Flicker Noise Testing System of Electron Bombarded Active Pixel Sensor
-
摘要:
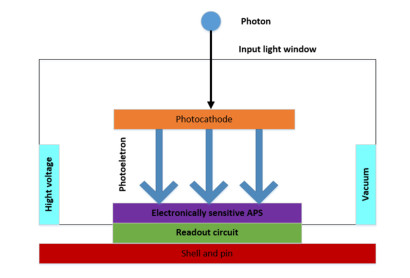
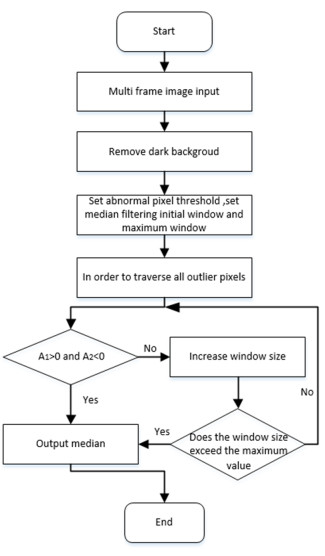
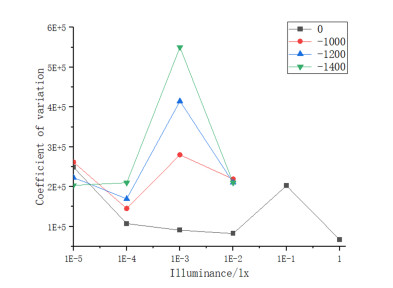
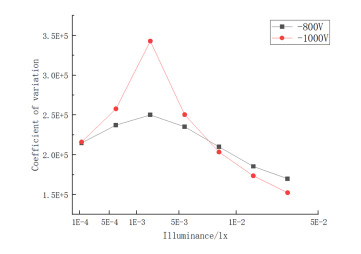
电子轰击有源像素传感器(electron bombarded active pixel sensor,EBAPS)是新型的真空-固体混合型数字微光夜视器件。闪烁噪声是影响EBAPS分辨力和成像质量的关键因素,然而,目前EBAPS闪烁噪声的测试研究不足。为此,本文首先开展EBAPS闪烁噪声测试方法研究,使用连通域检测算法筛选高亮噪点区域,提出异常像素点自适应中值替代的离散系数测试方法,在此基础上研制了EBAPS闪烁噪声测试系统,采用离散系数和高亮噪点数量作为闪烁噪声的表征参数,驱动EBAPS将不同测试条件下采集到的图像数据传输至上位机进行噪声处理与分析,测试结果表明:合适的测试照度为1.27×10-3 lx,高亮噪点数量在-1000~-1300 V范围内数量较少,-1300~-1500 V时高亮噪点数量则明显提升。离散系数和连通域数量重复度均在3%以内,验证了测试系统的稳定性,为国产EBAPS闪烁噪声测试提供有效手段。
Abstract:An electron bombarded active pixel sensor (EBAPS) is a novel vacuum-solid, hybrid, digital, low-light night vision device. Flicker noise is a key factor affecting the resolution and image quality of EBAPS; however, there is currently insufficient research on the testing of flicker noise in EBAPS. Hence, this study conducted research on EBAPS flicker noise testing methods using connected domain detection algorithms to filter out high-brightness noise spot areas and proposed an adaptive, median replacement, discrete coefficient testing method for abnormal pixel points. Based on these results, an EBAPS flicker-noise testing system was developed using the discrete coefficient and number of bright noise spots as parameters to characterize the flicker noise. The system drives the EBAPS to transfer image data collected under different test conditions to an upper computer for noise processing and analysis. The test results indicate that the appropriate test illuminance is 1.27×10−3 lx. Moreover, the number of high-brightness noise spots is relatively low in the −1000−1300 V range, and it significantly increases when the voltage is between −1300−1500 V. The repeatability of the discrete coefficient and number of connected domains was within 3%, thus verifying the stability of the testing system and providing an effective means by which to test flicker noise in domestic EBAPS.
-
Keywords:
- EBAPS /
- flicker noise /
- electronic multiplying /
- test system /
- connected domain detection algorithm
-
0. 引言
输电线路设备作为电力系统的重要部分,对输电线路的安全稳定运行起着至关重要的作用。而金属氧化物避雷器(MOA)是输电线路中常用设备,其作用是防止电气设备遭受过电压侵害,是输电线路中重要的结构支撑件。由于MOA在潮湿环境下,存在污秽、老化和爆裂等情况,因此准确地检测MOA故障是目前电网亟待解决问题之一[1]。
目前,传统的检测MOA故障方法主要有以下几种:①全电流[2];②谐波分析法[3];③容性电流补偿法[4];④基波阻性电流法[5];⑤基于温度的测量法等[6]。但以上方法在MOA运行过程中,MOA或监测装置表面污秽所产生的泄漏电流以及电网谐波对MOA在线监测的影响,会对所监测的特征量产生影响,进而使测量的数值存在误差,影响检测精度,同时存在成本高以及检测周期长等问题。而随着深度学习相关技术快速发展,由于具有识别精度高,无需人工监督,高效等优点,更适用于解决图像分类、目标识别等问题,并且取得显著效果[7]。
深度学习算法已广泛应用在输电线路设备故障检测中。本文所研究的红外图像MOA故障检测,可看作物体检测问题。主流的深度学习的目标检测算法包括两类:一类是基于区域的目标检测算法如Faster RCNN(Faster-regions with Convolutional Network)[8]与RFCN(Region-based Fully Convolutional Networks)[9]等,其中文献[10]基于Faster RCNN算法对变压器、套管、断路器等7种变电设备进行目标检测,实现设备的精准定位、识别。文献[11]采用了深度学习算法体系中基于区域建议网络的Faster RCNN算法实现对输变电红外图像发热故障的检测、识别及定位。以上算法虽然检测精度高,但速度相对较慢,不能满足实时性的要求。另一类是将检测问题转变为回归问题求解如SSD(Single Shot MultiBox Detector)、YOLO(You Only Look Once)算法[12-13]。文献[14]基于YOLOv3算法,通过添加卷积模块及调整部分超参数对其基础网络架构进行优化,以实现高压开关设备异常发热点的快速检测、识别和定位。文献[15]提出了一种基于多尺度特征融合的端到端红外小目标检测模型。文献[16]以小轿车和公交车红外图像为研究对象,构建了红外图像Pascal VOC数据集,训练了SSD网络,并利用训练好的网络检测了红外目标图像。以上算法虽提高了网络的检测效率,但是目标定位的准确率有所降低,而红外图像故障检测对模型准确率有较高的要求,选用Faster RCNN模型比较符合实际需求。但是已有实验证明Faster RCNN对中大型的目标具有良好的检测效果,但对小目标的检测效果不佳,如果直接使用原始的Faster RCNN模型,可能会造成漏检。
基于上述问题,本文提出一种基于改进YOLOv3的MOA故障检测方法。首先,将Darknet19网络代替YOLOv3的原始Darknet53网络。替换后的网络训练难度更低,在保证高识别精度情况下,识别速度更快,减少了冗余的计算。特征学习时针对样本中不同MOA长宽比例,通过K-means聚类算法对图像中的目标帧进行分析,重新聚类样本中心锚点框,得到合适的锚框数目和大小,提高了网络的检测规模。最后,利用改进YOLOv3模型完成MOA红外图像故障检测。
1. MOA红外图像故障在线检测方案
1.1 避雷器红外检测
如图 1(a)所示,当避雷器正常运行时,MOA红外热像仅有轻微的发热且整体分布均匀,没有明显温差变化。而且同一MOA不同部位的最大温差不会超过1 K,相间温差也很小。然而当发生故障时,往往会伴随着异常的温升现象。MOA常见的故障主要包括阀片老化和受潮。通过避雷器泄露电流中的有功分量会使阀片发热导致老化,阀片由于老化继续升温,而温升又进一步使阀片电阻下降导致损耗加大,最终形成恶性循环。MOA由于呼吸作用受潮,造成阀片电导率增大,从而导致阻性泄露电流增大,引起局部发热。总之,阀片老化和受潮的红外热像都表现为局部发热,特征热像图如图 1(b)所示,220 kV MOA上节存在明显局部过热。
根据标准[17]规定,图像特征判断法适用于如氧化锌避雷器电压致热型设备。在排除环境等因素影响后,通过对同类设备不同状态下的红外热像图进行对比分析,判断设备是否存在异常。
1.2 避雷器故障检测架构
如图 2所示,为本文MOA红外图像故障检测模型整体框架图。整个MOA红外图像故障检测流程如下:首先,通过无人机采集MOA红外图像,对采集的MOA红外图像分类,分为正负样本。由于拍摄的红外图像会受背景环境的影响,如光照、树等。因此,采用中值滤波法对MOA红外图像进行预处理。处理后的MOA红外图像对改进的YOLOv3模型进行训练,最后调用训练好的MOA红外故障检测模型对预处理后的MOA红外图像进行故障检测。检测流程先是对数据进行聚类分析,得到合适的锚框数目和大小,其次采用深层次特征提取网络进行特征提取,最后通过多尺度预测得到MOA检测结果。
1.3 图像预处理
由于在拍摄红外图像过程中受到大气辐射噪声以及拍摄背景的影响。这些噪声会降低图像对比度。因此,需对MOA红外图像进行降噪处理。本文采用中值滤波法[18]。将模板中的像素从小到大排序,并将当前像素值替换为排序序列的中间值。主要步骤如下:移动图片中的滤镜模板,将模板中心位置对应的像素作为当前像素。读取模板中每个像素的灰度值。将灰度值从小到大排序。取最终排序结果的中值像素,而不是当前像素值。在3×3滤波模板下,原始图像对应像素的灰度值如图 3所示。
2. 改进YOLOv3网络模型
2.1 YOLOv3网络结构修改
YOLOv3算法是Joseph Redmon等在2018年新提出的目标检测算法[19]。YOLOv3借鉴残差网络提出了Darknet53网络,利用残差结构降低了训练难度。此外,采用大量1×1的卷积核和步长为2,大小为3×3的卷积核来代替最大池,从而减少了参数的数目。由于Darknet53网络实现的检测类别众多,单个目标的检测复杂且冗余,而本文针对MOA红外图像进行目标检测。过多的参数会导致训练过于复杂,影响训练速度。
针对MOA,本文借鉴YOLOv3的多尺度检测部分,提出了一种参数少、计算复杂度低的目标检测网络,以降低训练难度,提高模型速度,同时也具有较高的识别精度。
用Darknet19网络代替YOLOv3的骨干网Darknet53,并对应用于多尺度预测的卷积层。与Darknet53网络相比,由于不在Darknet19中加入残差网络,训练速度得到了很大地提高。Darknet19的网络结构如表 1所示。
表 1 Darknet19网络结构Table 1. Network structure of Darknet19Type Fitlers Size/stride Output Convolutional 32 3×3/1 256×256 Maxpool 2×2/2 128×128 Convolutional 64 3×3/1 128×128 Maxpool 2×2/2 64×64 Convolutional 128 3×3/1 64×64 Convolutional 64 1×1/1 64×64 Convolutional 128 3×3/1 64×64 Maxpool 2×2/2 32×32 Convolutional 256 3×3/1 32×32 Convolutional 128 1×1/1 32×32 Convolutional 256 3×3/1 32×32 Maxpool 2×2/2 16×16 Convolutional 512 3×3/1 16×16 Convolutional 256 1×1/1 16×16 Convolutional 512 3×3/1 16×16 Convolutional 256 1×1/1 16×16 Convolutional 512 3×3/1 16×16 Maxpool 2×2/2 8×8 Convolutional 1024 3×3/1 8×8 Convolutional 512 1×1/1 8×8 Convolutional 1024 3×3/1 8×8 Convolutional 512 1×1/1 8×8 Convolutional 1024 3×3/1 8×8 卷积神经网络将预测每个单元中每个边界框的4个值,即坐标(x, y)、目标宽度w、高度h,分别表示为tx、ty、tw和th。如果目标中心与单元格中图像的左上角有偏差(cx, cy),并且锚框的高度和宽度为Pw和Ph,则修改后的边界框为:
$$ b_{x}=σ(t_{x})+c_{x} $$ (1) $$ b_{y}=σ(t_{y})+c_{y} $$ (2) $$ {b_w} = {P_w}{{\text{e}}^{{t_w}}} $$ (3) $$ {b_h} = {P_h}{{\text{e}}^{{t_h}}} $$ (4) 在YOLOv3中,引入了FPN网络。同时利用低层特征的高分辨率和高层次特征的信息,通过上采样对多尺度特征进行融合,检测出3个不同尺度的特征层上的目标。本文保留YOLOv3网络的多尺度预测,利用多尺度卷积层对不同尺度的目标进行检测,如表 2所示。
表 2 YOLOv3的先验框尺寸Table 2. Prior box size of YOLOv3Scale prediction Feature map size Anchor value Scale 1 13×13 (105, 153) (49, 250)(32, 132) Scale 2 26×26 (144, 43) (33, 78)(47, 56) Scale 3 52×52 (52, 25) (22, 34)(16, 15) 2.2 锚框的聚类分析
锚框是通过对数据集的目标帧进行聚类和分析得到的一组固定宽度和高度的初始候选帧。YOLOv3使用逻辑回归来预测锚框中包含对象的概率。如果锚框(Anchor Box)与真实目标包围盒之间的重叠率大于任何其他锚盒,则该锚框的概率为1。如果真实目标的锚框和边界框之间的重叠大于0.5,但不是最大值,则忽略预测。锚框的数量和大小直接影响网络结构对目标检测的精度和速度。YOLOv3使用K-means聚类算法[20]对目标帧进行聚类,并使用平均重叠平均IOU作为目标聚类的度量。目标函数如式(5)所示:
$$ {\text{arg max}}\frac{{\sum {_{i = 1}^k\sum {_{j = 1}^{{n_k}}{R_{{\text{IOU}}}}(B,C)} } }}{n} $$ (5) 式中:B是真实的地面目标;C是簇的中心;nk是K簇中心的样本数;n是样本总数;k为簇数;RIOU(B, C)表示簇中心盒和簇盒的交点。
选取k=0~20,分别对两个数据集进行聚类分析。锚框数(即k值)与平均IOU之间的曲线关系如图 4所示。随着k值的增大,目标函数的变化越来越慢,变化线的拐点可以看作是最优的锚框数目。通过这种多尺度检测,可以增强各尺度特征层的信息,对多幅图像中的小目标检测有较好的效果。多尺度检测的最终网络模型如图 5所示。
经过修改,在608×608尺度下,本文采用的Yolov3-Darknet19网络为74.963 BFLOPS,基于Darknet53的YOLOv3网络为139.481 BFLOPS。因此,Darknet19训练速度优于Darknet53。
3. 实验结果与分析
红外目标检测是实现MOA红外故障目标检测系统的核心环节,该方案采用改进的YOLOv3算法的目标检测方案。通过运用Darknet19深度学习框架进行样本训练。
3.1 数据采集及扩展
由于所采集的MOA红外图像数量有限,因此,本文通过对原始图像水平翻转、水平移动、缩放和亮度级别转换为人工图像,增加样本数量。增加的图像类标签没有改变,变换是在图像上随机进行的。在训练模型的过程中使用新的变换图像和原始图像。数据扩充的目的是为了提高模型的泛化能力。扩充后的数据集包含5602幅图片,并将图片的注释转换成相应的格式,得到图片的标注数据进行训练。
将实验数据按8:1:1的比例随机划分为训练集、测试集和验证集。在训练阶段,动量参数设置为0.9,采用批量随机梯度下降法进行优化,初始学习率为0.0001,衰减为0.0005,前1000次训练中,采样学习率为0.001,以稳定网络。随后,在40000和45000次训练中,采用steps策略根据衰减系数改变学习率,防止梯度消失问题。
本文采用多尺度训练策略来增强不同尺度下的鲁棒性。每10批训练集为一组,每组随机选取新的图像大小进行训练,训练范围为320×320~608×608,采样间隔为32。
如表 3所示,为YOLOv3-Darknet19训练环境。本文的评价依据主要是训练过程中的损失图像和两个模型训练后的实际检测效果。
表 3 YOLOv3-Darknet19训练环境Table 3. Training environment of YOLOv3-Darknet19Term configuration CPU Core i9 10900K GPU INVIDIA RTX 3080 Operating system Microsoft Windows10 Parallel computing library Cuda10.0+Cudnn7.4.1.5 Image processing Python3.7 Deep learning framework Darknet19 3.2 实验对比
本文对YOLOv3-Darknet19算法和YOLOv3- Darknet53算法进行了比较。同一数据集的训练时间分别为70 h和14 h。训练期间的两个网络损失变化曲线如图 6和图 7所示。从图 8所示的数据比较可以看出,Darknet19网络的损耗下降较快,数据波动较小,最终稳定值相对较小。
从实验结果可知,本文分别对两个网络训练的同一图像的权值进行测试,测试实例效果如图 9所示。通过本文所提出的YOLOv3-Darknet19可精准地对MOA红外故障图像进行识别检测。
基于以上两点的分析,本文提出的改进算法在使用相同训练集的情况下,在速度和识别率上有一定的保证,不存在未识别或错误情况。在识别单个目标时,网络结构的简化提高了训练速度,采用AP(Average Precision)值作为评价指标,识别精度可达96.3%。在检测速度方面,以图片为例,YOLOv3-Darknet53的识别速度为25.41 ms,YOLOv3- Darknet19的识别速度为6.75 ms,因此简化网络后,识别速度更快,帧数显著增加。在训练时间上,Darknet19网络的训练速度也更快,约为原网络的1/5,为参数和网络的微调提供了方便。
4. 总结
本文将YOLOv3目标检测算法应用到输电线路中,提出一种基于改进的YOLOv3算法用于MOA故障检测,由于本文只用于检测MOA,对YOLOv3网络结构以及锚框大小进行了修改,采用Darknet19网络代替原有的Darknet53网络,实验结果表明,改进后的YOLOv3网络在识别效果上没有下降,与原有的YOLOv3算法相比识别速度更快。YOLOv3-Darknet19的识别速度为6.75 ms,识别精度可达96.3%。因此简化网络后,识别速度更快,帧数显著增加。
-
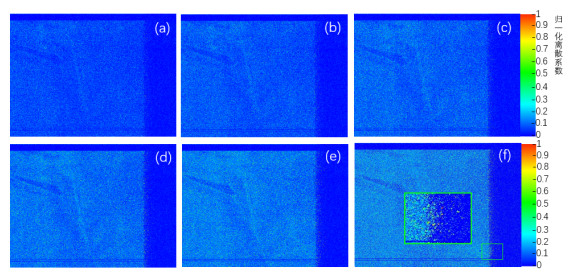
图 9 不同轰击电压下的离散系数热力图:(a) 电压为-1000 V;(b) 电压为-1100 V;(c) 电压为-1200 V;(d) 电压为-1300 V;(e) 电压为-1400 V;(f) 电压为-1500 V
Figure 9. Discrete coefficient thermodynamic diagram under different bombardment voltages (a)Voltage −1000 V; (b)Voltage −1100 V; (c)Voltage −1200 V; (d)Voltage −1300 V; (e)Voltage −1400 V; (f)Voltage −1500 V
表 1 -1000 V~-1500 V连通域数量
Table 1 Number of connected domains from −1000 to −1500 V
Bombardment voltage/V Number of tests Average value Repeatability/% 1 2 3 4 5 −1000 7.90 7.86 7.74 7.88 7.74 7.82 0.99 −1100 7.56 8.00 8.10 7.72 7.90 7.86 2.76 −1200 7.92 7.90 8.12 7.92 8.24 8.04 1.91 −1300 11.94 12.18 12.10 12.52 12.26 12.20 1.75 −1400 23.66 23.06 23.42 23.06 22.72 23.18 1.56 −1500 42.90 42.62 41.34 42.88 40.88 42.12 2.25 -
[1] 夏皓天, 钱芸生, 王逸伦, 等. 基于FPGA的低照度条件下EBAPS图像混合噪声去除算法[J]. 应用光学, 2022, 43(6): 1075-1087. XIA Haotian, QIAN Yunsheng, WANG Yilun, et al. Hybrid noise removal algorithm for EBAPS images under low illumination conditions based on FPGA[J]. Applied Optics, 2022, 43(6): 1075-1087.
[2] 严毅赟, 钱芸生, 张景智, 等. 电子轰击有源像素传感器光谱响应测试系统设计[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2022, 59(13): 123-128. YAN Yiyun, QIAN Yunsheng, ZHANG Jingzhi, et al. Design of a spectral response testing system for electronic bombardment active pixel sensors[J]. Progress in Laser and Optoelectronics, 2022, 59(13): 123-128.
[3] 刘亚宁, 桑鹏, 吕嘉玮, 等. 微型低功耗EBAPS相机技术[J]. 红外技术, 2019, 41(9): 810-818. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/hwjs201909003 LIU Yaning, SANG Peng, LV Jiawei, et al. Micro low-power EBAPS camera technology[J]. Infrared technology, 2019, 41(9): 810-818. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/hwjs201909003
[4] 唐小东. EBAPS电子轰击性能测试技术研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2019. TANG Xiaodong. Research on EBAPS Electronic Bombardment Performance Testing Technology[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Technology, 2019.
[5] 宋德, 石峰, 李野. 基底均匀掺杂下EBAPS电荷收集效率的模拟研究[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2016, 45(2): 48-52. SONG De, SHI Feng, LI Ye. Simulation study on the charge collection efficiency of EBAPS under uniform substrate doping[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2016, 45(2): 48-52.
[6] 周吉强. EBAPS中电子倍增层增益特性测试系统的研究[D]. 长春: 长春理工大学, 2018. ZHOU Jiqiang. Research on the Gain Characteristics Testing System of Electron Multiplier Layer in EBAPS[D]. Changchun: Changchun University of Technology, 2018.
[7] 朴雪. 电子轰击有源像素传感器电荷收集效率理论模拟研究[D]. 长春: 长春理工大学, 2017. PU Xue. Theoretical Simulation Study on Charge Collection Efficiency of Electronic Bombardment Active Pixel Sensors[D]. Changchun: Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2017.
[8] LI Tongtong, XIAO Chao, JIAO Gangcheng, et al Research on noise characteristics of EBAPS digital low light level device[C]//Proc. of SPIE of Ninth Symposium on Novel Photoelectronic Detection Technology and Applications, 2023, 12617: 126176F.
[9] 徐鹏霄, 唐光华, 唐家业, 等. EBCMOS混合型光电探测器研究[J]. 光电子技术, 2016, 36(4): 232-236, 252. XU Pengxiao, TANG Guanghua, TANG Jiaye, et al Research on EBCMOS hybrid photodetectors[J]. Optoelectronic Technology, 2016, 36(4): 232-236, 252.
[10] TANG X., QIAN Y, KONG X, et alA high-dynamic range CMOS camera based on dual-gain channels[J]. J. Real-Time Image Proc. , 2020, 17: 703-712. DOI: 10.1007/s11554-019-00877-8
[11] WANG Xuening, SONG De, JIAO Gangcheng, et al. Characterising backscattered electrons in EBCMOS[J]. IEEE Photonics Journal, 2022, 14(6): 1-5.
[12] 张海舟, 母一宁, 王连锴, 等. EBCMOS微光成像器件的研究[J]. 真空科学与技术学报, 2017, 37(10): 991-996. ZHANG Haizhou, MU Yining, WANG Liankai, et al. Research on EBCMOS low light imaging devices[J]. Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, 2017, 37(10): 991-996.
[13] 熊智鹏, 李琦, 王骐. 电子轰击型有源像素传感器在激光雷达的应用[J]. 激光与红外, 2012, 42(7): 6. XIONG Zhipeng, LI Qi, WANG Qi. Application of electronic bombardment active pixel sensors in Lidar[J]. Laser and Infrared, 2012, 42(7): 6.
[14] Tutt J H, Holland A D, Hall D J, et al. The noise performance of electron-multiplying charge-coupled devices at X-ray energies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices, 2012, 59(1): 167-175. DOI: 10.1109/TED.2011.2172611
[15] Dominjon A, Ageron M, Barbier R, et al. An ebCMOS camera system for marine bioluminescence observation: the LuSEApher prototype[J]. Nuclear Inst & Methods in Physics Research A, 2012, 695: 172-178.
[16] Cajgfinger T, Dominjon A, Barbier R. Single photon detection and localization accuracy with an ebCMOS camera[J]. Nuclear Inst & Methods in Physics Research A, 2015, 787: 176-181.
[17] WEI Kaixuan, FU Ying, YANG Jiaolong, et al. A physics-based noise formation model for extreme low-light raw denoising[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2020: 2758-2767.
[18] 杨敏杰. 基于低照度CMOS的闪烁噪声测试技术及降噪方法研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学. YANG Minjie. Research on Flicker Noise Testing Technology and Noise Reduction Methods Based on Low Illumination CMOS[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology.
[19] 刘欣妍, 钱芸生, 魏静雯. 打拿极光电倍增管逐级增益自动测试系统[J]. 应用光学, 2022, 43(6): 1117-1123. LIU Xinyan, QIAN Yunsheng, WEI Jingwen. The automatic test system for gradual gain of Tana aurora electric multiplier tube[J]. Applied Optics, 2022, 43(6): 1117-1123.




 下载:
下载: