Refined Infrared Object Detection Model for Power Equipment Based on Improved RetinaNet
-
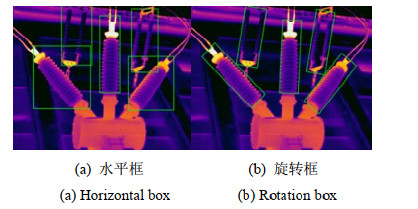
摘要: 电力设备在运行过程中会产生大量红外图像,当红外图像中的电力设备存在排列密集、具有倾斜角度、大长宽比的情况时,基于水平矩形框的目标检测网络只能给出目标概略位置,易发生目标检测区域重叠,引入冗余背景信息,使得检测结果不够精细。针对此问题,提出在RetinaNet目标检测网络中引入旋转矩形框机制,并在网络输入端引入Mosaic数据增强技术;将原特征提取网络中ReLU函数替换为梯度流更平滑的Mish激活函数;在原模型FPN模块后追加PAN模块进一步融合图像特征。最后利用现场采集的电力设备红外图像制作数据集,将改进后的模型与Faster R-CNN、YOLOv3、原RetinaNet三种基于水平矩形框定位的目标检测网络进行对比评估,实验表明改进后的模型可以更为精细地检测出密集场景下带有倾角的电力设备红外目标,在多类别电力设备检测准确率对比上高于以上3种模型。Abstract: A large number of infrared images are generated during the operation of power equipment. When the power equipment in the infrared image is densely arranged, incline-angled, and has a large aspect ratio, the target detection network based on a horizontal rectangular frame can only provide the approximate position of the target, which is prone to overlap with the target detection area and introduce redundant background information, giving detection results that are not sufficiently accurate. To solve this problem, we propose to introduce a rotating rectangular box mechanism into the retina net target detection network and mosaic data enhancement technology at the network input, replacing the ReLU function in the original backbone network with a smoother mish activation function of gradient flow; the Pan module is added after the FPN module of the original model to further fuse image features. Finally, the data set is made by using the power-equipment infrared images collected on-site. The improved model is compared and evaluated with three target detection networks based on horizontal rectangular frame positioning: fast R-CNN, YOLOv3, and original RetinaNet. The experiments show that the improved model can detect the infrared targets of power equipment with inclination in dense scenes more accurately, and the detection accuracy of multi-category power equipment is higher than that of the above three models.
-
Key words:
- infrared image /
- RetinaNet /
- power equipment /
- convolutional neural network /
- object detection
-
表 1 不同检测模型对比测试结果
Table 1. Comparison of the test results of different detectionmodels
Method AP mAP Breaker Insulator Switch PT CT Faster R-CNN 94.47 89.21 87.23 96.45 95.44 92.56 YOLOv3 90.62 86.52 82.09 92.03 91.37 88.53 RetinaNet 94.96 90.05 88.57 96.03 96.19 93.16 Ours method 97.51 92.84 90.61 98.69 97.86 95.50 -
[1] 谭宇璇, 樊绍胜. 基于图像增强与深度学习的变电设备红外热像识别方法[J/OL]. 中国电机工程学报, [2021-07-30]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/dtail/11.2107.tm.20210601.1000.002.html.TAN Yuxuan, FAN Shaosheng. Infrared thermal image recognition of substation equipment based on image enhancement and deep learn-ing[J/OL]. Proceedings of the CSEE, [2021-07-30]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/dtail/11.2107.tm.20210601.1000.002.html. [2] 冯振新, 周东国, 江翼, 等. 基于改进MSER算法的电力设备红外故障区域提取方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2019, 47(5): 123-128. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDQW201905015.htmFENG Zhenxin, ZHOU Dongguo, JIANG Yi, et al. Fault region extraction using improved MSER algorithm with application to the electrical system[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2019, 47(5): 123-128. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDQW201905015.htm [3] Jadin M S, Taib S. Recent progress in diagnosing the reliability of electrical equipment by using infrared thermography[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2012, 55(4): 236-245. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035395435610_ae85.html [4] 曾军, 王东杰, 范伟, 等. 基于红外热成像的电气设备组件识别研究[J]. 红外技术, 2021, 43(7): 679-687. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/58024112-8052-43d6-8a2d-dd2460dfa5e1ZENG Jun, WANG Dongjie, FAN Wei, et al. Research on electrical equipment component recognition based on infrared thermal imaging[J]. Infrared Technology, 2021, 43(7): 679-687. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/58024112-8052-43d6-8a2d-dd2460dfa5e1 [5] 朱惠玲, 牛哲文, 黄克灿, 等. 基于单阶段目标检测算法的变电设备红外图像目标识别及定位[J]. 电力自动化设备, 2021, 41(8): 217-224. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLZS202108032.htmZHU Huiling, NIU Zhewen, HUANG Kecan, et al. Infrared image target recognition and location of substation equipment based on single-stage target detection algorithm[J]. Power Automation Equipment, 2021, 41(8): 217-224. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLZS202108032.htm [6] 吴克河, 王敏鉴, 李渊博. 基于Mask R-CNN的电力设备红外图像分割技术研究[J]. 计算机与数字工程, 2020, 48(2): 417-422. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9722.2020.02.029WU Kehe, WANG Minjian, LI Yuanbo. Research on infrared image segmentation technology of power equipment based on mask R-CNN[J]. Computer & Digital Engineering, 2020, 48(2): 417-422. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9722.2020.02.029 [7] 刘云鹏, 裴少通, 武建华, 等. 基于深度学习的输变电设备异常发热点红外图片目标检测方法[J]. 南方电网技术, 2019, 13(2): 27-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NFDW201902006.htmLIU Yunpeng, PEI Shaotong, WU Jianhua, et al. Deep learning based target detection method for abnormal hot spots infrared images of trans-mission and transformation equipment[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2019, 13(2): 27-33. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NFDW201902006.htm [8] REN Shaoqing, HE Kaiming, Girshick R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[C]// Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada, 2015: 91-99. [9] Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLOv3: An incremental improvement[J/OL]. [2018-04-08]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.02767. [10] LIU W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, et al. SSD: single shot multibox detec-tor[C]// Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, 2016: 21-37 [11] 李文璞, 谢可, 廖逍, 等. 基于Faster RCNN变电设备红外图像缺陷识别方法[J]. 南方电网技术, 2019, 13(12): 79-84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NFDW201912012.htmLI Wenpu, XIE Ke, LIAO Xiao, et al. Intelligent diagnosis method of infrared image for transformer equipment based on improved faster RCNN[J]. Southern Power System Technology, 2019, 13(12): 79-84. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NFDW201912012.htm [12] 王永平, 张红民, 彭闯, 等. 基于YOLO v3的高压开关设备异常发热点目标检测方法[J]. 红外技术, 2020, 42(10): 983-987. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/hwjs202010011WANG Yongping, ZHANG Hongmin, PENG Chuang, et al. The Target detection method for abnormal heating point of high-voltage switchgear based on YOLO v3[J]. Infrared Technology, 2020, 42(10): 983-987. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/hwjs202010011 [13] 梁杰, 李磊, 周红丽. 基于改进SSD的舰船目标精细化检测方法[J]. 导航定位与授时, 2019, 6(5): 43-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DWSS201905009.htmLIANG Jie, LI Lei, ZHOU Hongli. A ship target refinement detection method based on improved SSD[J]. Navigation Positioning & Timing, 2019, 6(5): 43-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DWSS201905009.htm [14] LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]// Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2017: 2999-3007. [15] Bochkovskiy A, WANG C Y, LIAO H Y M. YOLOv4: optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[J/OL]. Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020, https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.10934. [16] Misra D. Mish: a self regularized non-monotonic neural activation func-tion[J/OL]. Computer Science, 2019, https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.08681. [17] LIU Shu, QI Lu, QIN Haifang, et al. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018: 8759-8768. [18] LIN T Y, Dollár P, Girshick R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017: 2117-2125. [19] Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2014, 39(4): 640-651. http://www.open-open.com/misc/goto?guid=4959637963303133294 [20] NAIR V, HINTON G E. Rectified linear units improve restricted boltz-mann machines[C]//Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Machine Learning(ICML-10), 2010: 807-814. [21] WEN Long, GAO Liang, LI Xinyu. A new deep transfer learning based on sparse auto-encoder for fault diagnosis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2019, 49(1): 136-144. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2017.2754287 -





 下载:
下载: