Mode Adaptive Infrared and Visible Image Fusion
-
摘要: 为解决低照度和烟雾等恶劣环境条件下融合图像目标对比度低、噪声较大的问题,提出一种模态自适应的红外与可见光图像融合方法(mode adaptive fusion, MAFusion)。首先,在生成器中将红外图像与可见光图像输入自适应加权模块,通过双流交互学习二者差异,得到两种模态对图像融合任务的不同贡献比重;然后,根据各模态特征的当前特性自主获得各模态特征的相应权重,进行加权融合得到融合特征;最后,为了提高模型的学习效率,补充融合图像的多尺度特征,在图像融合过程中加入残差块与跳跃残差组合模块,提升网络性能。在TNO和KAIST数据集上进行融合质量测评,结果表明:主观评价上,提出的方法视觉效果良好;客观评价上,信息熵、互信息和基于噪声的评价性能指标均优于对比方法。Abstract: To solve the problems of low contrast and high noise of fused images in low illumination and smoky environments, a mode-adaptive infrared and visible image fusion method (MAFusion) is proposed. Firstly, the infrared and visible images are input into the adaptive weighting module in the generator, and the difference between them is learned through two streams interactive learning. The different contribution proportion of the two modes to the image fusion task in different environments is obtained. Then, according to the characteristics of each modal feature, the corresponding weights of each modal feature are obtained independently, and the fusion feature is obtained by weighted fusion. Finally, to improve the learning efficiency of the model and supplement the multi-scale features of the fused image, a residual block and jump connection combination module are added to the image fusion process to improve the network performance. The fusion quality was evaluated using the TNO and KAIST datasets. The results show that the visual effect of the proposed method is good in subjective evaluation, and the performance indexes of information entropy, mutual information, and noise-based evaluation are better than those of the comparison method.
-
Key words:
- image fusion /
- mode adaptive /
- GAN /
- ResNet
-
表 1 生成器网络整体结构
Table 1. Overall structure of generator network
layer k s n1 Input n2 Output fill function Feature extraction l0_ir 5×5 1 1 VIS 128 Conv0_ir VALID LReLU l0_vis 5×5 1 1 IR 128 Conv0_vis VALID LReLU Adaptive weighting module L11_w_ir 3×3 1 256 Concat(Conv0_ir, Conv0_vis) 128 ir_weight SAME LReLU L22_w_vis 3×3 1 256 Concat(Conv0_ir, Conv0_vis) 128 vis_weight SAME LReLU Routine
convolutionLayer1 5×5 1 256 Concat[multiply(Conv0_ir, ir_weight),
multiply(Conv0_vis, vis_weight)]128 Net1 VALID LReLU Residual block Layer2 3×3 1 128 Net1 128 Net2 SAME LReLU Layer3 3×3 1 128 Net2 128 Net3 SAME - Add1 - - - Net1/Net3 - Net1+Net3 - LReLU Transfer layer Layer4 3×3 1 128 LReLU(Net1+Net3) 128 Net4 SAME LReLU Jump residual Add2 - - - Net1/net4 - Net1+net4 - - Output layer Layer5 3×3 1 128 Net4 64 Net5 VALID LReLU Layer6 3×3 1 64 Net5 32 Net6 VALID LReLU Layer7 1×1 1 32 Net6 1 Fused VALID tanh 表 2 判别器网络整体结构
Table 2. Overall structure of discriminator network
Layer k s n1 Input n2 Output Padding Activation function Conv_1 5×5 2 1 VIS/Fused 32 Net1 VALID LReLU Conv_2 3×3 2 32 Net1 64 Net2 VALID LReLU Conv_3 3×3 2 64 Net2 128 Net3 VALID LReLU Conv_4 3×3 2 128 Net3 256 Net4 VALID LReLU Line_5 - - - Net4 - Net5(6*6*256) - - Output - - - Net5 1 Discriminant value (1) - - 表 4 KAIST数据集“道路与行人”融合图像客观评价
Table 4. Objective evaluation of "road and pedestrian" fusion image in KAIST dataset
Methods EN MI Nabf ADF 5.7176 11.4352 0.0782 WLS 5.8693 11.7387 0.2129 densefuse 6.0565 12.1129 0.0121 U2Fusion 5.3543 10.7086 0.0809 FusionGAN 5.8022 11.6044 0.0389 MAFusion 6.3678 12.5356 0.0447 Note:Bold font is the best value 表 5 KAIST数据集14组融合图像客观评价指标均值
Table 5. Mean value of objective evaluation of 14 groups fusion images in KAIST dataset
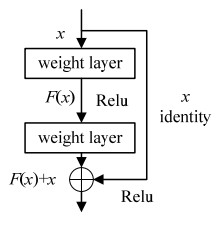
Methods EN MI Nabf ADF 6.2336 12.4673 0.0930 WLS 6.4248 12.8496 0.2465 CBF 6.5413 13.0827 0.1551 Densefuse 6.6039 13.2078 0.0223 U2Fusion 5.9722 11.9444 0.1318 FusionGAN 6.2516 12.5033 0.0921 MAFusion 6.7086 13.4042 0.0562 Note:Bold font is the best value 表 6 TNO数据集“烟雾中的士兵”融合图像客观评价
Table 6. Objective evaluation of "a soldier in the smog" fusion image in TNO dataset
Methods EN MI Nabf ADF 6.4886 13.1772 0.104 FusionGAN 6.3959 12.7919 0.026 MAFusion 6.6097 13.2193 0.018 Note:Bold font is the best value 表 7 TNO数据集“士兵与车辆”融合图像客观评价
Table 7. Objective evaluation of " Soldiers and vehicles " fusion image in TNO dataset
Methods EN MI Nabf ADF 6.4620 12.9241 0.1582 WLS 6.9916 13.9833 0.2652 Densefuse 7.0227 14.0453 0.0931 U2Fusion 7.1399 14.2797 0.4285 FusionGAN 7.0007 14.0015 0.1093 MAFusion 7.2017 14.4033 0.0801 Note:Bold font is the best value 表 8 TNO数据集18组融合图像客观评价指标均值
Table 8. Mean value of objective evaluation of 18 groups fusion images in TNO dataset
Methods EN MI Nabf ADF 6.6001 13.2003 0.0896 WLS 6.9157 13.8314 0.2404 CBF 6.9846 13.9697 0.3921 Densefuse 6.9482 13.8964 0.0854 U2Fusion 7.0457 14.0915 0.3313 FusionGAN 6.9058 13.8116 0.0892 MAFusion 7.0653 14.1306 0.0608 Note:Bold font is the best value 表 9 KAIST数据集消融实验客观评价
Table 9. Objective evaluation of ablation experiment in KAIST dataset
Method FusionGAN Direct stacking Two way feature extraction and adaptive weighting Ordinary convolution Residual block Jump residual block EN MI Nabf ① √ √ - √ - - 6.3787 12.7574 0.0921 ② √ √ - - √ √ 6.5284 13.0567 0.0607 ③ √ - √ - √ √ 6.7086 13.4042 0.0562 Note:Bold font is the best value -
[1] 段辉军, 王志刚, 王彦. 基于改进YOLO网络的双通道显著性目标识别算法[J]. 激光与红外, 2020, 50(11): 1370-1378. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2020.11.014DUAN H J, WANG Z, WANG Y. Two-channel saliency object recognition algorithm based on improved YOLO network[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2020, 50(11): 1370-1378. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2020.11.014 [2] 李舒涵, 宏科, 武治宇. 基于红外与可见光图像融合的交通标志检测[J]. 现代电子技术, 2020, 43(3): 45-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDJ202003012.htmLI S H, XU H K, WU Z Y. Traffic sign detection based on infrared and visible image fusion[J]. Modern Electronics Technique, 2020, 43(3): 45-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDJ202003012.htm [3] Reinhard E, Adhikhmin M, Gooch B, et al. Color transfer between images[J]. IEEE Comput. Graph. Appl. , 2001, 21(5): 34-41. http://www.cs.northwestern.edu/~bgooch/PDFs/ColorTransfer.pdf [4] Kumar P, Mittal A, Kumar P. Fusion of thermal infrared and visible spectrum video for robust surveillance[C]// Proceedings of the Indian Conference on Computer Vision, Graphics and Image Processing, 2006: 528-539. [5] 常新亚, 丁一帆, 郭梦瑶. 应用整体结构信息分层匹配的红外与可见光遥感图像融合方法[J]. 航天器工程, 2020, 29(1): 100-104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2020.01.015CHANG X Y, DING Y F, GUO M Y. Infrared and visible image fusion method using hierarchical matching of overall structural information[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2020, 29(1): 100-104. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2020.01.015 [6] Bavirisetti D P, Dhuli R. Fusion of infrared and visible sensor images based on anisotropic diffusion and karhunen-loeve transform[J]. IEEE Sensors, 2016, 16(1): 203-209. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2015.2478655 [7] Kumar B S. Image fusion based on pixel significance using cross bilateral filter[J]. Signal Image Video Process, 2015, 9(5): 1193-1204. doi: 10.1007/s11760-013-0556-9 [8] MA J, ZHOU Z, WANG B. Infrared and visible image fusion based on visual saliency map and weighted least square optimization[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2017, 82: 8-17. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1350449516305928 [9] LIU Y, WANG Z. Simultaneous image fusion and denoising with adaptive sparse representation[J]. IET Image Process, 2014, 9(5): 347-357. doi: 10.1049/iet-ipr.2014.0311 [10] Burt P, Adelson E. The Laplacian pyramid as a compact image code[J]. IEEE Trans. Commun. , 1983, 31(4): 532-540. doi: 10.1109/TCOM.1983.1095851 [11] 马雪亮, 柳慧超. 基于多尺度分析的红外与可见光图像融合研究[J]. 电子测试, 2020, 24(4): 57-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WDZC202024021.htmMA Xueliang, LIU Huichao. Research on infrared and visible image fusion based on multiscale analysis[J]. Electronic Test, 2020, 24(4): 57-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WDZC202024021.htm [12] LI S, YIN H, FANG L. Group-sparse representation with dictionary learning for medical image denoising and fusion[J]. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. , 2012, 59(12): 3450-3459. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2012.2217493 [13] Prabhakar K R, Srikar V S, Babu R V. DeepFuse: A deep unsupervised approach for exposure fusion with extreme exposure image[C]//Proc of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2017: 4724-4732. [14] MA J Y, YU W, LIANG P W, et al. FusionGAN: A generative adversarial network for infrared and visible image fusion[J]. Information Fusion, 2019, 48: 11-26. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2018.09.004 [15] LI H, WU X J, Kittler J. Infrared and visible image fusion using a deep learning framework[C]//The 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), 2018: 2705-2710. [16] LI H, WU X. DenseFuse: A fusion approach to infrared and visible images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(5): 2614-2623. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2887342 [17] 董安勇, 杜庆治, 苏斌, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 红外技术, 2020, 42(7): 660-669. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/59ccddf6-ee9a-43da-983b-35ee872dd707DONG Anyong, DU Qingzhi, SU Bin, et al. Infrared and visible image fusion based on convolutional neural network[J]. Infrared Technology, 2020, 42(7): 660-669. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/59ccddf6-ee9a-43da-983b-35ee872dd707 [18] XU Han, MA Jiayi, JIANG Junjun, et al. U2Fusion: A unified unsupervised image fusion network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 44: 502-518. [19] Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, et al. Generative adversarial nets[C]//Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2014: 2672-2680. [20] HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2016: 770-778. [21] Figshare. TNO Image Fusion Dataset[OL]. [2018-09-15]. https://flgshare.com/articles/TNOImageFusionDataset/1008029. [22] Hwang S, Park J, Kim N, et al. Multispectral pedestrian detection: benchmark dataset and baseline[C]//2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2015: 1037-1045. [23] Roberts J W, Aardt J V, Ahmed F. Assessment of image fusion procedures using entropy, image quality, and multispectral classification[J]. Appl. Remote Sens. , 2008, 2(1): 023522-023522-28. doi: 10.1117/1.2945910 [24] QU G, ZHANG D, YAN P. Information measure for performance of image fusion[J]. Electron Lett. , 2002, 38(7): 313-315. doi: 10.1049/el:20020212 [25] Kumar B K S. Multifocus and multispectral image fusion based on pixel significance using discrete cosine harmonic wavelet transform[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2013, 7(6): 1125-1143. doi: 10.1007/s11760-012-0361-x -





 下载:
下载: