Thermal Infrared Target Tracking Algorithm Based on KL Divergence and Channel Selection
-
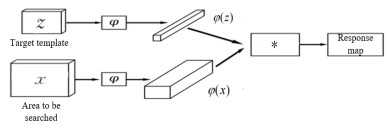
摘要: 为了解决单一跟踪器无法有效应对复杂背景及目标外观的显著变化,对于热红外目标跟踪准确度不高的问题,基于全卷积孪生网络提出了一种多响应图集成的跟踪算法用于热红外跟踪。首先,使用预训练的卷积神经网络来提取热红外目标的多个卷积层的特征并进行通道选择,在此基础上分别构建3个对应的跟踪器,每个跟踪器独立执行跟踪并返回一个响应图。然后,利用Kullback–Leibler(KL)散度对多个响应图进行优化集成,得到一个更强的响应图。最后利用集成后的响应图来确定目标位置。为了评估所提算法的性能,在当前最全面的热红外跟踪基准LSOTB-TIR(Large-Scale Thermal Infrared Object Tracking Benchmark)上进行了实验。实验结果表明,所提算法能够适应复杂多样的红外跟踪场景,综合性能超过了现有的红外跟踪算法。Abstract: To solve the problem that a single tracker cannot effectively deal with the complex background and significant changes in target appearance, leading to the problem of low accuracy of thermal infrared target tracking, a tracking algorithm based on a fully-convolutional Siamese network is proposed for thermal infrared tracking. First, a pre-trained convolution neural network is used to extract the features of multiple convolution layers of thermal infrared targets and select channels. On this basis, three corresponding trackers are constructed, and each tracker performs tracking independently and returns a response map. Then, the Kullback Leibler (KL) divergence is used to optimize and integrate multiple response maps to obtain a stronger response map. Finally, the integrated response map is used to determine the target location. To evaluate the performance of the proposed algorithm, experiments were conducted using the most comprehensive thermal infrared tracking benchmark, LSOTB-TIR. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm can adapt to complex and diverse infrared tracking scenes, and its comprehensive performance is better than that of existing infrared tracking algorithms.
-
表 1 LSOTB-TIR定义的的4种热红外挑战属性
Table 1. Four thermal infrared challenge attributes defined by LSOTB-TIR
Infrared challenge attributes Specific definitions Aspect Ratio
Variation(ARV)The aspect ratio of the target exceeds [0.5, 2] during tracking Intensity Variation
(Ⅳ)The intensity of the target changes during tracking Thermal Crossover
(TC)Two targets of the same intensity cross each other Distractor(DIS) There are interfering objects similar to the target around the target -
[1] LIU Q, LU X H, HE Z Y, et al. Deep convolutional neural networks for thermal infrared object tracking[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2017, 134: 189-198. [2] LI X, LIU Q, FAN Nana, et al. Hierarchical spatial-aware Siamese network for thermal infrared object tracking[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2019, 166: 71-81. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2018.12.011 [3] LIU Q, LI X, HE Z Y, et al. Learning deep multi-level similarity for thermal infrared object tracking[J]. IEEE Transaction on Multimedia, 2021, 23: 2124-2126. [4] LIU Q, LI X, HE Z Y, et al. Multi-task driven feature models for thermal infrared tracking[C]//Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2020: 11604-11611. [5] 张晋, 王元余, 林丹丹, 等. 基于相关滤波的红外目标跟踪抗遮挡处理[J]. 红外技术, 2022, 44(3): 277-285. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/98939f6c-0de2-4692-9c34-9eabbb68205eZHANG Jin, WANG Yuanyu, LIN Dandan, et al. Anti-occlusion process of infrared target tracking based on correlation filters[J]. Infrared Technology, 2022, 44(3): 277-285. http://hwjs.nvir.cn/article/id/98939f6c-0de2-4692-9c34-9eabbb68205e [6] 李畅, 杨德东, 宋鹏, 等. 基于全局感知孪生网络的红外目标跟踪[J]. 光学学报, 2021, 41(6): 0615002-1-0615002-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXXB202106019.htmLI Chang, YANG Dedong, SONG Pen, et al. Global-Aware siamese network for thermal infrared object tracking[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2021, 41(6): 0615002-1-0615002-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXXB202106019.htm [7] MA C, HUANG J B, YANG X, et al. Hierarchical convolutional features for visual racking[C]//IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2015: 3074-3082. [8] LI X, MA C, WU B Y, et al. Target-aware deep tracking[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2019: 1369-1378. [9] Bertinetto L, Valmadre J, Henriques J F, et al. Fully-convolutional siamese networks for object tracking[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision, 2016: 850-865. [10] Selvaraju R, Cogswell M, Das A, et al. Grad-cam: visual explanations from deep networks via gradient based localization[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2017: 618-626. [11] Nam H, Han B. Learning multi-domain convolutional neural networks for visual tracking[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016: 4293-4302. [12] Danelljan M, Bhat G, Khan F S, et al. Atom: Accurate tracking by overlap max-imization[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2019: 4660-4669. [13] Felsberg M, Kristan M, others. The thermal infrared visual object tracking VOT-TIR2016 challenge results[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, 2016: 824-849. [14] LIU Q, HE Z, LI X, et al. PTB-TIR: A thermal infrared pedestrian tracking bench-mark[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2019, 22(3): 666-675. [15] LIU Q, LI X, LI C L. LSOTB-TIR: A large-scale high-diversity thermal infrared object tracking benchmark[C/OL]//Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, 2020, https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.00836. -





 下载:
下载: