Indoor Human Fall Detection Method Based on Infrared Images and Back-Projection Algorithm
-
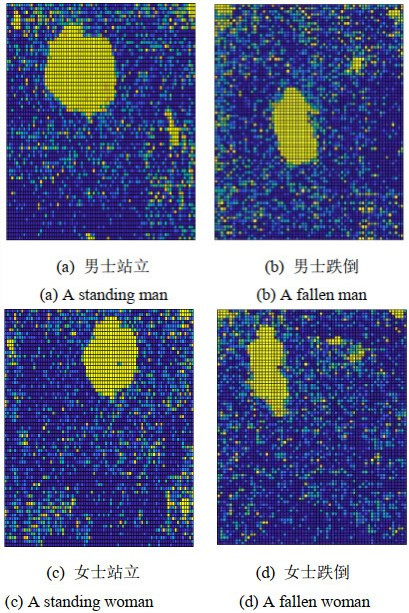
摘要: 研究表明跌倒是我国老年人伤害的主要原因,缩短跌倒到救治的时间能降低跌倒造成的伤害。为此,室内老年人跌倒检测需求逐年增加。红外传感器具有受光照影响小,保护隐私等优点,越来越广泛地应用于室内人体跌倒检测中。然而,由于红外图像存在分辨率低、信噪比差等缺陷,导致传统方法的检测精度较低。针对这个问题,本文提出一种基于逆向投影算法的室内人体跌倒检测方法。首先,通过人体温度计算出人体与传感器之间的距离;其次,结合图像信息,逆推出人体在真实世界的高度;最后,对获取的人体真实高度数据进行平滑处理,并根据其变化情况进行跌倒检测。实验结果表明,本文所提方法的检测准确率达到98.57%,优于传统非逆向投影方法,其性能完全可以应用于实际检测中。Abstract: Falls are reported to be a major cause of injury in China's elderly population. Shortening the time between the fall and subsequent treatment can reduce injuries caused by falls; therefore, the demand for indoor fall detection is increasing annually. Infrared image-based human fall detection methods are becoming increasingly popular owing to advantages such as being unaffected by light and non-intrusive. However, the traditional methods perform low accuracy because it is difficult to extract the features from the infrared videos at low resolution and high noise. Hence, this paper proposes an indoor human fall detection method based on a back-projection algorithm. First, the distance between the human body and the sensor is calculated using the human body temperature. Second, the height of the human body in the real world is reversely deduced using image information. Finally, the human body height data are smoothed and used for fall detection based on the height variation. The experimental results show that the detection accuracy of the proposed method is 98.57%, which is better than that of traditional projection methods. Therefore, it can be used for detection in real-life situations.
-
表 1 行走实验数据
Table 1. Walking experiment data
Route Human body height change by non-back projection algorithm Δw1/pixel Human body height change by back projection algorithm Δw2/mm Minimum Maximum Average value Minimum Maximum Average value 1 6 8 7 43 165 106 2 9 11 10 48 187 118 3 12 14 13 52 223 138 4 8 10 9 45 182 115 5 5 7 6 41 158 102 表 2 跌倒实验数据
Table 2. Fall experiment data
Route Human body height change by non-back projection algorithm Δf1/pixel Human body height change by back projection algorithm Δf1/mm Minimum Maximum Average value Minimum Maximum Average value 1 17 20 18 991 1475 1233 2 16 18 17 986 1465 1128 3 12 15 13 886 1174 1032 4 15 17 16 975 1253 1114 5 17 19 18 988 1484 1238 表 3 动作要求
Table 3. Action requirements
Fall action Fall down Non-fall action Walk back and forth Sit on the chair Standing Lying in bed Squat fast 表 4 检测情况混淆矩阵
Table 4. Confusion matrix of detection results
Real state Predictor state Fall Non-fallng Fall 79 1 Walk 0 40 Sit 0 40 Stand 0 40 Lay 0 40 Squat 3 37 表 5 本文方法与其他方法对比结果
Table 5. Results comparison
Method of this paper Reference [16] Sensitivity/(%) 98.75 91.25 Specificity/(%) 98.50 86.50 Accuracy/(%) 98.57 87.86 -
[1] 邓志锋, 闵卫东, 邹松. 一种基于CNN和人体椭圆轮廓运动特征的摔倒检测方法[J]. 图学学报, 2018, 39(6): 1042-1047. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCTX201806005.htmDENG Zhifeng, MIN Weidong, ZOU Song. A fall detection method based on CNN and motion features of human elliptical contour[J]. Journal of Graphics, 2018, 39(6): 1042-1047. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCTX201806005.htm [2] Giovanna S, Ivanoe D, Giuseppe D P. A supervised approach to automatically extract a set of rules to support fall detection in an mHealth system[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2015, 34: 205-216. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2015.04.060 [3] 胡双杰, 秦建邦, 郭薇. 基于特征自动提取的跌倒检测算法[J]. 传感技术学报, 2018, 31(12): 1842-1847. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CGJS201812011.htmHU Shuangjie, QIN Jianbang, GUO Wei. A fall detection algorithm with automatic feature extraction[J]. Chinese Journal of Sensors and Actuators, 2018, 31(12): 1842-1847. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CGJS201812011.htm [4] 郑毅, 李凤, 张丽, 等. 基于长短时记忆网络的人体姿态检测方法[J]. 计算机应用, 2018, 38(6): 1568-1574. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJY201806008.htmZHENG Yi, LI Feng, ZHANG Li, et al. Human posture detection method based on long short term memory network[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2018, 38(6): 1568-1574. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJY201806008.htm [5] Giuffrida D, Benetti G, Martini D D, et al. Fall detection with supervised machine learning using wearable sensor[C]//Proceedings of 17th International Conference on Industrial Informatics (INDIN) of IEEE, 2019: 253-259. [6] Kumar V S, Acharya K G, Sandeep B, et al. Wearable sensor-based human fall detection wireless system[J]. Wireless Communication Networks and Internet of Things, 2019, 493: 217-234 doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-8663-2_23 [7] Mehmood A, Nadeem A, Ashraf M, et al. A novel fall detection algorithm for elderly using Shimmer wearable sensors[J]. Health and Technology, 2019, 9(4): 631-646. doi: 10.1007/s12553-019-00298-4 [8] Kerdjidj O, Ramzan N, Ghanem K, et al. Fall detection and human activity classification using wearable sensors and compressed sensing[J]. Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing, 2020, 11(1): 349-361. doi: 10.1007/s12652-019-01214-4 [9] MIN W D, CUI H, RAO H, et al. Detection of human falls on furniture using scene analysis based on deep learning and activity characteristics[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6(99): 9324-9335. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000040195826110_71bc.html [10] KONG Y Q, HUANG J H, HUANG S S, et al. Learning spatiotemporal representations for human fall detection in surveillance video[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2019, 59: 215-230. doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2019.01.024 [11] QIU Z, LIANG X Q, CHEN Q Q, et al. Old man fall detection based on surveillance video object tracking[C]//Proceedings of 10th International Symposium on Parallel Architectures, Algorithms and Programming, 2019: 159-167. [12] FAN K B, WANG P, ZHUANG S. Human fall detection using slow feature analysis[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2019, 78: 9101-9128. doi: 10.1007/s11042-018-5638-9 [13] Shota M, Jihoon H and Tomoaki O. A fall detection system using low resolution infrared array sensor[C]//Proceedings of 25th International Symposium on Personal, Indoor and Mobile Radio Communications of IEEE, 2014: 2109-2113. [14] 杨任兵, 程文播, 钱庆, 等. 红外图像中基于多特征提取的跌倒检测算法研究[J]. 红外技术, 2017, 39(12): 1131-1138. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/hwjs201712011YANG Renbing, CHENG Wenbo, QIAN Qing, et al. Research on fall detection algorithm based on multi-feature extraction in infrared image[J]. Infrared Technology, 2017, 39(12): 1131-1138. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/hwjs201712011 [15] 王召军, 许志猛, 陈良琴. 基于红外阵列传感器的人体行为识别系统研究[J]. 红外技术, 2020, 42(3): 231-237. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/hwjs202003005WANG Zhaojun, XU Zhimeng, CHEN Liangqin. Human behavior recognition system based on infrared array sensors[J]. Infrared Technology, 2020, 42(3): 231-237. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/hwjs202003005 [16] LIANG Q S, YU L, ZHAI X P, et al. Activity recognition based on thermopile imaging array sensor[C]//Proceedings of International Conference on Electro/Information Technology (EIT) of IEEE, 2018: 770-773. -





 下载:
下载: