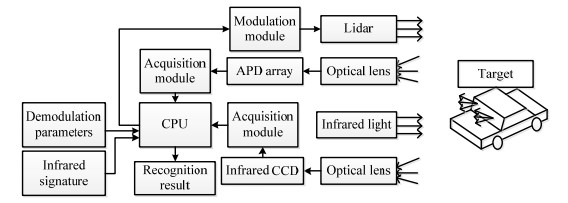
Research on 3D Target Recognition Algorithm Based on Infrared Features
-
摘要: 基于三维特征的目标识别存在相似点云域容易误判、总数据运算量大等问题,而造成目标检出率低和误判率高。为了提高目标识别准确度与速度,提出了基于红外特征的三维目标识别算法。系统同时获取目标区域的二维红外图像与三维点云数据,利用目标红外特性的显著特征获得目标的投影范围,并计算系统与目标的位姿关系。根据红外特征映射关系计算点云数据中目标的限定范围,由此大幅缩减需要匹配计算的点云总量。在相同背景条件下对同一目标车辆进行测试,记录分析了3种不同测试角度条件下的识别数据。结果显示,传统点云识别算法的目标检出率均值为93.4%,误判率均值为19.5%,收敛耗时4.77 s。本算法的目标检出率均值为98.7%,误判率均值为1.5%,收敛耗时1.23 s。由此可见,基于红外特征的目标识别算法的检出率和误判率都更有优势,且处理速度更快。Abstract: Target recognition based on 3D features has problems, such as easy misjudgment in similar point cloud domains and large amounts of total data computation, which results in a low target detection rate and high misjudgment rate. To improve the accuracy and speed of target recognition, a three-dimensional target recognition algorithm based on infrared features was proposed. The system simultaneously obtains the 2D infrared image and 3D point cloud data of the target area, obtains the projection range of the target using the salient features of the target's infrared characteristics, and calculates the pose relationship between the system and the target. The limited range of the target in the point cloud data is calculated according to the infrared feature mapping relationship, thereby significantly reducing the total number of point clouds that need to be matched and calculated. In the experiment, the same target vehicle was tested under the same background conditions, and the recognition data for three different test angles were recorded and analyzed. The obtained results indicated that the average target detection rate of the conventional point cloud recognition algorithm, average false positive rate, and convergence time were 93.4%, 19.5%, and 4.77 s, respectively. In addition, the average target detection rate of this algorithm, average false positive rate, and convergence time were 98.7%, 1.5%, and 1.23 s, respectively. It can be inferred that the detection and misjudgment rates of the target recognition algorithm based on infrared features are more advantageous, and the processing speed is faster.
-
Key words:
- target recognition /
- infrared features /
- data fusion /
- limited range
-
表 1 识别结果对比数据
Table 1. Identification results comparison
Comparison
groupG1 G2 G3 Pd/% Pf/% Pd/% Pf/% Pd/% Pf/% DMM 99.4 2.2 94.2 2.5 93.6 2.7 EB 96.2 17.5 90.4 24.6 93.5 16.4 SV 91.7 5.2 97.9 4.9 98.2 5.4 IFTR 99.3 1.6 98.2 1.7 98.7 1.3 -
[1] REN S, HE K, Girshick R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Real-time target detection in regional planning Network[J]. IEEE Pair Model Analysis and Machinery Information, 2017, 39(6): 1137-1149. [2] GUO Y L, Sohel F, Bennamoun M, et al. A novel local surface feature for 3D object recognition under clutter and occlusion[J]. Information Sciences, 2015, 293: 196-213. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2014.09.015 [3] 王果, 王成, 张振鑫, 等. 利用车载激光点云的分车带识别及单木分割方法[J]. 激光与红外, 2020, 50(11): 1333-1337. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2020.11.008WANG Guo, WANG Cheng, ZHANG Zhenxin, et al. Single tree segmentation method of urban distributing belt based on vehicle-borne laser point cloud data[J]. Laser & Infrared, 2020, 50(11): 1333-1337. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5078.2020.11.008 [4] 胡海瑛, 惠振阳, 李娜. 基于多基元特征向量融合的机载LiDAR点云分类[J]. 中国激光, 2020, 47(8): 229-239. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJZZ202008029.htmHU Haiying, HUI Zhenyang, LI Na. Airborne LiDAR point cloud classification based on multiple-entity eigenvector fusion[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020, 47(8): 229-239. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JJZZ202008029.htm [5] Sochor J, Spaňhel J, Herout A. Boxcars: improving fine-grained recognition of vehicles using 3-d bounding boxes in traffic surveillance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2018, 20(1): 97-108. [6] Sochor J, Herout A, Havel J. BoxCars: 3D boxes as CNN input for improved fine-grained vehicle recognition[C]// IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2016: 3006-3015. [7] Dubská M, Herout A, Juránek R, et al. Fully automatic roadside camera calibration for traffic surveillance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2014, 16(3): 1162-1171. [8] Dubská M, Herout A, Sochor J. Automatic camera calibration for traffic understanding[C]// Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference(BMVC), 2014: 1-12. [9] GISEOK K, JAE- SOO C. Vision- Based vehicle detection and inter- vehicle distance estimation for driver alarm system[J]. Optical Review, 2012, 25(6): 388- 393. [10] 薛培林, 吴愿, 殷国栋, 等. 基于信息融合的城市自主车辆实时目标识别[J]. 机械工程学报, 2020, 56(12): 165-173. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXXB202012021.htmXUE Peilin, WU Yuan, YIN Guodong, et al. Real-time target recognition for urban autonomous vehicles based on information fusion[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56(12): 165-173. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXXB202012021.htm [11] 仝选悦, 吴冉, 杨新锋, 等. 红外与激光融合目标识别方法[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2018, 47(5): 158-165. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYJ201805025.htmTONG Xuanyue, WU Ran, YANG Xinfeng, et al. Fusion target recognition method of infrared and laser[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2018, 47(5): 158-165. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYJ201805025.htm [12] YAN Y, MAO Y, LI B. Second: sparsely embedded convolutional detection[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(10): 3337/1-17. -





 下载:
下载: