Modeling and Verification of Ground Point Source for Mid-Wave Infrared Detection
-
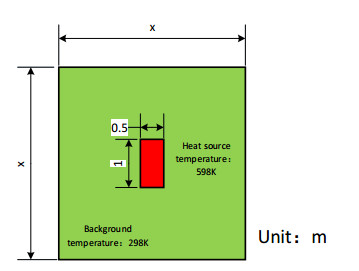
摘要: 红外系统在大范围内对异常热源点目标的探测需要平衡像元分辨率与温度灵敏度之间的关系。在探测器规模一定时,现有星载红外载荷存在幅宽大时灵敏度不够、空间分辨率高时幅宽小的问题。针对上述问题,本文提出利用时间延时积分(time delay intergration,TDI)算法处理图像的大视场异常点热源探测初步方案,在一定条件下,达到探测所需的温度灵敏度要求时,能做到217 km×122 km的理论幅宽。同时搭建了一套高灵敏度红外成像实验系统,开展了测试与模拟探测实验,结果表明本方案在实现202 km×114 km幅宽情况下,灵敏度性能约37 mK,满足大范围异常点热源探测的要求。考虑到目标和背景的太阳光反射率等问题,实际应用时取200 m像元分辨率,对应幅宽128 km×102 km。Abstract: The detection of anomalous heat source point targets in a wide range of infrared systems requires a balance between the pixel resolution and temperature sensitivity. Given that the scale of the detector is stable, the existing space-borne infrared payloads have insufficient sensitivity when the amplitude is large and small amplitude when the spatial resolution is high. In response to these problems, in this study, we propose a preliminary plan for detecting heat sources at abnormal points in a large field of view using a time-delay integration (TDI) algorithm to process images. Under certain conditions, the temperature sensitivity requirements for detection can be satisfied and a theoretical width of 217 km × 122 km can be achieved. A set of high-sensitivity infrared imaging experimental systems was built, and testing and simulation-based detection experiments were conducted. The results show that the sensitivity performance of this scheme is approximately 37 mK when a width of 202 km× 114 km is realized, which fulfills the requirements for detecting a large-scale abnormal point heat source. Considering the solar reflectance of the target and background, a pixel resolution of 200 m is used in practical applications, which corresponds to a width of 128 km×102 km.
-
图 7 推扫成像模拟探测实验现场示意图:(a) 探测器系统及电控转台实物;(b) 探测器系统与目标位置关系实物图;(c) 模拟热源实物
Figure 7. Schematic diagram of the push-broom imaging simulation detection experiment site (a) The physical diagram of the detector system and the electric control turntable; (b) The physical diagram of the positional relationship between the detector system and the target; (c) The physical diagram of the simulated heat source
图 8 模拟探测实验结果:(a) 热源像元及其同一行附近的像元DN值曲线;(b) 经8阶TDI处理后的热源像元及其同一行附近的像元DN值曲线;(c) 经16阶TDI处理后的热源像元及其同一行附近的像元DN值曲线;(d) 经25阶TDI处理后的热源像元及其同一行附近的像元DN值曲线
Figure 8. The results of the simulated detection experiment: (a) The DN value curve of the heat source pixel and the pixel near the same row; (b) The heat source pixel and the DN value curve of the pixel near the same row after 8th-order TDI processing; (c) The DN value curve of the heat source pixel after 16-level TDI processing and the pixel near the same row; (d) The heat source pixel after the 25-level TDI processing and the DN value curve of the pixel near the same row
表 1 红外探测系统参数理论值
Table 1. Theoretical values of detector parameters that meet the heat source detection standards of preset scenarios
Parameter Value Working wavelength 3.7~4.8 μm F# 2 Scan width 217 km×122 km Orbit height 500 km NETD ≤6.25 mK Focal length 21.6 mm Distance between the center of pixels 15 μm×15 μm Spatial resolution 346 m 表 2 部分阶数TDI算法处理后模拟热源所在像元DN值与背景像元DN值均值差值
Table 2. The difference between the DN value of the pixel where the simulated heat source is located and the average DN value of the background pixel after processing by the partial order TDI algorithm
TDI stage DN for pixel contain the heat source DN1 Average DN for background pixels DN2 DN1− DN2 Raw picture 579 552.8 26.2 8 576 549 26.2 16 582 536.9 45.1 25 570 524.4 45.6 -
[1] 李伟克, 殷继艳, 郭赞全, 等. 2019年世界代表性国家和地区森林火灾发送概况分析[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2020, 39(9): 1280-1284. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2020.09.026LI Weike, YIN Jiyan, GUO Zanquan, et al. Analysis of forest fires in representative countries and regions in the world in 2019[J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2020, 39(9): 1280-1284. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2020.09.026 [2] 栾婷婷, 王亚坤, 张馨仪. 2008-2018年我国森林火灾事故统计分析[J]. 安全, 2020, 41(10): 32-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ANQU202010010.htmLUAN Tingting, WANG Yakun, ZHANG Xinyi. Statistical analysis of forest fire accidents in china from 2008 to 2018[J]. Safety & Security, 2020, 41(10): 32-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ANQU202010010.htm [3] 李文岩. 宽幅航天相机焦面关键技术研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所), 2020.LI Wenyan. Research on the key technology of the focal plane of a wide-format space camera [D]. Changchun: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2020. [4] 刘妍妍. 大视场长焦平面TDI CCD拼接相机最优成像技术研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2016.LIU Yanyan. Research on Optimal Imaging Technology of Large Field of View and Long Focal Plane TDI CCD Stitching Camera[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2016. [5] 胡芬, 金淑英. 高分辨率光学遥感卫星宽幅成像技术发展浅析[J]. 地理信息世界, 2017, 24(5): 45-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHRK201705010.htmHU Fen, JIN Shuying. Analysis on the development of high-resolution optical remote sensing satellite wide-format imaging technology[J]. Geographic Information World, 2017, 24(5): 45-50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHRK201705010.htm [6] 吕旺, 董瑶海, 沈毅力, 等. 静止气象卫星轨道运动的成像补偿研究[J]. 遥感学报, 2019, 23(2): 185-195. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGXB201902001.htmLYU Wang, DONG Yaohai, SHEN Yili, et al. Research on imaging compensation of orbital motion of stationary meteorological satellites[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2019, 23(2): 185-195. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGXB201902001.htm [7] 覃先林, 李晓彤, 刘树超, 等. 中国林火卫星遥感预警监测技术研究进展[J]. 遥感学报, 2020(5): 511-520. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGXB202005002.htmQIN Xianlin, LI Xiaotong, LIU Shuchao, et al. Forest fire early warning and monitoring techniques using satellite remote sensing in China[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2020(5): 511-520. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGXB202005002.htm [8] 张博铭, 苏晓峰, 崔坤, 等. 开窗高帧频下红外面阵数字TDI实现方式研究[J]. 激光与红外, 2016, 46(10): 1250-1255. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGHW201610017.htmZHANG Boming, SU Xiaofeng, CUI Kun, et al. Research on digital TDI implementation way based on windowing and high frame rate infrared FPA[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2016, 46(10): 1250-1255. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGHW201610017.htm [9] NIE Kaiming, YAO Suying. A 128-stage analog accumulator for CMOS TDI image sensor[J]. IEEE Trans. CIR-CUI-TS and Systems, 2014, 61(7): 1952-1961. [10] Lepage G, Bogaerts Jan, Meynants Guy. Time-delay-integration architectures in CMOS image sensors[J]. IEEE Trans. Electron Device-S, 2009, 56(11): 2524-2533. [11] 周世椿. 高级红外光电工程导论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014.ZHOU Shichun. Introduction to Advanced Infrared Optoelectronic Engineering[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2014. [12] 彭焕良. 红外焦平面热成像技术的发展[J]. 激光与红外, 2006, 36(S1) : 776-780. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGHW2006S1010.htmPENG Huanliang. The development of the IRFPA thermal imaging technology[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2006, 36(S1): 776-780. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGHW2006S1010.htm [13] 董海, 罗冠泰, 余明权, 等. 利用IRFPA的开窗功能实现成像系统的双帧频双画幅输出[J]. 激光与红外, 2011, 41(3): 278-283. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGHW201103009.htmDONG Hai, LUO Guantai, YU Mingquan, et al. Double frame rate and double picture implementation in IRFPA with region-of-interest capability imaging system[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2011, 41(3): 278-283. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGHW201103009.htm -





 下载:
下载: