Deep Learning Method for Action Recognition Based on Low Resolution Infrared Sensors
-
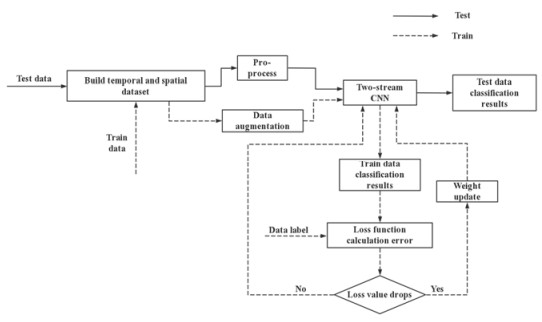
摘要: 近年来动作识别成为计算机视觉领域的研究热点,不同于针对视频图像进行的研究,本文针对低分辨率红外传感器采集到的温度数据,提出了一种基于此类红外传感器的双流卷积神经网络动作识别方法。空间和时间数据分别以原始温度值的形式同时输入改进的双流卷积神经网络中,最终将空间流网络和时间流网络的概率矢量进行加权融合,得到最终的动作类别。实验结果表明,在手动采集的数据集上,平均识别准确率可达到98.2%,其中弯腰、摔倒和行走动作的识别准确率均达99%,可以有效地对其进行识别。Abstract: In recent years, action recognition has become a popular research topic in the field of computer vision. In contrast to research on video or images, this study proposes a two-stream convolution neural network method based on temperature data collected by a low-resolution infrared sensor. The spatial and temporal data were input into the two-stream convolution neural network in the form of collected temperature data, and the class scores of the spatial and temporal stream networks were late weighted and merged to obtain the final action category. The results indicate that the average accuracy of recognition can reach 98.2% on the manually collected dataset and 99% for bending, falling, and walking actions, indicating that the proposed net can recognize actions effectively.
-
Key words:
- action recognition /
- two-stream CNN /
- low resolution infrared sensor /
- deep learning
-
表 1 不同环境温度、安装场景下的阈值对比
Table 1. Comparison of thresholds under different ambient temperatures and installation spaces
Ambient temperature Laboratory Living room 22℃ 1.66 1.65 26℃ 1.71 1.73 30℃ 1.75 1.76 表 2 单流、双流CNN识别准确率
Table 2. Accuracy of one-stream and two-stream
Temporal one-stream Spatial one-stream Two-stream Bend 97% 88% 99% Fall 96% 91% 99% Sit 84% 85% 96% Stand 91% 81% 98% Walk 98% 97% 99% Accuracy 93.2% 88.4% 98.2% -
[1] 张艳梅, 马晓霞, 赫继梅, 等. 失能老人跌倒的影响因素及长期照护服务需求[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2019, 39(17): 4355-4357. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2019.17.076ZHANG Yanmei, MA Xiaoxia, HE Jimei, et al. Influencing factors of falls and demand for long-term care services in the disabled elderly[J]. Chinese Journal of Gerontology, 2019, 39(17): 4355-4357. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2019.17.076 [2] Hsieh Chungyang, LIN Weiyang. Video-based human action and hand gesture recognition by fusing factored matrices of dual tensors[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2017, 76(6): 7575-7594. doi: 10.1007/s11042-016-3407-1 [3] 王玉坤, 高炜欣, 王征, 等. 基于加速度传感器的人体姿态实时识别[J]. 计算机工程与设计, 2016, 37(11): 3092-3096. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJSJ201611041.htmWANG Yukun, GAO Weixin, WANG Zheng, et al. Real-time human activity pattern recognition based on acceleration[J]. Computer Engineering and Design, 2016, 37(11): 3092-3096. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJSJ201611041.htm [4] 杜英魁, 姚俊豪, 刘鑫, 等. 基于电阻式薄膜压力传感器组的人体坐姿感知终端[J]. 传感器与微系统, 2020, 39(1): 78-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CGQJ202001022.htmDU Yingkui, YAO Junhao, LIU Xin, et al. Human body sitting posture sensing terminal based on resistive thin film pressure sensor groups[J]. Transducer and Microsystem Technologies, 2020, 39(1): 78-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CGQJ202001022.htm [5] Kobiyama Yuta, ZHAO Qiangfu, Omomo Kazuk, et al. Analyzing correlation of resident activities based on infrared sensors[C]//IEEE International Conference on Awareness Science and Technology, 2015: 1-6. [6] Mashiyama S, HONG J, Ohtsuki T. Activity recognition using low resolution infrared array senso[C]//IEEE International Conference on Communications, 2015: 495-500. [7] 杨任兵, 程文播, 钱庆, 等. 红外图像中基于多特征提取的跌倒检测算法研究[J]. 红外技术, 2017, 39(12): 1131-1138. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/hwjs201712011YANG Renbin, CHEN Wenbo, QIAN Qing, et al. Fall detection algorithm based on multi feature extraction in infrared image[J]. Infrared Technology, 2017, 39(12): 1131-1138. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/hwjs201712011 [8] 张昱彤, 翟旭平, 汪静. 一种基于低分辨红外传感器的动作识别方法[J]. 红外技术, 2022, 44(1): 47-53. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/5bca603e-2b3d-471c-a852-70344620d4bcZHANG Yutong, ZHAI Xuping, WANG Jing. Activity recognition approach using a low-resolution infrared sensor[J]. Infrared Technology, 2022, 44(1): 47-53. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/5bca603e-2b3d-471c-a852-70344620d4bc [9] Akula A, Shah A K, Ghosh R. Deep learning approach for human action recognition in infrared images[J]. Cognitive Systems Research, 2018, 50(8): 146-154. [10] 王召军, 许志猛. 基于低分辨率红外阵列传感器的人体身份和动作识别[J]. 电气技术, 2019, 20(11): 6-10, 26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3800.2019.11.004WANG Zhaojun, XU Zhimeng. Human identity and motion recognition based on low resolution infrared array sensor[J]. Electrical Engineering, 2019, 20(11): 6-10, 26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-3800.2019.11.004 [11] Takayuki Kawashima, Yasutomo Kawanishi, IchiroIde Hiroshi Murase. Action recognition from extremely low-resolution thermal image sequence[C]//2017 14th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance (AVSS), 2017: 1-6, Doi: 10.1109/AVSS.2017.8078497. [12] FAN Xiuyi, ZHANG Huiguo, LEUNG Cyril, et al. Robust unobtrusive fall detection using infrared array sensor[J]. IEEE International Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Integration for Intelligent Systems (MFI), 2017, 5(4): 194-199. [13] Polla F, Laurent H, Emile B. Action recognition from low-resolution infrared sensor for indoor use: a comparative study between deep learning and classical approaches[C]//2019 20th IEEE International Conference on Mobile Data Management (MDM), 2019: 409-414. [14] Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2014, 1(4): 568-576. [15] Feichtenhofer C, Pinz A, Zisserman A. Convolutional two-stream network fusion for video action recognition[C]//IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition CVPR, 2016: 1933-1941. [16] Trofimova A A, Masciadri A, Veronese F, et al. Salice, indoor human detection based on thermal array sensor data and adaptive background estimation[J]. Journal of Computer and Communications, 2017, 5(4): 16-28. doi: 10.4236/jcc.2017.54002 [17] Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]//ICLR, 2015: 1-14. [18] WANG L, ZANG J, ZHANG Q, et al. Action recognition by an attention-aware temporal weighted convolutional neural network[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(7): 1979. doi: 10.3390/s18071979 [19] HE K, ZHANG X, Ren S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//CVPR, 2016: 770-778. Doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2016.90. -





 下载:
下载: