Civil Drone Detection Based on Deep Convolutional Neural Networks: a Survey
-
摘要: 小型民用无人机预警探测是公共安全领域的热点问题,也是视觉目标检测领域的研究难点。采用手工特征的经典目标检测方法在语义信息的提取和表征方面存在局限性,因此基于深度卷积神经网络的目标检测方法在近年已成为业内主流技术手段。围绕基于深度卷积神经网络的小型民用无人机检测技术发展现状,本文介绍了计算机视觉目标检测领域中基于深度卷积神经网络的双阶段算法和单阶段检测算法,针对小型无人机检测任务分别总结了面向静态图像和视频数据的无人机目标检测方法,进而探讨了无人机视觉检测中亟待解决的瓶颈性问题,最后对该领域研究的未来发展趋势进行了讨论和展望。Abstract: Vision-based early warnings against civil drones are crucial in the field of public security and are also challenging in visual object detection. Because conventional target detection methods built on handcrafted features are limited in terms of high-level semantic feature representations, methods based on deep convolutional neural networks (DCNNs) have facilitated the main trend in target detection over the past several years. Focusing on the development of civil drone-detection technology based on DCNNs, this paper introduces the advancements in DCNN-based object detection algorithms, including two-stage and one-stage algorithms. Subsequently, existing drone-detection methods developed for still images and videos are summarized separately. In particular, motion information extraction approaches to drone detection are investigated. Furthermore, the main bottlenecks in drone detection are discussed. Finally, potentially promising solutions and future development directions in the drone-detection field are presented.
-
图 11 无人机检测的难点和瓶颈性问题示例图像
注:第一行:目标小尺寸且缺乏外观信息[47, 55, 62];第二行:背景复杂多样[47-48];第三行:目标尺度异质性问题[53]
Figure 11. Image examples to demonstrate difficulties and bottlenecks in drone detection
Note: Row 1: Targets that are small and weak in appearance information[47, 55, 62]; Row 2: Targets in complex and diverse backgrounds[47-48]; Row 3: Targets that have heterogeneous scales [53])
表 1 视觉目标检测领域代表性算法归纳
Table 1. Summary of representative algorithms in the visual object detection field
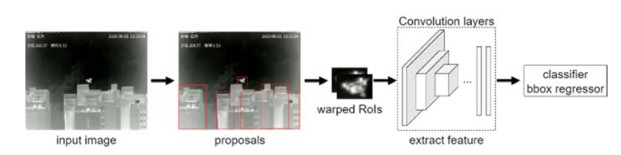
Model Year Backbone Characteristics Two-stage R-CNN[15] 2014 AlexNet[16] Integrate CNN classification and proposal generation; need multi-stage training; time-consuming and space-consuming. SPPNet[17] 2015 ZFNet[19] Introduce the spatial pyramid pooling (SPP) into CNNs. Fast R-CNN[18] 2015 AlexNet、VGG16[20] Introduce regions of interest (RoIs) pooling layer; difficult to achieve real-time detection. Faster R-CNN[21] 2015 ZFNet、VGG Introducing region proposal network (RPN) to generate high-quality proposals; complex training procedures and poor real-time performance. ION[22] 2016 IRNN[23] Improve performance on small object detection by employing context and multi-scale skip pooling. R-FCN[24] 2016 ResNet101[25] Apply the fully convolutional neural network (FCN) to Faster R-CNN to share the computation of the entire network, improving detection speed. FPN[26] 2017 ResNet101 Propose a feature pyramid model to handle scale variation issues in object detection. Mask R-CNN[27] 2018 ResNeXt[28]、FPN Add parallel branches to extend Faster R-CNN to achieve object segmentation, which cannot be detected in real-time. PANet[29] 2018 FPN Bottom-up enhancement path and adaptive feature pooling are introduced. TridentNet[30] 2019 ResNet101 Elucidating the effect of receptive field on objects of different sizes in object detection tasks. CPNDet[31] 2020 Hourglass104[32] Generate anchor-free proposals; two-step classification for filtering proposals. One-stage YOLOv1[33] 2016 GoogLeNet[34] End-to-end real-time detection does not produce proposals but has poor detection accuracy and difficult to detect small cluster objects. SSD[35] 2016 VGG16 Combined with CNN and YOLOv1 model, SSD detects on multi-scale layers, which is faster and more accurate than YOLOv1. YOLOv2[36] 2016 DarkNet19 Propose DarkNet19 to achieve high precision and high speed, but it is still difficult to detect small objects. RetinaNet[37] 2018 ResNeXt101+FPN Proposed focal loss function to solve the extreme foreground-background class imbalance problem. YOLOv3[38] 2018 DarkNet53 Improving performance on small objects by multi-scale detection. STDN[39] 2018 DenseNet169[40] Resolve multi-scale objects by employing a scale transformation module. CornerNet[41] 2019 Hourglass104 Regard the object detection task as a key point detection problem,by inferencing two key points (upper left and lower right corners) as the prediction box. YOLOv4[42] 2020 CSPDarknet53 Faster and more accurate object detection in terms of mosaic data augmentation and self-adversarial training tips. DETR[43] 2020 ResNet101 Introduce transformer structure to object detection field, but the performance for small targets needs to be improved. -
[1] WANG J, LIU Y, SONG H. Counter-unmanned aircraft system (s)(C-UAS): State of the art, challenges, and future trends[J]. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 2021, 36(3): 4-29. [2] LI Xiaoping, LEI Songze, ZHANG Boxing, et al. Fast aerial UAV detection using improved inter-frame difference and SVM[C]//Journal of Physics: Conference Series. IOP Publishing, 2019, 1187(3): 032082. [3] WANG C, WANG T, WANG E, et al. Flying small target detection for anti-UAV based on a Gaussian mixture model in a compressive sensing domain[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(9): 2168. doi: 10.3390/s19092168 [4] Seidaliyeva U, Akhmetov D, Ilipbayeva L, et al. Real-time and accurate drone detection in a video with a static background[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(14): 3856. doi: 10.3390/s20143856 [5] ZHAO W, CHEN X, CHENG J, et al. An application of scale-invariant feature transform in iris recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/ACIS 12th International Conference on Computer and Information Science, IEEE, 2013: 219-222. [6] SHU C, DING X, FANG C. Histogram of the oriented gradient for face recognition[J]. Tsinghua Science and Technology, 2011, 16(2): 216-224. doi: 10.1016/S1007-0214(11)70032-3 [7] SHEN Y K, CHIU C T. Local binary pattern orientation based face recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, IEEE, 2015: 1091-1095. [8] YUAN Xiaofang, WANG Yaonan. Parameter selection of support vector machine for function approximation based on chaos optimization[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2008, 19(1): 191-197. doi: 10.1016/S1004-4132(08)60066-3 [9] FENG J, WANG L, Sugiyama M, et al. Boosting and margin theory[J]. Frontiers of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 2012, 7(1): 127-133. doi: 10.1007/s11460-012-0188-9 [10] WEI L, HONG Z, Gui-Jin H. NMS-based blurred image sub-pixel registration[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Image Analysis and Signal Processing. IEEE, 2011: 98-101. [11] 罗会兰, 陈鸿坤. 基于深度学习的目标检测研究综述[J]. 电子学报, 2020, 48(6): 1230-1239. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.06.026LUO Huilan, CHEN Hongkun. Survey of object detection based on deep learning[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2020, 48(6): 1230-1239. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.06.026 [12] Bosquet B, Mucientes M, Brea V M. STDNet: exploiting high resolution feature maps for small object detection[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 91: 103615. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2020.103615 [13] SUN H, YANG J, SHEN J, et al. TIB-Net: Drone detection network with tiny iterative backbone[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 130697-130707. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3009518 [14] LIU L, OUYANG W, WANG X, et al. Deep learning for generic object detection: a survey[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2020, 128(2): 261-318. doi: 10.1007/s11263-019-01247-4 [15] Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, et al. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2014: 580-587. [16] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2012, 25: 1097-1105. [17] HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1904-1916. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2389824 [18] Girshick R. Fast R-CNN[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2015: 1440-1448. [19] Zeiler M D, Fergus R. Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, 2014: 818-833. [20] Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[J/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1409.1556, 2014. [21] REN S, HE K, Girshick R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 39(6): 1137-1149. [22] Bell S, Lawrence Zitnick C, Bala K, et al. Inside-outside net: detecting objects in context with skip pooling and recurrent neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016: 2874-2883. [23] LE Q V, Jaitly N, Hinton G E. A simple way to initialize recurrent networks of rectified linear units[J/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1504.00941, 2015. [24] DAI J, LI Y, HE K, et al. R-FCN: Object detection via region-based fully convolutional networks[J/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1605.06409, 2016. [25] HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016: 770-778. [26] LIN T Y, Dollár P, Girshick R, et al. Feature pyramid networks for object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017: 2117-2125. [27] He K, Gkioxari G, Dollár P, et al. Mask R-CNN[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2017: 2961-2969. [28] XIE S, Girshick R, Dollár P, et al. Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017: 1492-1500. [29] LIU S, QI L, QIN H, et al. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018: 8759-8768. [30] LI Y, CHEN Y, WANG N, et al. Scale-aware trident networks for object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2019: 6054-6063. [31] DUAN K, XIE L, QI H, et al. Corner proposal network for anchor-free, two-stage object detection[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, Cham, 2020: 399-416. [32] Newell A, YANG K, DENG J. Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, 2016: 483-499. [33] Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, et al. You only look once: unified, real-time object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016: 779-788. [34] Szegedy C, LIU W, JIA Y, et al. Going deeper with convolutions [C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2015: 1-9. [35] LIU W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, et al. SSD: single shot multibox detector[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, 2016: 21-37. [36] Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger[C]// Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017: 7263-7271. [37] LIN T Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2017: 2980-2988. [38] Redmon J, Farhadi A. YOLOv3: An incremental improvement[J/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1804.02767, 2018. [39] ZHOU P, NI B, GENG C, et al. Scale-transferrable object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018: 528-537. [40] HUANG G, LIU Z, Van Der Maaten L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017: 4700-4708. [41] LAW H, DENG J. Cornernet: Detecting objects as paired keypoints[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, 2018: 734-750. [42] Bochkovskiy A, WANG C Y, LIAO H Y M. YOLOv4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection[J/OL]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2004.10934, 2020. [43] Carion N, Massa F, Synnaeve G, et al. End-to-end object detection with transformers[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision. Springer, Cham, 2020: 213-229. [44] JIANG N, WANG K, PENG X, et al. Anti-UAV: A large multi-modal benchmark for UAV tracking[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2101.08466, 2021. [45] ZHAO J, WANG G, LI J, et al. The 2nd Anti-UAV Workshop & Challenge: Methods and results[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2108.09909, 2021. [46] Coluccia A, Fascista A, Schumann A, et al. Drone-vs-Bird detection challenge at IEEE AVSS2019[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance. IEEE, 2019: 1-7. [47] WU M, XIE W, SHI X, et al. Real-time drone detection using deep learning approach[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning and Intelligent Communications, 2018: 22-32. [48] ZHAO W, ZHANG Q, LI H, et al. Low-altitude UAV detection method based on one-staged detection framework[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Computer Technology, Information Science and Communications IEEE, 2020: 112-117. [49] Magoulianitis V, Ataloglou D, Dimou A, et al. Does deep super-resolution enhance UAV detection?[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance IEEE, 2019: 1-6. [50] Kim J, Kwon Lee J, Mu Lee K. Accurate image super-resolution using very deep convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016: 1646-1654. [51] Craye C, Ardjoune S. Spatio-temporal semantic segmentation for drone detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance. IEEE, 2019: 1-5. [52] Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-assisted Intervention, 2015: 234-241. [53] Aker C. End-to-end Networks for Detection and Tracking of Micro Unmanned Aerial Vehicles[D]. Ankara, Turkey: Middle East Technical University, 2018. [54] 张锡联, 段海滨. 一种基于Gabor深度学习的无人机目标检测算法[J]. 空间控制技术与应用, 2019, 45(4): 38-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1579.2019.04.005ZHANG X, DUAN H. A target detection algorithm for UAV based on Gabor deep learning[J]. Aerospace Control and Application, 2019, 45(4): 38-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1579.2019.04.005 [55] 马旗, 朱斌, 张宏伟, 等. 基于优化YOLOv3的低空无人机检测识别方法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2019, 56(20): 279-286. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGDJ201920027.htmMA Q, ZHU B, ZHANG H, et al. Low-Altitude UAV detection and recognition method based on optimized YOLOv3[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2019, 56(20): 279-286. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGDJ201920027.htm [56] Cohen M B, Elder S, Musco C, et al. Dimensionality reduction for k-means clustering and low rank approximation[C]//Proceedings of the Forty-Seventh Annual ACM Symposium on Theory of Computing, 2015: 163-172. [57] Saqib M, Khan S D, Sharma N, et al. A study on detecting drones using deep convolutional neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance. IEEE, 2017: 1-5. [58] Nalamati M, Kapoor A, Saqib M, et al. Drone detection in long-range surveillance videos[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance. IEEE, 2019: 1-6. [59] Aker C, Kalkan S. Using deep networks for drone detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance. IEEE, 2017: 1-6. [60] 张汝榛, 张建林, 祁小平, 等. 复杂场景下的红外目标检测[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(10): 128-137. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDGC202010010.htmZHANG R, ZHANG J, QI X, et al. Infrared target detection and recognition in complex scene[J]. Opto-Eletronic Engineering, 2020, 47(10): 128-137. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDGC202010010.htm [61] 刘俊明, 孟卫华. 融合全卷积神经网络和视觉显著性的红外小目标检测[J]. 光子学报, 2020, 49(7): 46-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZXB202007006.htmLIU J, MENG W. Infrared small target detection based on fully convolutional neural network and visual saliency[J]. Acta Photonica Sincia, 2020, 49(7): 46-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GZXB202007006.htm [62] 马旗, 朱斌, 程正东, 等. 基于双通道的快速低空无人机检测识别方法[J]. 光学学报, 2019, 39(12): 105-115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXXB201912012.htmMA Q, ZHU B, CHENG Z, et al. Detection and recognition method of fast low-altitude unmanned aerial vehicle based on dual channel[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2019, 39(12): 105-115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXXB201912012.htm [63] CUI Z, YANG J, JIANG S, et al. An infrared small target detection algorithm based on high-speed local contrast method[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2016, 76: 474-481. [64] ZHAO Y, PAN H, DU C, et al. Bilateral two-dimensional least mean square filter for infrared small target detection[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2014, 65: 17-23. [65] Lange H. Real-time contrasted target detection for IR imagery based on a multiscale top hat filter[C]//Signal Processing, Sensor Fusion, and Target Recognition VIII. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 1999, 3720: 214-226. [66] BAI X, ZHOU F, ZHANG S, et al. Top-Hat by the reconstruction operation-based infrared small target detection[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference in Electrics, Communication and Automatic Control Proceedings, 2012: 867-873. [67] 王刚, 陈永光, 杨锁昌, 等. 采用图像块对比特性的红外弱小目标检测[J]. 光学精密工程, 2015, 23(5): 1424-1433. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXJM201505029.htmWANG G, CHEN Y, YANG S, et al. Infrared dim and small target detection using image block contrast characteristics[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2015, 23(5): 1424-1433. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXJM201505029.htm [68] 吴双忱, 左峥嵘. 基于深度卷积神经网络的红外小目标检测[J]. 红外与毫米波学报, 2019, 38(3): 371-380. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYH201903019.htmWU S, ZUO Z. Infrared small target detection based on deep convolutional neural network[J]. Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2019, 38(3): 371-380. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWYH201903019.htm [69] 李俊宏, 张萍, 王晓玮, 等. 红外弱小目标检测算法综述[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2020, 25(9): 1739-1753. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTB202009002.htmLI J, ZHANG P, WANG X, et al. A survey of infrared dim target detection algorithms[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2020, 25(9): 1739-1753. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGTB202009002.htm [70] Horn B K P, Schunck B G. Determining optical flow[C]//Techniques and Applications of Image Understanding. International Society for Optics and Photonics, 1981, 281: 319-331. [71] Lucas B D, Kanade T. An iterative image registration technique with an application to stereo vision[C]//Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 1981: 674-679. [72] Dosovitskiy A, Fischer P, Ilg E, et al. Flownet: Learning optical flow with convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2015: 2758-2766. [73] Ilg E, Mayer N, Saikia T, et al. FlowNet 2.0: Evolution of optical flow estimation with deep networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017: 2462-2470. [74] Teed Z, Deng J. Raft: Recurrent all-pairs field transforms for optical flow[C]// Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, 2020: 402-419. [75] ZHU X, XIONG Y, DAI J, et al. Deep feature flow for video recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017: 2349-2358. [76] ZHU X, WANG Y, DAI J, et al. Flow-guided feature aggregation for video object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2017: 408-417. [77] Rozantsev A, Lepetit V, Fua P. Flying objects detection from a single moving camera[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2015: 4128-4136. [78] Bertinetto L, Valmadre J, Henriques J F, et al. Fully-convolutional siamese networks for object tracking[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, 2016: 850-865. [79] Stewart R, Andriluka M, Ng A Y. End-to-end people detection in crowded scenes[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016: 2325-2333. [80] ZHAO B, ZHAO B, TANG L, et al. Deep spatial-temporal joint feature representation for video object detection[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(3): 774. [81] 刘宜成, 廖鹭川, 张劲, 等. 基于轨迹和形态识别的无人机检测方法[J]. 计算机工程, 2020, 46(12): 283-289. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJC202012038.htmLIU Y, LIAO L, ZHANG J, et al. UAV detection method based on trajectory and shape recognition[J]. Computer Engineering, 2018, 18(3): 774. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSJC202012038.htm [82] 吴飞, 阳春华, 兰旭光, 等. 人工智能的回顾与展望[J]. 中国科学基金, 2018, 32(3): 243-250. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKJJ201803002.htmWU F, YANG C H, LAN X, et al. Retrospect and prospect of artificial intelligence[J]. Bulletin of National Natural Science Foundation of China, 2018, 32(3): 243-250. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZKJJ201803002.htm -





 下载:
下载: