Infrared Moving-point Target Semi-Automatic Labeling Algorithm Based on Target Enhancement and Visual Tracking
-
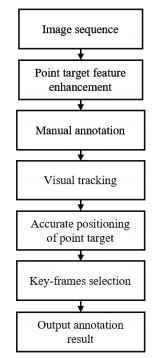
摘要: 本文针对红外视频数据标注效率低、标注质量差等问题,提出了一种基于目标增强和视觉跟踪的红外序列图像中运动点目标半自动标注方法。首先对一段连续时间内的红外序列图像进行配准和背景对消以增强目标特征;然后使用视觉跟踪算法对增强后的特征进行高效自动定位;最后通过相位谱重构得到单帧图像的目标显著图,进而确定目标的准确坐标;在自动标注过程中,利用相邻帧标注结果的差异性选择关键帧,可以让标注人员快速定位可能发生错误的图像帧并对其进行手动标注。实验结果表明该算法可以显著降低标注人员的参与度,有效解决数据标注作业中周期长、质量难以保证的问题。Abstract: Infrared video data annotation has the problems of low efficiency and poor quality. In this paper, a semi-automatic labeling method for moving point targets in infrared sequence images is proposed based on target enhancement and visual tracking to solve it. First, infrared sequence images in a continuous period of time were registered and fused to enhance the target features. Second, a visual tracking algorithm was utilized to locate the fused features efficiently and automatically. Lastly, a saliency map was obtained through phase spectrum reconstruction, and the exact coordinates of a target were obtained. During automatic annotation, the difference between the annotation results of adjacent frames was used to select key frames, which enabled the annotators to locate the image frames that had errors and manually annotated them quickly. The results of the experiments showed that the algorithm significantly reduced the participation of annotators and effectively solved the problems of long period and poor quality assurance in data annotation.
-
Key words:
- semi-automatic annotations /
- infrared point target /
- visual tracking /
- image sequences
-
表 1 数据集的基本信息
Table 1. General information of dataset
Data segment Number of frames Average signal-to-noise ratio Scenario description Data5 3000 5.45 Remote detection Data6 399 5.11 Target from near to far Data8 399 6.07 Target from near to far Data11 745 2.88 Target from near to far Data12 1500 5.20 Target midway maneuver Data13 763 1.98 Target from far to near, dim target Data15 751 3.42 Target midway maneuver, dim target Data17 500 3.32 Target midway maneuver Data19 1000 3.84 Target midway maneuver Data21 500 0.42 Remote detection Data22 500 2.20 Target from near to far 表 2 给出首帧标注信息的标注结果
Table 2. Annotation results with initialization information
Data segment Data5 Data6 Data8 Data11 Data12 Data13 Data15 Data17 Data19 Data21 Data22 NE 3000 399 399 745 1500 763 751 500 1000 500 500 NMA 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Accuracy 98.3% 97.8% 97.4% 97.3% 98.2% 94.5% 92.3% 99.2% 99% 97.4% 100% 表 3 半自动标注结果
Table 3. Semi-automatic annotation results
Data segment Data5 Data6 Data8 Data11 Data12 Data13 Data15 Data17 Data19 Data21 Data22 NE 48 8 11 20 27 42 56 4 10 13 0 NK 64 14 11 17 37 37 78 10 10 13 2 NCK 39 5 8 7 19 24 51 2 6 8 0 Accuracy 99.6% 99.2% 99.2% 98.2% 99.5% 97.6% 99.3% 99.6% 99.6% 99% 100% -
[1] Yuen J, Russell B, Liu C, et al. Labelme video: building a video database with human annotations[C]// 12th International Conference on Computer Vision(ICCV), IEEE, 2009: 1451-1458. [2] Lee J H, Lee K S, Jo G S. Representation method of the moving object trajectories by interpolation with dynamic sampling[C]//2013 International Conference on Information Science and Applications (ICISA), IEEE, 2013: 1-4. [3] Gil-Jiménez P, Gómez-Moreno H, López-Sastre R, et al. Geometric bounding box interpolation: an alternative for efficient video annotation[J]. EURASIP Journal on Image and Video Processing, 2016, 2016(1): 1-13. doi: 10.1186/s13640-015-0097-y [4] Vondrick C, Patterson D, Ramanan D. Efficiently scaling up crowdsourced video annotation[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2013, 101(1): 184-204. doi: 10.1007/s11263-012-0564-1 [5] Vondrick C, Ramanan D. Video annotation and tracking with active learning[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2011, 24: 28-36. [6] Buchanan A, Fitzgibbon A. Interactive feature tracking using K-D trees and dynamic programming[C]// IEEE Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern Recognition (CVPR), IEEE, 2006: 626-633. [7] Agarwala A, Hertzmann A, Salesin D H, et al. Key frame-based tracking for rotoscoping and animation[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2004, 23(3): 584-591. doi: 10.1145/1015706.1015764 [8] Biresaw T A, Nawaz T, Ferryman J, et al. Vitbat: video tracking and behavior annotation tool[C]//13th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS), IEEE, 2016: 295-301. [9] Bakliwal P, Hegde G M, Jawahar C V. Collaborative Contributions for Better Annotations[C]//The International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications(VISAPP), Scite Press, 2017: 353-360. [10] CHEN B, LING H, ZENG X, et al. Scribblebox: interactive annotation framework for video object segmentation[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Berlin Springer, 2020: 293-310. [11] Lowe D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91-110. doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94 [12] Henriques J F, Caseiro R, Martins P, et al. High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2014, 37(3): 583-596. [13] WANG M, LIU Y, HUANG Z. Large margin object tracking with circulant feature maps[C]//The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR), New York: IEEE, 2017: 4021-4029. [14] 回丙伟, 宋志勇, 范红旗, 等. 地/空背景下红外图像弱小飞机目标检测跟踪数据集[J]. 中国科学数据, 2020, 5(3): 286-297. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXGZ202003030.htmHUI Bingwei, SONG Zhiyong, FAN Hongqi, et al. A dataset for infrared detection and tracking of dim-small aircraft targets under ground/air background[J]. China Sci. Data, 2020, 5(3): 286-297. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXGZ202003030.htm -





 下载:
下载: