Infrared Image Non-uniformity Correction Algorithm Based on Lightweight Multiscale Downsampling Network
-
摘要:
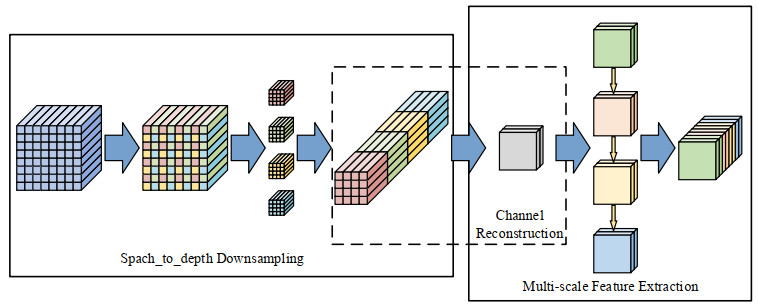
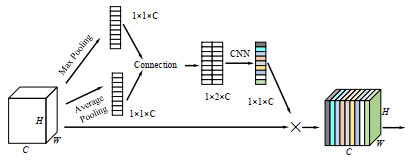
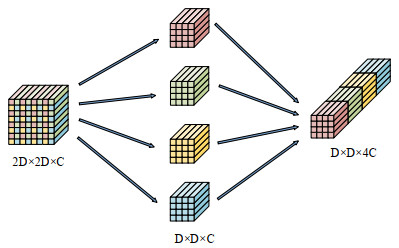
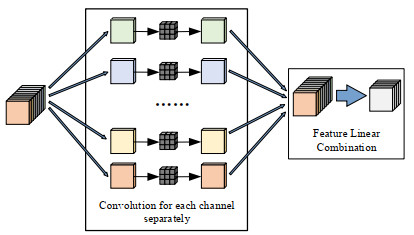
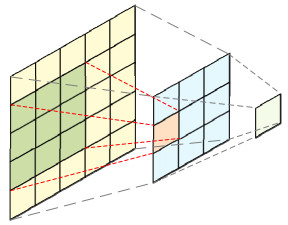
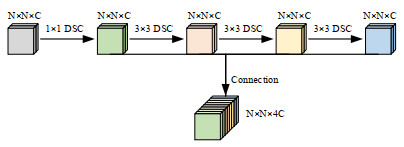
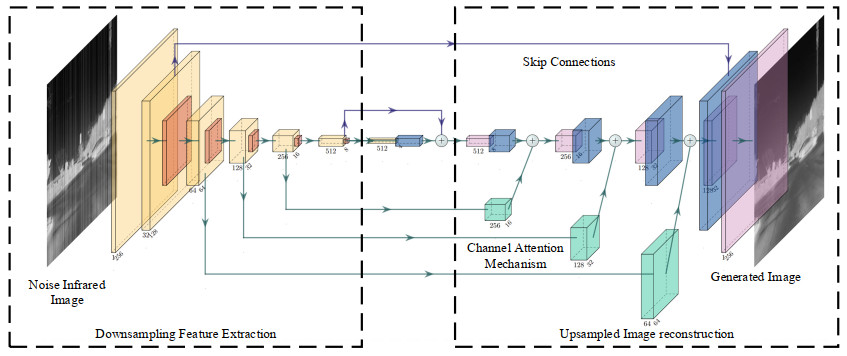
红外成像系统常由于探测单元的非均匀性导致成像结果出现条纹噪声。基于深度学习的红外图像非均匀校正算法为取得较好的校正结果,通常采用复杂度高的网络结构,导致计算量庞大。本文提出了一种轻量化网络的红外图像非均匀校正算法,并针对Unet网络的编码过程设计了一种轻量化多尺度下采样模块(Lightweight Multi-scale Downsampling Module, LMDM)。LMDM通过像素拆分和通道重构实现特征图下采样,利用多个串联的深度可分离卷积(Depth-wise Separable Convolution, DSC)实现多尺度特征提取。此外,该算法引入轻量化通道注意力机制用于调整特征权重,实现更好的上下文信息融合。实验结果表明,与对比算法相比,本文提出的算法在保证校正图像纹理清晰、细节丰富和边缘锐利的前提下,内存占用降低70%以上,红外图像处理速度提升24%以上。
Abstract:Infrared imaging systems often produce fringe noise in imaging results owing to the non-uniformity of the detection unit. To obtain better correction results, most deep learning-based infrared image non-uniformity correction algorithms adopt complex network structures, which increase the computational cost. This study proposes a lightweight network-based infrared image non-uniformity correction algorithm and designs a lightweight multi-scale downsampling module (LMDM) for the encoding process of the Unet network. The LMDM uses pixel splitting and channel reconstruction to realize feature map downsampling and realizes multi-scale feature extraction using multiple cascaded depth-wise separable convolutions (DSC). In addition, the algorithm introduces a lightweight channel attention mechanism for adjusting feature weights to achieve better contextual information fusion. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm reduces memory use by more than 70% and improves the processing speed of the infrared images by more than 24% compared with the comparison algorithm while ensuring that the corrected image has a clear texture, rich details, and sharp edges.
-
-
表 1 模型训练环境
Table 1 Model training environment
Indicator Parameters CPU AMD Ryzen7 5800H GPU NVIDIA RTX 3060 RAM size 16G VRAM size 6GB CUDA vision 10.0 Deep learning framework Tensorflow-gpu-2.3.0 Batch size 16 Optimization algorithm Adam Learning rate 0.0001 Decay rate 0.9 表 2 各网络内存消耗
Table 2 Memory consumption of each network
Network Weight/kB Feature-map /M LMDM(Ours) 0.3672 1.7500 Unet 0.8476 5.5000 MobleNetV1 0.9883 4.6875 MobileNetV3 1.1875 4.5000 ConvNet 11.5078 21.7500 GhostNet 2.0156 20.5000 表 3 网络校正速度和内存对比
Table 3 Network correction speed and memory comparison
Algorithm Time-consuming of
100 images/sNetwork consumes
memory/MBOurs 2.17 49.82 Unet 3.73 182.36 RAN 2.89 518.85 表 4 各算法平均PSNR和SSIM
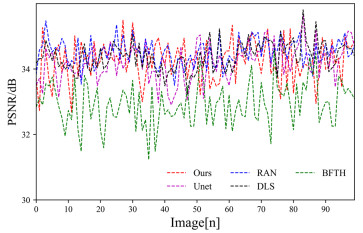
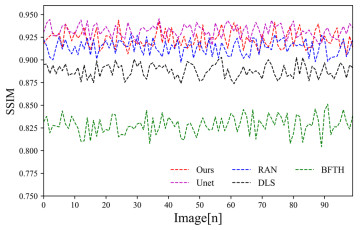
Table 4 PSNR and SSIM of each algorithm
Algorithms PSNR SSIM Ours 34.25 0.9230 Unet 34.20 0.9306 BFTH 32.93 0.8285 DLS 34.38 0.8881 RAN 34.51 0.9128 表 5 各算法平均粗糙度指标
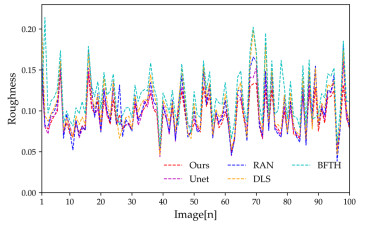
Table 5 Roughness of each algorithm
Algorithms BFTH DLS RAN Unet Ours Roughness 0.1176 0.1052 0.1052 0.0972 0.0933 -
[1] 樊凡. 基于场景的红外非均匀性校正算法研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2015. FAN Fan. Research on the Infrared Scene Based Nonuniformity Correction Algorithm[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2015.
[2] HOU Huixin, LI Qing, LIU Shangqian, et al. Nonuniformity and its correction principle of infrared focal plane arrays[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2003, 3(6): 46-48.
[3] ZHOU Huixin, LI Qing, LIU Shangqian, et al. Nonuniformity and its correction principle of infrared focal plane arrays[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2003, 3(6): 46-48.
[4] Scribner D A, Sarkady K A, Kruer M R, et al. Adaptive nonuniformity correction for IR focal-plane arrays using neural networks[C]//International Society for Optics and Photonics, 1991: 100-109.
[5] 牟新刚, 崔健, 周晓. 基于全卷积网络的红外图像非均匀性校正算法[J]. 红外技术, 2022, 44(1): 21-27. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/cn/article/id/1dc81b37-2449-459f-a97a-284832f6be2e MOU Xingang, CUI Jian, ZHOU Xiao. Infrared image non-uniformity correction algorithm based on full convolutional network[J]. Infrared Technology, 2022, 44(1): 21-27. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/cn/article/id/1dc81b37-2449-459f-a97a-284832f6be2e
[6] 陆俊杰. 基于深度学习的红外探测器非均匀性校正算法研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2020. LU Junjie. Nonuniform Image Correction for Infrared Detector Based on Deep Learning[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2020.
[7] HE Zewei, CAO Yanpeng, DONG Jiangxin, et al. Single-image-based nonuniformity correction of uncooled long-wave infrared detectors: a deep-learning approach[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(18): 155-164. DOI: 10.1364/AO.57.00D155
[8] Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]//Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention-MICCAI, 2015: 234-241.
[9] JIE H, LI S, GANG S. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019, 42(8): 2011-2023.
[10] JIANG Y, TAN Z, WANG J, et al. GiraffeDet: a heavy-neck paradigm for object detection[J/OL]. arXiv, 2022, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/358493689_GiraffeDet_A_Heavy-Neck_Paradigm_for_Object_Detection.
[11] LIU F, XU H, QI M, et al. Depth-wise separable convolution attention module for garbage image classification[J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(5): 1-18.
[12] Szegedy C, LIU W, JIA Y, et al. Going deeper with convolutions[J/OL]. IEEE Computer Society, 2014, https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7298594.
[13] Bal A, Alam M S. Automatic target tracking in FLIR image sequences[C]//Proceedings of SPIE - The International Society for Optical Engineering, 2005, 54(5): 1846-1852.
[14] Berg A, Ahlberg J, Felsberg M. A thermal object tracking benchmark[C]// IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video & Signal Based Surveillance, 2015, DOI: 10.1109/AVSS.2015.7301772.
[15] Channappayya S S, Bovik A C, Heath R W. Rate bounds on SSIM index of quantized images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2008, 17(9): 1624-1639. DOI: 10.1109/TIP.2008.2001400
[16] Mathieu M, Couprie C, Lecun Y. Deep multi-scale video prediction beyond mean square error[C/OL]//ICLR, 2016, http://arxiv.org/pdf/1511.05440.pdf.
[17] 崔健. 基于深度学习的红外探测器非均匀性校正算法研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2021. CUI Jian. Research on Non-Uniformity Correction Algorithm of Infrared Detector Based on Deep Learning[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2021.
[18] Howard A G, ZHU M, Chen B. et al. MobileNets: efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[J/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1704.04861, 2017, https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04861.
[19] Howard A, Sandler M, Chu G et al. Searching for MobileNetV3[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2019: 1314-1324.
[20] LIU Z, MAO H, WU C Y, et al. A ConvNet for the 2020s[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2022: 11966-11976.
[21] HAN K, WANG Y, TIAN Q, et al. GhostNet: more features from cheap operations[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2020: 1577-1586.
[22] ZUO C, CHEN Q, GU G, et al. New temporal high-pass filter nonuniformity correction based on bilateral filter[J]. Optical Review, 2011, 18: 197-202. DOI: 10.1007/s10043-011-0042-y
[23] HE Zewei, CAO Yanpeng, DONG Yafei, et al. Single-image-based nonuniformity correction of uncooled long-wave infrared detectors: a deep-learning approach[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57: D155-D164. DOI: 10.1364/AO.57.00D155
[24] XU K, ZHAO Y, LI F, et al. Single infrared image stripe removal via deep multi-scale dense connection convolutional neural network[J]. Infrared Physics and Technology, 2022(121): 104008-104008. Doi: 10.1016/j. infrared.2021.104008.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 肖沁,李正周,刘海毅. 基于场景自适应方向引导滤波的红外成像非均匀性校正方法. 光子学报. 2024(11): 253-265 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: