Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Based on Information Bottleneck Siamese Autoencoder Network
-
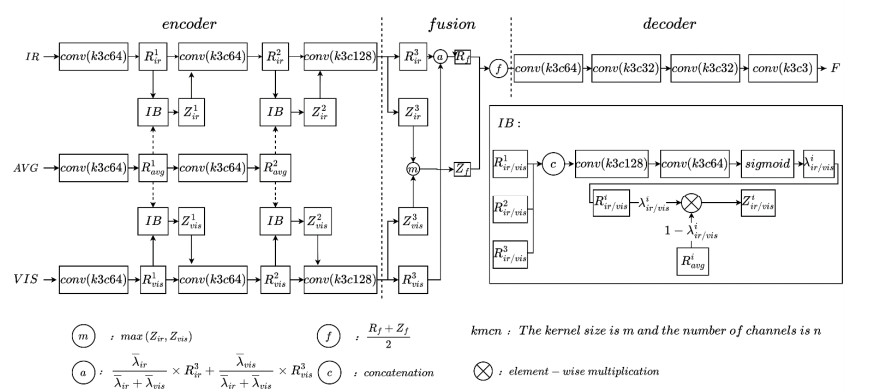
摘要: 红外与可见光图像融合方法中存在信息提取和特征解耦不充分、可解释性较低等问题,为了充分提取并融合源图像有效信息,本文提出了一种基于信息瓶颈孪生自编码网络的红外与可见光图像融合方法(DIBF:Double Information Bottleneck Fusion)。该方法通过在孪生分支上构建信息瓶颈模块实现互补特征与冗余特征的解耦,进而将互补信息的表达过程对应于信息瓶颈前半部分的特征拟合过程,将冗余特征的压缩过程对应于信息瓶颈后半部分的特征压缩过程,巧妙地将图像融合中信息提取与融合表述为信息瓶颈权衡问题,通过寻找信息最优表达来实现融合。在信息瓶颈模块中,网络通过训练得到特征的信息权重图,并依据信息权重图,使用均值特征对冗余特征进行压缩,同时通过损失函数促进互补信息的表达,压缩与表达两部分权衡优化同步进行,冗余信息和互补信息也在此过程中得到解耦。在融合阶段,将信息权重图应用在融合规则中,提高了融合图像的信息丰富性。通过在标准图像TNO数据集上进行主客观实验,与传统和近来融合方法进行比较分析,结果显示本文方法能有效融合红外与可见光图像中的有用信息,在视觉感知和定量指标上均取得较好的效果。Abstract: Infrared and visible image fusion methods have problems such as insufficient information extraction, feature decoupling, and low interpretability. In order to fully extract and fuse the effective information of the source image, this paper proposes an infrared and visible image fusion method based on information bottleneck siamese autoencoder network (DIBF: Double Information Bottleneck Fusion). This method realizes the disentanglement of complementary features and redundant features by constructing an information bottleneck module on the twin branch. The expression process of complementary information corresponds to the feature fitting process of the first half of the information bottleneck. The compression process of redundant features corresponds to the feature compression process in the second half of the information bottleneck. This method cleverly expresses information extraction and fusion in image fusion as an information bottleneck trade-off problem, and achieves fusion by finding the optimal expression of information. In the information bottleneck module, the network obtains the information weight map of the feature through training, and uses the mean feature to compress the redundant features according to the information weight map. This method promotes the expression of complementary information through the loss function, and the two parts of compression and expression are balanced and optimized simultaneously. In this process, redundant information and complementary information are also decoupled. In the fusion stage, the information weight map is applied in the fusion rules, which improves the information richness of the fused images. Through subjective and objective experiments on the standard TNO dataset, compared with traditional and recent fusion methods, the results show that the method in this paper can effectively fuse useful information in infrared and visible images, and achieved good results on both visual perception and quantitative indicators.
-
Key words:
- information bottleneck /
- Siamese /
- disentangled representations /
- infrared and visible /
- image fusion
-
表 1 各融合方法在“soldier behind smoke”图像上的客观评价
Table 1. Objective evaluation of each fusion method on the "Soldier behind smoke" image
SSIM↑ EN↑ QCV↓ CC↑ Qs↑ Qnice↑ GTF 0.6140 6.5523 525.7348 0.7198 0.6932 0.8041 Densefuse 0.7034 7.0214 285.2439 0.7659 0.7461 0.8067 DRF 0.5065 6.1229 1465.5026 0.4732 0.4955 0.8030 DIDFuse 0.6235 7.3882 764.3228 0.7654 0.6548 0.8029 SDNet 0.6738 6.7770 442.1754 0.8144 0.7628 0.8037 LPSR 0.6996 7.0479 374.1844 0.7445 0.7145 0.8059 DIBF 0.7057 7.2659 361.5213 0.7082 0.8045 0.8132 表 2 7种融合方法在“Kaptein”图像上的客观评价
Table 2. Objective evaluation of each fusion method on the " Kaptein " image
SSIM↑ EN↑ QCV↓ CC↑ Qs↑ Qnice↑ GTF 0.7112 6.9551 1876.9564 0.6421 0.7530 0.8079 Densfuse 0.7234 6.9105 638.447 0.7170 0.7371 0.8046 DRF 0.6775 6.7797 1076.7219 0.7517 0.6801 0.8045 DIDFuse 0.5218 6.6008 724.3656 0.6760 0.6948 0.8032 SDNet 0.7374 6.6134 1299.0327 0.7956 0.8290 0.8053 LPSR 0.7746 6.6977 602.4592 0.6960 0.8047 0.8048 DIBF 0.7789 6.9155 415.9648 0.7656 0.8349 0.8125 表 3 各方法在TNO数据集上的客观评价
Table 3. Objective evaluation of each method on TNO dataset
SSIM↑ EN↑ QCV↓ CC↑ Qs↑ Qnice↑ GTF 0.6816 6.7623 1089.6147 0.6388 0.7278 0.8075 Densfuse 0.7201 6.8161 527.9315 0.7077 0.7995 0.8052 DRF 0.6356 6.7744 858.1153 0.6741 0.6710 0.8045 DIDFuse 0.5046 6.6725 725.3649 0.6459 0.6721 0.8021 SDNet 0.6808 6.6822 773.5541 0.6894 0.7797 0.8060 LPSR 0.7394 6.4793 541.8054 0.7048 0.8020 0.8050 DIBF 0.7432 6.6954 367.5232 0.7082 0.8073 0.8166 表 4 40对图像消融实验客观指标
Table 4. Objective indicators of 40 pairs of image ablation experiments
SSIM↑ EN↑ QCV↓ CC↑ Qs↑ Qnice↑ Only Z is fused 0.6125 6.5611 1077.1563 0.6055 0.6986 0.7895 Only R is fused 0.7019 6.6682 525.6256 0.6411 0.7536 0.7999 Only λir/vis1 is used during the fusion of R 0.5986 6.5867 868.3145 0.6649 0.6745 0.8048 Only λir/vis2 is used during the fusion of R 0.5043 6.4123 925.3452 0.5479 0.6354 0.7958 DIBF 0.7432 6.6954 367.5232 0.7082 0.8073 0.8166 -
[1] 张冬冬, 王春平, 付强. 深度学习框架下的红外与可见光图像融合算法综述[J]. 激光与红外, 2022, 52(9): 1288-1298. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2022.09.004ZHANG D D, WANG C P, FU Q. Overview of infrared and visible image fusion algorithms based on deep learning framework[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2022, 52(9): 1288-1298. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2022.09.004 [2] MA J, MA Y, LI C. Infrared and visible image fusion methods and applications: a survey[J]. Information Fusion, 2019, 45: 153-178. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2018.02.004 [3] 陈永, 张娇娇, 王镇. 多尺度密集连接注意力的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 光学精密工程, 2022, 30(18): 2253-2266.CHEN Y, ZHANG J J, WANG Z. Infrared and visible image fusion based on multi-scale dense attention connection network[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(18): 2253-2266. [4] 孙彬, 诸葛吴为, 高云翔, 等. 基于潜在低秩表示的红外和可见光图像融合[J]. 红外技术, 2022, 44(8): 853-862. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/7fc3a60d-61bb-454f-ad00-e925eeb54576SUN B, ZHUGE W W, GAO Y X, et al. Infrared and visible lmage fusion based on latent low-rank representation[J]. Infrared Technology, 2022, 44(8): 853-862. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/7fc3a60d-61bb-454f-ad00-e925eeb54576 [5] 杨孙运, 奚峥皓, 王汉东, 等. 基于NSCT和最小化-局部平均梯度的图像融合[J]. 红外技术, 2021, 43(1): 13-20. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/144252d1-978c-4c1e-85ad-e0b8d5e03bf6YANG S Y, XI Z H, WANG H D, et al. Image fusion based on NSCT and minimum-local mean gradient [J]. Infrared Technology, 2021, 43(1): 13-20. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/144252d1-978c-4c1e-85ad-e0b8d5e03bf6 [6] 刘智嘉, 贾鹏, 夏寅辉. 基于红外与可见光图像融合技术发展与性能评价[J]. 激光与红外, 2019, 49(5): 123-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGHW201905022.htmLIU Z J, JIA P, XIA Y H, et al. Development and performance evaluation of infrared and visual image fusion technology[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2019, 49(5): 123-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGHW201905022.htm [7] Lee H Y, Tseng H Y, Mao Q, et al. Drit++: Diverse image-to-image translation via disentangled representations[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(10): 2402-2417. [8] 马梁, 苟于涛, 雷涛, 等. 基于多尺度特征融合的遥感图像小目标检测[J]. 光电工程, 2022, 49(4): 49-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDGC202204005.htmMA L, GOU Y T, LEI T, et al. Small object detection based on multi-scale feature fusion using remote sensing images[J]. Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2022, 49(4): 49-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDGC202204005.htm [9] 雷大江, 杜加浩, 张莉萍, 等. 联合多流融合和多尺度学习的卷积神经网络遥感图像融合方法[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(1): 237-244. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYX202201025.htmLEI D J, DU J H, ZHANG L P, et al. Multi-stream architecture and multi-scale convolutional neural network for remote sensing image fusion[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(1): 237-244. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZYX202201025.htm [10] 李明, 刘帆, 李婧芝. 结合卷积注意模块与卷积自编码器的细节注入遥感图像融合[J]. 光子学报, 2022, 51(6): 406-418. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZXB202206038.htmLI M, LIU F, LI J Z. Combining convolutional attention module and convolutional autoencoder for detail injection remote sensing image fusion[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2022, 51(6): 406-418. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZXB202206038.htm [11] 刘博, 韩广良, 罗惠元. 基于多尺度细节的孪生卷积神经网络图像融合算法[J]. 液晶与显示, 2021, 36(9): 1283-1293. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJYS202109009.htmLIU B, HAN G L, LUO H Y. Image fusion algorithm based on multi-scale detail siamese convolutional neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Liquid Crystals and Displays, 2021, 36(9): 1283-1293. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YJYS202109009.htm [12] Krishna V A, Reddy A A, Nagajyothi D. Signature recognition using siamese neural networks[C]//IEEE International Conference on Mobile Networks and Wireless Communications (ICMNWC), 2021: 1-4. [13] LI H, WU X J. DenseFuse: A fusion approach to infrared and visible images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 28(5): 2614-2623. [14] LI H, WU X J, Durrani T. NestFuse: An infrared and visible image fusion architecture based on nest connection and spatial/channel attention models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 69(12): 9645-9656. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2020.3005230 [15] LU B, CHEN J C, Chellappa R. Unsupervised domain-specific deblurring via disentangled representations[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019: 10225-10234. [16] WANG G, HAN H, SHAN S, et al. Cross-domain face presentation attack detection via multi-domain disentangled representation learning[C]// Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020: 6678-6687. [17] 文载道, 王佳蕊, 王小旭, 等. 解耦表征学习综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(2): 351-374. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO202202003.htmWEN Z D, WANG J R, WANG X X, et al. A review of disentangled representation learning[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(2): 351-374. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MOTO202202003.htm [18] ZHAO Z, XU S, ZHANG C, et al. DIDFuse: Deep image decomposition for infrared and visible image fusion[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2003.09210, 2020. [19] XU H, WANG X, MA J. DRF: Disentangled representation for visible and infrared image fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 1-13. [20] XU H, GONG M, TIAN X, et al. CUFD: An encoder–decoder network for visible and infrared image fusion based on common and unique feature decomposition[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2022, 218: 103407. doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2022.103407 [21] Tishby N, Pereira F C, Bialek W. The information bottleneck method[J]. arXiv preprint physics/0004057, 2000. [22] Tishby N, Zaslavsky N. Deep learning and the information bottleneck principle[C]// IEEE Information Theory Workshop (ITW). IEEE, 2015: 1-5. [23] Shwartz-Ziv R, Tishby N. Opening the black box of deep neural networks via information[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1703.00810, 2017. [24] Alemi A A, Fischer I, Dillon J V, et al. Deep variational information bottleneck[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1612.00410, 2016. [25] Tishby N, Zaslavsky N. Deep learning and the information bottleneck principle[C]//IEEE Information Theory Workshop (ITW). IEEE, 2015: 1-5. [26] ZHANG Y, LIU Y, SUN P, et al. IFCNN: A general image fusion framework based on convolutional neural network[J]. Information Fusion, 2020, 54: 99-118. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2019.07.011 [27] MA J, CHEN C, LI C, et al. Infrared and visible image fusion via gradient transfer and total variation minimization[J]. Information Fusion, 2016, 31: 100-109. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2016.02.001 [28] ZHANG H, MA J. SDNet: A versatile squeeze-and-decomposition network for real-time image fusion[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2021, 129(10): 2761-2785. doi: 10.1007/s11263-021-01501-8 [29] LIU Y, LIU S, WANG Z. A general framework for image fusion based on multi-scale transform and sparse representation[J]. Information Fusion, 2015, 24: 147-164. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2014.09.004 -





 下载:
下载: