Infrared and Visible Binocular Registration Algorithm Based on Region Search Under Geometric Constraints
-
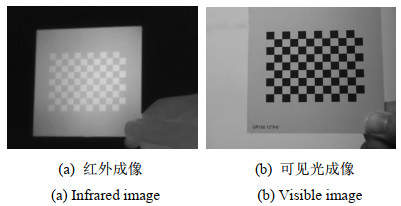
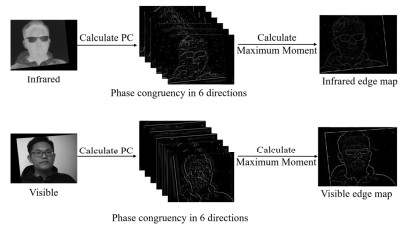
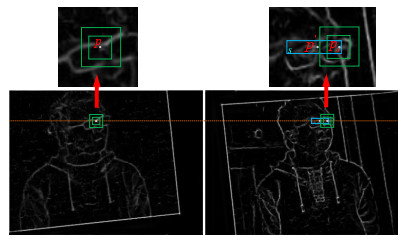
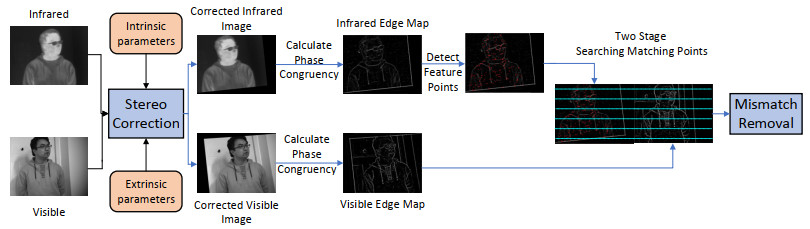
摘要: 针对相对位置固定的红外和可见光双目相机配准任务,现有算法没有考虑到两者相对位置固定的先验知识,存在配准精度低、几何定位差异大等问题,适用性差。提出一种基于几何约束下区域搜索的红外可见光双目图像配准方法。首先借助红外和可见光双目相机的标定信息对红外和可见光图像进行立体校正使二者处于同一高度之上。接着借助于相位一致性计算红外与可见光的边缘特征图,然后在红外边缘图上提取特征点,最后提出两阶段的同名特征点搜索方法,以红外特征点为基准在可见光边缘图局部区域内搜索同名特征点。在第一阶段以归一化互相关(Normalized cross-correlation,NCC)为相似性度量计算两边缘图的整体水平偏移,预测同名特征点初始位置,在第二阶段提出多尺度加权NCC作为相似性度量,在初始同名特征点位置周围精确搜索同名特征点。在构造的真实环境数据集上进行实验,实验结果表明相对于其他对比算法,在特征点匹配数量和准确率以及主观视觉上的配准效果都优于其他对比算法。Abstract: For the registration task of infrared and visible binocular cameras with fixed relative positions, existing algorithms do not consider the prior fixed relative positions of the two cameras, resulting in problems, such as low registration accuracy, large differences in geometric positioning, and poor applicability. An infrared and visible binocular image registration method based on region search under geometric constraints. First, stereo correction was performed on the infrared and visible images using the calibration information of the infrared and visible binocular cameras, such that they were at the same height. Second, infrared and visible edge maps were obtained using phase congruency and feature points were extracted from the infrared edge map. Finally, a two-stage feature point search method is proposed to search for feature points with the same name in the local area of the visible edge map based on the infrared feature points. In the first stage, normalized cross-correlation (NCC) was used as a similarity metric to calculate the overall horizontal offset of the two edge maps, and the initial positions of feature points with the same name were predicted. In the second stage, a multiscale-weighted NCC was proposed as a similarity metric to accurately search for feature points with the same name around the initial location of feature points of the same name. Then, experiments were performed on the constructed real-environment dataset. The experimental results show that compared with other comparison methods, the number and accuracy of matching points and registration results in subjective vision are better.
-
Keywords:
- image registration /
- infrared image /
- visible image /
- phase congruency /
- binocular camera
-
-
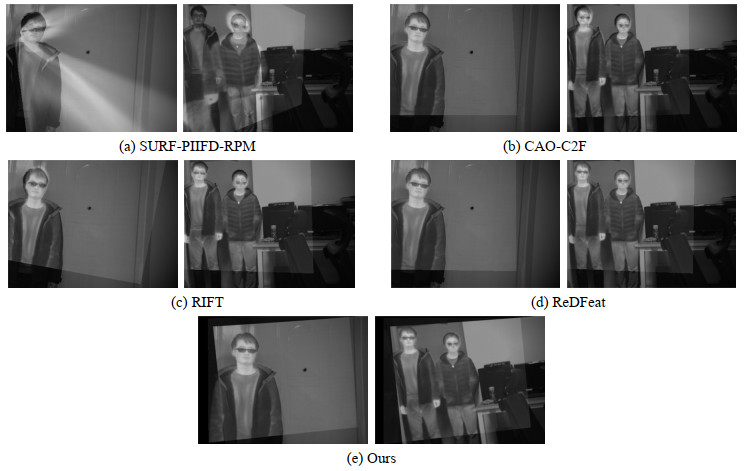
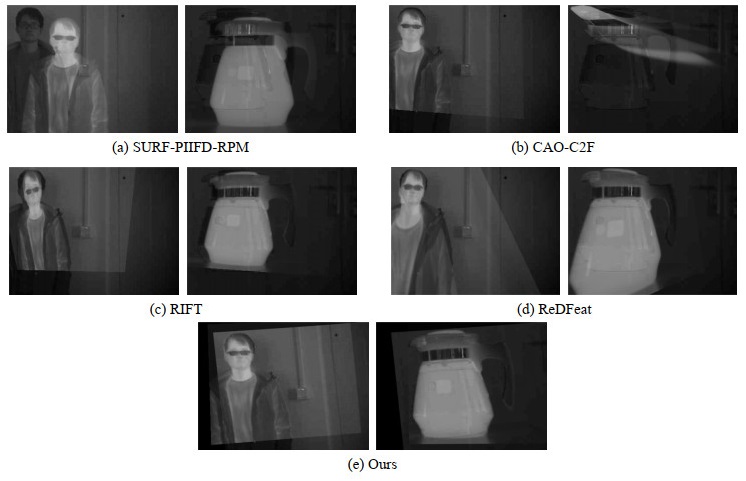
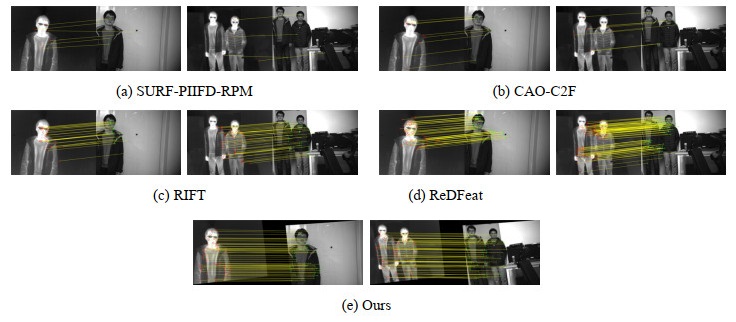
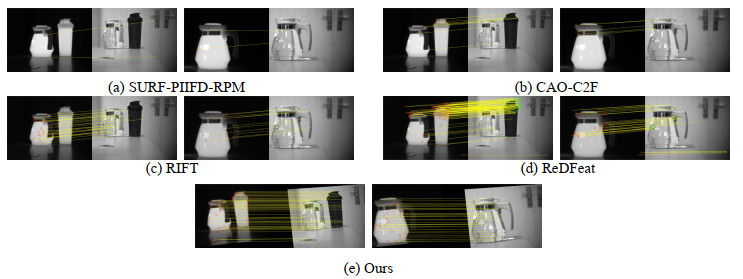
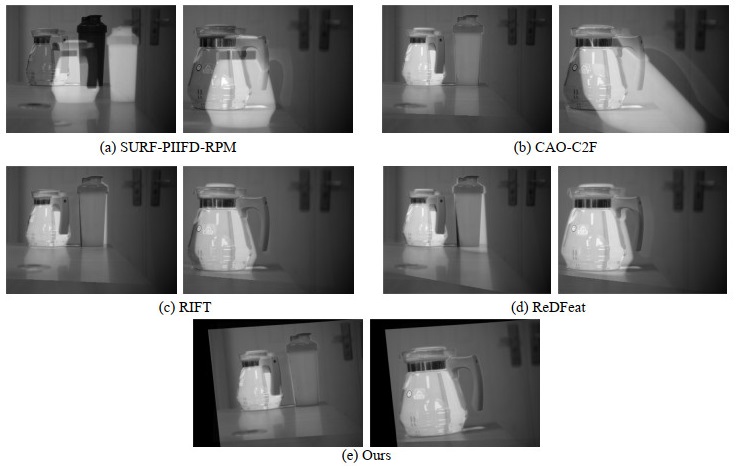
表 1 实验结果对比
Table 1 Comparison of experimental results
Image Group Algorithm NUM CMR First Group SURF-PIIFD-RPM 5.7 66.0% CAO-C2F 6.3 76.8% RIFT 42.2 83.7% ReDFeat 107.3 80.0% OURS 67.6 91.1% Second Group SURF-PIIFD-RPM 2.8 59.2% CAO-C2F 7.3 69.5% RIFT 26.4 83.2% ReDFeat 127.4 76.8% OURS 34.0 91.6% Third Group SURF-PIIFD-RPM 1.8 28.3% CAO-C2F 4.6 27.5% RIFT 10.8 82.5% ReDfeat 22.3 62.2% OURS 37.3 88.1% -
[1] LI Y, YU F Y, CAI Q, et al. Image fusion of fault detection in power system based on deep learning[J]. Cluster Computing the Journal of Networks Software Tools and Applications, 2019, 22(4): 9435-9443.
[2] 付添, 邓长征, 韩欣月, 等. 基于深度学习的电力设备红外与可见光图像配准[J]. 红外技术, 2022, 44(9): 936-943. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/1f007d8f-ee0d-4cd3-b609-1084e911d70a FU T, DENG C, HAN X, et al. Infrared and visible image registration for power equipments based on deep learning[J]. Infrared Technology, 2022, 44(9): 936-943. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/1f007d8f-ee0d-4cd3-b609-1084e911d70a
[3] 黄颖杰, 梅领亮, 王勇, 等. 基于红外与可见光图像融合的无人机探测研究[J]. 电脑知识与技术, 2022, 18(7): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DNZS202207001.htm HUANG Y, MEI L, WANG Y, et al. Research on unmanned aerial vehicle detection based on fusion of infrared and visible light images[J]. Computer Knowledge and Technology, 2022, 18(7): 1-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DNZS202207001.htm
[4] 王戈, 钟如意, 黄浩, 等. 基于轻量级人脸识别的智慧地铁云支付系统搭建[J]. 湖北大学学报: 自然科学版, 2021, 43(4): 437-442. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDZK202104012.htm WANG G, ZHONG R, HUANG H, et al. Construction of intelligent metro cloud payment system based on lightweight face recognition[J]. Journal of Hubei University: Natural Science, 2021, 43(4): 437-442. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HDZK202104012.htm
[5] Banuls A, Mandow A, Vazquez-Martin R, et al. Object detection from thermal infrared and visible light cameras in search and rescue scenes[C]// IEEE International Symposium on Safety, Security, and Rescue Robotics (SSRR), 2020: 380-386.
[6] JIANG X, MA J, XIAO G, et al. A review of multimodal image matching: Methods and applications[J]. Information Fusion, 2021, 73: 22-71. DOI: 10.1016/j.inffus.2021.02.012
[7] 李云红, 刘宇栋, 苏雪平, 等. 红外与可见光图像配准技术研究综述[J]. 红外技术, 2022, 44(7): 641-651. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/77ef812e-5018-435f-a023-771b550bedc7 LIU Y, LIU Y, SU X, et al. Review of Infrared and visible image registration [J]. Infrared Technology, 2022, 44(7): 641-651. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/77ef812e-5018-435f-a023-771b550bedc7
[8] YU K, MA J, HU F, et al. A grayscale weight with window algorithm for infrared and visible image registration[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2019, 99: 178-186.
[9] Yedukondala D C, Pejhman G, Pfefer T, et al. Free-Form deformation approach for registration of visible and infrared facial images in fever screening[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(2): 125. DOI: 10.3390/s18010125
[10] WANG G, WANG Z, CHEN Y, et al. Robust point matching method for multimodal retinal image registration[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2015, 19: 68-76. DOI: 10.1016/j.bspc.2015.03.004
[11] Bay H, Ess A, Tuytelaars T, et al. Speeded-up robust features (SURF)[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2008, 110(3): 346-359. DOI: 10.1016/j.cviu.2007.09.014
[12] CHEN J, TIAN J, Lee N, et al. A partial intensity invariant feature descriptor for multimodal retinal image registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2010, 57(7): 1707-1718. DOI: 10.1109/TBME.2010.2042169
[13] JIANG Q, LIU Y, YAN Y, et al. A contour angle orientation for power equipment infrared and visible image registration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 2020, 36(4): 2559-2569.
[14] LI J, HU Q, AI M. RIFT: Multi-modal image matching based on radiation-variation insensitive feature transform[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 29: 3296-3310.
[15] WANG L, GAO C, ZHAO Y, et al. Infrared and visible image registration using transformer adversarial network[C]// 25th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). IEEE, 2018: 1248-1252.
[16] Arar M, Ginger Y, Danon D, et al. Unsupervised multi-modal image registration via geometry preserving image-to-image translation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020: 13410-13419.
[17] DENG Y, MA J. ReDFeat: Recoupling detection and description for multimodal feature learning[J/OL]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022: 591-602. https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.07439.
[18] ZHANG Z. A flexible new technique for camera calibration[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2000, 22(11): 1330-1334. DOI: 10.1109/34.888718
[19] Fusiello A, Trucco E, Verri A. A compact algorithm for rectification of stereo pairs[J]. Machine Vision & Applications, 2000, 12(1): 16-22.
[20] Peter Kovesi. Phase congruency detects corners and edges[C]//Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications, 2003: 309-318.
[21] Edward R, Tom D. Machine learning for high-speed corner detection[C]//Computer vision - ECCV, 2006: 430-443.
[22] Neubeck A, Van Gool L. Efficient non-maximum suppression[C]//Pattern Recognition, ICPR, 2006: 850-855.
[23] YE Y, SHAN J, Bruzzone L, et al. Robust registration of multimodal remote sensing images based on structural similarity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(6): 2941-2958.
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: