1245-1259. DOI: 10.1007/s00371-023-02844-8
[20] Basar S, Ali M, Ochoa-Ruiz G, et al. A novel defocused image segmentation method based on PCNN and LBP[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 87219-87240. DOI: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3084905
[21] 朱亚辉, 高逦. 基于复合分解与直觉模糊集的红外与可见光图像融合方法[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2021, 39(4): 930-936. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBGD202104028.htm ZHU Yahui, GAO Li. Infrared and visible image fusion method based on composite decomposition and intuitive fuzzy set[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2021, 39(4): 930-936. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBGD202104028.htm
[22] 余映, 吴青龙, 邵凯旋, 等. 超复数域小波变换的显著性检测[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2019, 41(9): 2231-2238. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYX201909028.htm YU Ying, WU Qinglong, SHAO Kaixuan, et al. Significance detection of wavelet transform in hypercomplex domain[J]. Journal of Electronics and Information Technology, 2019, 41(9): 2231-2238. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYX201909028.htm
[23] ZHANG Y, HAN J. Differential privacy fuzzy C-means clustering algorithm based on Gaussian kernel function[J]. PLOS ONE, 2021, 16(3): 1-20.
[24] 郭全民, 柴改霞, 李翰山. 夜视抗晕光融合图像自适应分区质量评价[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(7): 1750-1757. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYX202007025.htm GUO Quanmin, CHAI Gaixia, LI Hanshan. Quality evaluation of adaptive partition of night vision anti-halo fusion image[J]. Journal of Electronics and Information Technology, 2020, 42(7): 1750-1757. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYX202007025.htm
[25] 杜云, 郑羽纶, 孟凡华. 基于Otsu法和直方图规定化相结合的苹果图像分割研究[J]. 科技创新与应用, 2019(28): 15-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CXYY201928004.htm DU Yun, ZHENG Yulun, MENG Fanhua. Research on apple image segmentation based on Otsu method and histogram regularization [J]. Science and Technology Innovation and Application, 2019(28): 15-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CXYY201928004.htm
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 李绍军,李英杰,李威,徐哲,王国右,徐妍,荆凡胜. 车载升降式光电云台共振抑制方法研究. 红外技术. 2024(04): 406-412 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: