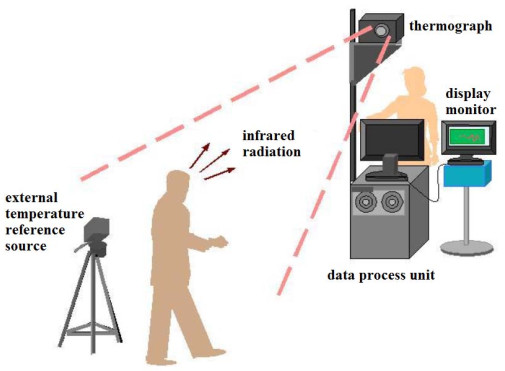
Analysis of Temperature Measurement Accuracy in Fever-Screening Thermograph
-
摘要: 介绍了发热筛查热成像系统的发展历程和系统构成及热像仪测温的基本原理,指出热像仪的内辐射对测温准确性具有明显影响,分析了发热筛查热成像系统用黑体参考源消除内辐射影响的工作原理。介绍了发热筛查热成像系统的测温准确性评价模型及其主要参数的要求,逐项分析了这些参数与热像仪噪声、黑体参考源及使用环境等因素的关系,发现热像仪的时间低频噪声和空间低频噪声是影响测温准确性的关键因素,指出黑体参考源可以消除时间低频噪声的影响,基于外挡片的两点校正法可以消除空间低频噪声的影响,从而使发热筛查热成像系统满足人体测温准确性要求。Abstract: The development and system composition of a fever-screening thermograph and the basic principle of a thermal imager's temperature measurement are introduced. It is observed that the thermal imager's internal radiation clearly influences the accuracy of the temperature measurement. This paper introduces an evaluation model for the temperature measurement accuracy of a fever-screening thermograph and its main parameters. By analyzing the relationship between these parameters and the thermal imager noise, the blackbody reference source, and the environment, the temporal and spatial low-frequency noise of the thermal imager are found to be the key factors affecting the accuracy of the temperature measurement. Moreover, the influence of temporal low-frequency noise can be eliminated using a blackbody reference source, and the influence of spatial low-frequency noise can be eliminated using the two-point correction method based on an external shutter. Thus, the fever-screening thermograph can meet the accuracy requirements of human body temperature measurement.
-
表 1 测温结果不确定度的组成参数
Table 1. Parameters of uncertainty of temperature measurement results
Parameters of uncertainty Parameter content Value requirements uD Drift of screening thermograph The combined effect of drift and instability≤0.2℃ uS Instability of screening thermograph uU Non-uniformity of screening thermograph ≤0.2℃ uMRTD MRTD of screening thermograph ≤0.1℃ uER External temperature reference source In the range of 33℃-40℃:
Temperature accuracy≤0.3℃
The combined effect of drift and instability≤0.1℃uothers Other factors Not given -
[1] World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic [EB/OL]. [2021-08-19]. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019. [2] 刘雨薇, 龚仁蓉, 许瑞华, 等. 新型冠状病毒肺炎疫情期间发热筛查相关问题的证据总结[J]. 护理研究, 2020, 34(6): 929-933. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXHZ202006002.htmLIU Yuwei, GONG Renrong, XU Ruihua, et al. Evidence summary of issues related to fever screening during epidemic of corona virus disease 2019[J]. Chinese Nursing Research, 2020, 34(6): 929-933. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SXHZ202006002.htm [3] Pejman Ghassemi, T Joshua Pfefer, Jon P Casamento, et al. Best practices for standardized performance testing of infrared thermographs intended for fever screening[J]. PLOS ONE, 2018, 13(9): e0203302. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0203302 [4] CHIOU W, LIN P, CHIOU H Y, et al. Infrared thermography to massscreen suspected SARS patients with fever[J]. Asia-Pacific Journal of Public Health, 2005, 17: 26-28. doi: 10.1177/101053950501700107 [5] WU Yigang Michael. Stop outbreak of SARS with infrared cameras[C]// Proceedings of SPIE, Thermosense XXVI, 2004, 5405: 98-105. [6] Hiroshi Nishiura, Kazuko Kamiya. Fever screening during the influenza (H1N1-2009) pandemic at Narita international airport, Japan[J]. BMC Infectious Diseases, 2011(11): 111. [7] Kyung Sook Cho, Jangho Yoon. Fever screening and detection of febrile arrivals at an international airport in korea: association among self-reported fever, infrared thermal camera scanning, and tympanic temperature[J]. Epidemiology and Health, 2014, 36: e2014004. doi: 10.4178/epih/e2014004 [8] Cosford P. Advantages of airport screening for Ebola[J]. Brit. Med. J., 2014, 349: G6585(doi: 10.1136/bmj.g6585" target="_blank">https://doi.org/ 10.1136/bmj.g6585). [9] IEC. Medical electrical equipment—deployment, implementation and operational guidelines for identifying febrile humans using a screening thermograph: CSA ISO/TR 13154[S]. Switzerland: ISO Copyright Office, 2017. [10] IEC. Medical electrical equipment — Part 2-59: Particular requirements for the basic safety and essential performance of screening thermographs for human febrile temperature screening: 80601-2-59[S]. Switzerland: ISO Copyright Office, 2017. [11] Yang How Tana, Chee Wah Teoa, Eric Ong, et al. Development and deployment of infrared fever screening systems[C]//Proc. of SPIE, Thermosense XXVI, 2004, 5405: 68-78. [12] 吴继平, 张桂玲, 杨楚明. 工业检测型红外热像仪: GB/T19870 —2018[S]. 全国工业过程测量控制和自动化标准化技术委员会[2018-05-14].WU Jiping, ZHANG Guiling, YANG Chuming. Industrial inspecting thermal imagers: GB/T19870—2018[S]. National Industrial Process Measurement Control and Automation Standardization Technical Committee[2018-05-14]. [13] 白廷柱, 金伟其. 光电成像原理与技术[M]. 北京: 北京理工大学出版社, 2006.BAI Tingzhu, JIN Weiqi. Principle and Technology of Photoelectric Imaging[M]. Beijing: Beijing University of Technology Press, 2006. [14] Usamentiaga R, Venegas P, Guerediaga J, et al. Infrared thermography for temperature measurement and non-destructive testing[J]. Sensors, 2014, 14(7): 12305-12348. doi: 10.3390/s140712305 [15] 武汉凯尔文光电技术有限公司产品中心. JQ-D70Z热成像人体测温黑体[EB/OL]. [2021-08-19]. https://http://www.whkelvin.com/pros_show.php?id=84.Product Center of Wuhan Kelvin Photoelectric Technology Co. Ltd. JQ-D70Z blackbody of screening thermograph[EB/OL]. [2021-08-19]. https://http://www.whkelvin.com/pros_show.php?id=84. [16] Pascoe D, Ring E, Mercer J, et al. International standards for pandemic screening using infrared thermography[C]//Proc. of SPIE, Medical Imaging 2010: Biomedical Applications in Molecular, Structural, and Functional Imaging, 2010, 7626: 76261Z. -





 下载:
下载: