The Influence of Deep Transfer Learning Pre-training on Infrared Wake Image Recognition
-
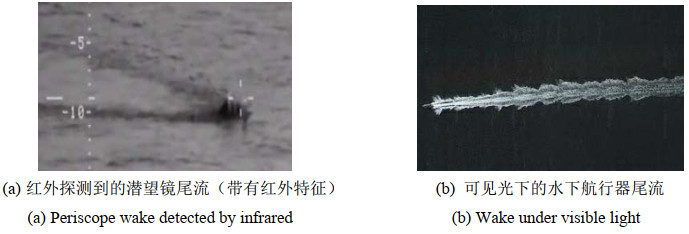
摘要: 随着水下航行器噪声水平的不断降低,水下航行器形成的尾流红外成像特征就成为其主要可探测的特征源之一,利用水下航行器尾流的水面红外特征来探测水下航行器的踪迹逐渐发展成为一种新的探测方式。由于人工判别尾流特征的效率低,准确性不高,采用人工智能深度学习的方式能够得到较大的改善。本文以水下航行器尾流红外特征识别为研究核心,通过图像分类制作了混合类的样本集,利用迁移学习比较不同预训练网的对尾流的训练效果,讨论预训练网内部参数对尾流训练效果的影响,结合Faster-RCNN算法,最终测试对尾流的识别精度,在45个2类尾流的小样本集下,预训练之后的网络在识别准确度上增加了21.43%,误检率下降了2.14%,带有红外特征的图像在定位精准率上比可见光图像高18.18%。该预训练测试对未来研究尾流探测结合卷积神经网络的识别有一定的应用潜力。
-
关键词:
- 红外特征 /
- 尾流 /
- 深度学习 /
- 迁移学习 /
- faster-RCN
Abstract: With lower underwater vehicle noise levels, the infrared imaging characteristics of underwater vehicle wake have become one of the main detectable sources. Using the infrared characteristics of underwater vehicle wakes to detect underwater vehicle traces has gradually developed into a popular detection method. Because of the low efficiency and inaccuracy of artificial wake characteristics identification, the adopted artificial intelligence deep learning method can be greatly improved. In this study, the infrared feature recognition of underwater vehicle wake is the primary focus. A sample set of mixed classes was made by image classification. The training effect of different pre-training networks was compared using migration learning. The influence of the internal parameters of the pre-training networks on the training effect of the wake was discussed. Finally, in the small sample set of 45 two kinds of wake, the recognition accuracy of the network after pre-training increased by 21.43%, the false detection rate decreased by 2.14%, and the positioning accuracy of the image with infrared characteristics was 18.18% higher than that of the visible image. This pre-training test has a certain application potential for future research on wake detection combined with convolution neural network recognition.-
Key words:
- infrared characteristics /
- wake /
- deep learning /
- transfer learning /
- faster-RCNN
-
表 1 3种基本网络对比结果
Table 1. Comparison results of three basic networks
Pre-training network Google VGG19 AlexNet Accuracy 83.33% 100% 100% Time 5min 34s 61min 49s 13min 13s Stability Bad Good Good 表 2 Frequency参数对AlexNet网络影响结果
Table 2. Influence results of frequency parameters on AlexNet network
Frequency 1 2 3 4 5 Accuracy 83.33% 100% 100% 100% 100% Rounds 3 5 5 5 5 Time 8min28s 19min21s 13min13s 12min21s 18min34s Stability Better Better Better Good Better 表 3 Patience参数对AlexNet网络影响结果
Table 3. Results of influence of patience parameters on AlexNet network
Patience 1 3 5 7 Accuracy 100% 100% 100% 100% Rounds 2 5 5 5 Time 6min 44s 15min 46s 12min 21s 16min 30s 表 4 45个样本集/14个测试集(2类)下的实验结果
Table 4. Experimental results under 45 sample sets and 14 test sets (Category 2)
Network type Accuracy Missed rate Error rate Periscope wake as positive
(infrared image)Ship wake as positive
(visible light image)Precise rate Recall rate Precise rate Recall rate Untrained 0.5714 35.71% 11.11% 66.67% 100% 100% 85.71% Transfer learning 0.7857 7.14% 8.97% 100% 75% 81.82% 100% 表 5 65个样本集/14个测试集下(2类)的实验结果
Table 5. Experimental results of 65 sample sets and 14 test sets (Category 2)
Network type Accuracy Missed rate Error rate Periscope wake as positive
(infrared image)Ship wake as positive
(visible light image)Precise rate Recall rate Precise rate Recall rate Untrained 0.7143 7.14% 16.67% 55.56% 100% 100% 87.5% Transfer learning 0.7857 7.14% 13.63% 71.43% 100% 100% 75% 表 6 85个样本集/14个测试集下(2类)的实验结果
Table 6. Experimental results of 85 sample sets and 14 test sets (Category 2)
Network type Accuracy Missed rate Error rate Periscope wake as positive
(infrared image)Ship wake as positive
(visible light image)Precise rate Recall rate Precise rate Recall rate Untrained 0.3571 14.29% 63.33% 33.33% 75% 83.33% 62.5% Transfer learning 0.6429 14.29% 14.29% 100% 100% 70% 100% -
[1] 王雨农. 基于视觉注意机制的神经网络模型研究及应用[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2017.WANG Yunong. Research on Visual Attention Based Neural Network Model and its Application[D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2017. [2] Rumelhart D, Mcclelland J. Learning internal representations by error propagation[M]//Parallel Distributed Processing: Explorations in the Microstructure of Cognition, Massachusetts: MIT Press, 1986: 318-362. [3] 尹勰, 闫磊. 基于深度卷积神经网络的图像目标检测[J]. 工业控制计算机, 2017, 30(4): 96-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYKJ201704040.htmYIN Xie, YAN Lei. Image target detection based on deep convolutional neural network [J]. Industrial Control Computer, 2017, 30(4): 96-97. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYKJ201704040.htm [4] Razavian A S, Azizpour H, Sullivan J, et al. CNN features off-the-shelf: an astounding baseline for recognition[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, 2014: 512-519. [5] Zeiler M D, Fergus R. Visualizing and Understanding Convolutional Networks[M]//Computer Vision-ECCV, Springer International Publishing, 2014. [6] 胡炎, 单子力, 高峰. 基于Faster-RCNN和多分辨率SAR的海上舰船目标检测[J]. 无线电工程, 2018, 48(2): 96-100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WXDG201802005.htmHU Yan, SHAN Zili, GAO Feng. Ship target detection based on faster-RCNN and multi-resolution SAR[J]. Radio Engineering, 2018, 48(2): 96-100. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WXDG201802005.htm [7] 李新. 基于红外热像技术连铸板坯裂纹预报方法研究[D]. 唐山: 华北理工大学, 2015.LI Xin. Research on Crack Prediction Method of Continuous Casting Slab Based on Infrared Thermography[D]. Tangshan : North China University of Technology, 2015. [8] 张健, 杨立, 袁江涛. 水下航行器热尾流试验研究[J]. 实验流体力学, 2008, 22(3): 9-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LTLC200803002.htmZHANG Jian, YANG Li, YUAN Jiangtao. Experimental study on thermal wake of underwater vehicles[J]. Experimental Fluid Mechanics, 2008, 22(3): 9-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LTLC200803002.htm [9] 贺林. 水喷淋消声器设计与实验研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2006.HE Lin. Design and Experimental Study of Water Spray Muffler[D]. Harbin : Harbin Engineering University, 2006. [10] 伍伟明. 基于Faster R-CNN的目标检测算法的研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2018.WU Weiming. Research on Target Detection Algorithm Based on Faster R-CNN[D]. Guangzhou : South China University of Technology, 2018. [11] 刘万军, 梁雪剑, 曲海成. 自适应增强卷积神经网络图像识别[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2019, 22(12): 1723-1736. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTB201712008.htmLIU Wanjun, LIANG Xuejian, QU Haicheng. Adaptive enhanced convolutional neural network image recognition[J]. Chinese Journal of Image Graphics, 2019, 22(12): 1723-1736. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTB201712008.htm [12] Lecun Y, Boser B, Denker J, et al. Back propagation applied to handwritten zip code recognition[J]. Neural Computation, 1989, 1(4): 541-551. doi: 10.1162/neco.1989.1.4.541 [13] 王红霞, 周家奇, 辜承昊, 等. 用于图像分类的卷积神经网络中激活函数的设计[J]. 浙江大学学报: 工学版, 2019, 53(7): 1363-1373. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDZC201907016.htmWANG Hongxia, ZHOU Jiaqi, GU Chenghao, et al. Design of activation functions in convolutional neural networks for image classification[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University: Engineering Edition, 2019, 53(7): 1363-1373. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDZC201907016.htm -





 下载:
下载: