Remote Raman Spectroscopy in Natural Environments
-
摘要: 拉曼光谱遥测技术主要用于在安全距离之下对一些危险品、违禁品、变质食品等进行现场快速检测。早期拉曼光谱遥测技术大多采用可见光或近红外激光拉曼光谱技术,为了避免环境光影响,常在实验室或夜间进行。近年来,因日盲紫外激光的拉曼光谱检测具有共振效应强、不受环境光干扰、人眼相对安全等诸多特性逐渐开始被广泛应用。本文在分析自然环境下远程拉曼光谱遥测技术基础原理上,归纳了国内外可见光或近红外激光拉曼光谱遥测技术和国内外紫外激光拉曼光谱遥测技术的研究进展和现状,分析了远程紫外激光拉曼光谱应用在反恐、禁毒和食品安全等领域的优势,最后总结了自然环境下拉曼光谱遥测技术的研究难点和发展趋势。Abstract: Remote Raman spectroscopy is used primarily for on-site rapid detection of dangerous goods, contraband, and deteriorated food from a safe distance. Early applications of remote Raman spectroscopy used visible or near-infrared lasers to excite the Raman spectrum. Such experiments were often conducted in the laboratory or at night, to avoid the influence of environmental light. Recently, solar-blind ultraviolet Raman spectroscopy has been widely used because of its advantages compared to visible or near-infrared approaches. Their advantages include a strong resonance effect, lack of interference from ambient light, and relative safety for the human eye. This study reviews the development of remote visible or near-infrared and ultraviolet Raman spectroscopy based on the analysis of the basic principles in natural environments. The advantages of remote ultraviolet Raman spectroscopy in the fields of anti-terrorism, drug control, and food safety are highlighted. The current challenges and development trends in remote Raman spectroscopy in natural environments are summarized.
-
Key words:
- solar-blind ultraviolet /
- Raman spectroscopy /
- remote detection /
- natural environment
-
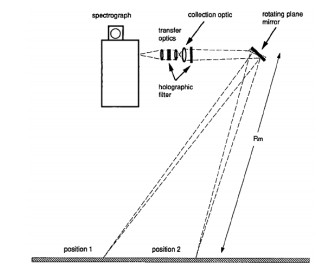
图 11 用于远程化学分析的双组分系统,在目标附近使用了紧凑远程Raman+LIBS系统和远距聚焦透镜(L)。(a)用于分析垂直表面目标和(b)结合折叠镜(M) 用于分析地面化学品目标
Figure 11. A two-component system for remote chemical analysis, which uses a compact remote Raman+LIBS system and a remote focusing lens (L) near the target. (a) For analyzing vertical surface targets and (b) combined with folding mirror (M) for analyzing ground chemical targets
-
[1] Guozhen W. Raman Spectroscopy: An Intensity Approach[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016. [2] Colthup N. Introduction to Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2012. [3] 肖新月, 余振喜. 化学药品对照品图谱集: 红外、拉曼、紫外光谱[M]. 北京: 中国医学科技出版社, 2014.XIAO Xinyue, YU Zhenxi. Atlas of Chemical Reference Substances: Infrared, Raman and UV Spectra[M]. Beijing: The Medicine Science and Technology Press of China, 2014. [4] Okuno M, Hamaguchi H. Multifocus confocal Raman microspectroscopy for fast multimode vibrational imaging of living cells[J]. Optics Letters, 2012, 35(24): 4096-4098. [5] Schlücker S, Kiefer W. Surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy: analytical, biophysical and life science applications[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2011, 401(8): 2329-2330. doi: 10.1007/s00216-011-5321-8 [6] Cooney J. Satellite observations using Raman component of laser backscatter[C]//Proceedings of the Symposium on Electromagnetic Sensing of the Earth from Satellites, New York: Polytechnic Institute of Brooklyn Press, 1967, 1-10. [7] Leonared D A. Observation of Raman scattering from the atmosphere using a pulsed nitrogen ultraviolet laser[J]. Nature, 1967, 216(5111): 142-143. doi: 10.1038/216142a0 [8] Hirschfeld T. Range independence of signal in variable focus remote Raman spectrometry[J]. Applied Optics, 1974, 13(6): 1435-1437. doi: 10.1364/AO.13.001435 [9] Raymond M. Laser Remote Sensing: Fundamentals and Applications[M]. New York: John Wiley & Sons, 1984. [10] Wu M, Ray M, Fung K H, et al. Stand-off detection of chemicals by UV Raman spectroscopy[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2000, 54(6): 800-806. doi: 10.1366/0003702001950418 [11] Ray M D, Sedlacek A J, WU M. Ultraviolet mini-Raman lidar for stand-off, in situ identification of chemical surface contaminants[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2000, 71(9): 3485-3489. doi: 10.1063/1.1288255 [12] Wallin S, Pettersson A, Östmark H, et al. Laser-based stand-off detection of explosives: a critical review[J]. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 2009, 395(2): 259-274. doi: 10.1007/s00216-009-2844-3 [13] Angel S M, Kulp T J, Vess T M. Remote-Raman spectroscopy at intermediate ranges using low-power cw lasers[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 1992, 46(7): 1085-1091. doi: 10.1366/0003702924124132 [14] Sharma S K, Angel S M, Ghosh M, et al. Remote pulsed laser Raman spectroscopy system for mineral analysis on planetary surfaces to 66 meters[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2002, 56(6): 699-705. doi: 10.1366/000370202760077630 [15] Sharma S K, Lucey P G, Ghosh M, et al. Stand-off Raman spectroscopic detection of minerals on planetary surfaces[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2003, 59(10): 2391-2407. doi: 10.1016/S1386-1425(03)00080-5 [16] Misra A K, Sharma S K, Chio C H, et al. Pulsed remote Raman system for daytime measurements of mineral spectra[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2005, 61(10): 2281-2287. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2005.02.027 [17] Misra A K, Sharma S K, Lucey P G. Remote Raman spectroscopic detection of minerals and organics under illuminated conditions from a distance of 10 m using a single 532 nm laser pulse[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2006, 60(2): 223-228. doi: 10.1366/000370206776023412 [18] Carter J C, Scaffidi J, Burnett S, et al. Stand-off Raman detection using dispersive and tunable filter based systems[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2005, 61(10): 2288-2298. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2005.02.028 [19] Carter J C, Angel S M, Lawrence-Snyder M, et al. Stand-off detection of high explosive materials at 50 meters in ambient light conditions using a small Raman instrument[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2005, 59(6): 769-775. doi: 10.1366/0003702054280612 [20] Pettersson A, Johansson I, Wallin S, et al. Near Real-Time stand-off detection of explosives in a realistic outdoor environment at 55 m distance[J]. Propellants Explosives Pyrotechnics, 2009, 34(4): 297-306. doi: 10.1002/prep.200800055 [21] Fleger Y, Nagli L, Gaft M, et al. Narrow gated Raman and luminescence of explosives[J]. Journal of Luminescence, 2009, 129(9): 979-983. doi: 10.1016/j.jlumin.2009.04.008 [22] Sharma S K, Misra A K, Clegg S M, et al. Time-resolved remote Raman study of minerals under supercritical CO2 and high temperatures relevant to Venus exploration[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2010, 368(1922): 3167-3191. doi: 10.1098/rsta.2010.0034 [23] Ramirez-Cedeno M L, Ortiz-Rivera W, Pacheco-Londono L C, et al. Remote detection of hazardous liquids concealed in glass and plastic containers[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2010, 10(3): 693-698. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2009.2036373 [24] Pettersson A, Wallin S, Östmark H, et al. Explosives stand-off detection using Raman spectrpscopy: from bulk towards trace detection[C]//Detection and Sensing of Mines, Explosive Objects, and Obscured Targets XV, 2010: 7664: 76641K. [25] Rull F, Vegas A, Sansano A, et al. Analysis of arctic ices by remote Raman spectroscopy[J]. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2011, 80(1): 148-155. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2011.04.007 [26] Chung J H, Cho S G. Nanosecond gated Raman spectroscopy for standoff detection of hazardous materials[J]. Bulletin- Korean Chemical Society, 2014, 35(12): 3547-3552. doi: 10.5012/bkcs.2014.35.12.3547 [27] Gulati K K, Gambhir V, Reddy M N. Detection of nitro-aromatic compound in soil and sand using time gated Raman spectroscopy[J]. Defence Science Journal, 2017, 67(5): 588-591. doi: 10.14429/dsj.67.10290 [28] Guimbretière, G, Duraipandian S, Ricci T. Field remote stokes/anti-stokes Raman characterization of sulfur in hydrothermal vents[J]. Journal of Raman Spectroscopy, 2018, 49: 1385-1394. doi: 10.1002/jrs.5378 [29] Kubitza S, Schröder S, Rammelkamp K, et al. Evaluation of close-up remote cw-Raman spectroscopy for in-situ planetary exploration[C]//50th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, 2019, 2132: 2421-2425. [30] Misra A K, Acosta-Maeda T E, Porter J N, et al. A two components approach for long range remote Raman and laser-induced breakdown (LIBS) spectroscopy using low laser pulse energy[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2019, 73(3): 320-328. doi: 10.1177/0003702818812144 [31] Egan M J, Acosta-Maeda T E, Angel S M, et al. One-mirror, one-grating spatial heterodyne spectrometer for remote-sensing Raman spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Raman Spectroscopy, 2020, 51: 1794-1801. doi: 10.1002/jrs.5788 [32] Gasser C, González-Cabrera M, Ayora-Cañada M J, et al. Comparing mapping and direct hyperspectral imaging in stand-off Raman spectroscopy for remote material identification[J]. Journal of Raman Spectroscopy, 2019, 50: 1034-1043. doi: 10.1002/jrs.5607 [33] Misra A K, Acosta-Maeda T E, Porter J N, et al. Remote Raman detection of chemicals from 1752 m during afternoon daylight[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2019, 74(2): 233-240. [34] Sandford M W, Misra A K, Acosta-Maeda T E, et al. Detecting minerals and organics relevant to planetary exploration using a compact portable remote Raman system at 122 meters[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2021, 75(3): 299-306. doi: 10.1177/0003702820943669 [35] 刘鑫, 薛晨阳, 熊继军, 等. 微型远程拉曼在深空探测中应用的可行性研究[C]//工程科技Ⅱ辑, 2008: 187-191.LIU Xin, XUE Chenyang, XIONG Jijun, et al. Feasibility study of micro remote Raman system for deep space detection[C]//Engineering Technology Part Ⅱ, 2008: 187-191. [36] 郝凤龙, 姜玲玲, 于海辉, 等. 基于拉曼光谱技术的毒品检测仪器研究[J]. 国外电子测量技术, 2016, 35(12): 40-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8978.2016.12.010HAO F, JIANG L, YU H, et al. Research on drug detecting instrument based on raman spectroscopy[J]. Foreign Electronic Measurement Technology, 2016, 35(12): 40-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8978.2016.12.010 [37] 张丹. 用于火星表面物质探测的拉曼光谱技术研究[D]. 西安: 中科院研究生院西安光机所, 2015.ZHANG D. Study of Raman Spectrum Technique for Material Detection on Mars Surface[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2015. [38] 张莉, 郑海洋, 王颖萍, 等. 远距离探测拉曼光谱特性[J]. 物理学报, 2016, 65(5): 134-143. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WLXB201605018.htmZHANG L, ZHENG H Y, WANG Y P, et al. Remote Raman spectra characteristics[J]. Acta Phys. Sin, 2016, 65(5): 134-143. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WLXB201605018.htm [39] 胡广骁, 熊伟, 罗海燕, 等. 用于远程探测的空间外差拉曼光谱技术研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2016, 36(12): 3951-3957. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201612030.htmHU G X, XIONG W, LUO H Y, et al. The research of spatial heterodyne Raman spectroscopy with standoff detection[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2016, 36(12): 3951-3957. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUAN201612030.htm [40] 姚齐峰, 王帅, 娄小平, 等. 基于远程拉曼光谱的物质检测研究[J]. 工具技术, 2017, 51(9): 135-138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2017.09.034YAO Q F, WANG S, LOU X P, et al. Stand-off Raman spectrum detection for explosive materials[J]. Tool Engineering, 2017, 51(9): 135-138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7008.2017.09.034 [41] Mccain S T, Guenther B D, Brady D J, et al. Coded-aperture Raman imaging for standoff explosive detection[C]//Chemical, Biological, Radiological, Nuclear, and Explosives (CBRNE) Sensing XⅢ, 2012, 8358: 83580Q. [42] Chirico R, Almaviva S, Botti S, et al. Stand-off detection of traces of explosives and precursors on fabrics by UV Raman spectroscopy[C]// Optics and Photonics for Counterterrorism, Crime Fighting, and Defence Ⅷ, 2012, 8546: 8546: 283-287. [43] Fulton J. Remote detection of explosives using Raman spectroscopy[C]//Chemical, Biological, Radiological, Nuclear, and Explosives (CBRNE) Sensing XⅡ, 2011, 8018(1): 413-413. [44] Almaviva S, Angelni F, Chirico R, et al. Eye-safe UV Raman spectroscopy for remote detection of explosives and their precursors in fingerprint concentration[C]//Optics and Photonics for Counterterrorism, Crime Fighting, and Defence X; and Optical Materials and Biomaterials in Security and Defence Systems Technology XI, 2014, 9253: 925303. [45] Glimtoft M, Bââth P, Saari H, et al. Towards eye-safe standoff Raman imaging systems[C]//Detection and Sensing of Mines, Explosive Objects, and Obscured Targets XIX, 2014, 9072: 907210. [46] Carroll J A, Izake E L, Cletus B, et al. Eye-safe UV stand-off Raman spectroscopy for the ranged detection of explosives in the field[J]. Journal of Raman Spectroscopy, 2015, 46(3): 333-338. doi: 10.1002/jrs.4642 [47] Sharma S K, Ismail S, Angel S M, et al. Remote Raman and laser-induced fluorescence (RLIF) emission instrument for detection of mineral, organic, and biogenic materials on Mars to 100 meters radial distance[C]//Instruments, Science, and Methods for Geospace and Planetary Remote Sensing, 2004, 5660: 128-138. [48] Gaft M, Nagli L. UV gated Raman spectroscopy for standoff detection of explosives[J]. Optical Materials, 2008, 30(11): 1739-1746. doi: 10.1016/j.optmat.2007.11.013 [49] Yellampalle B, Lemoff B E. Raman albedo and deep-UV resonance Raman signatures of explosives[C]//Active and Passive Signatures IV, 2013, 8734: 87340G. [50] 中国国防科技信息中心. 美拟研发小型高效紫外激光器用于生化探测[N/OL]. [2014-03-06]. 中国新闻网, http://www.chinanews.com/mil/2014/03-06/5916245.Shtml.China Defense Science and Technology Information Center. U.S. intends to develop a small high-efficiency ultraviolet laser for biochemical detection[N/OL]. [2014-03-06]. China News, http://www.chinanews.com/mil/2014/03-06/5916245.shtml. [51] Kozu T, Yamaguchi M, Kawaguchi M, et al. Evaluating of diamond like carbon using deep UV Raman spectroscopy[J]. Integrated Ferroelectrics, 2013, 157(1): 147-156. [52] Skulinova M, Lefebvre C, Sobron P, et al. Time-resolved stand-off UV-Raman spectroscopy for planetary exploration[J]. Planetary and Space Science, 2014, 92: 88-100. doi: 10.1016/j.pss.2014.01.010 [53] Almaviva S, Chirico R, Nuvoli M, et al. A new eye-safe UV Raman spectrometer for the remote detection of energetic materials in fingerprint concentrations: characterization by PCA and ROC analyzes[J]. Talanta, 2015, 144(8): 420. [54] Chirico R, Almaviva S, Colao F, et al. Proximal detection of traces of energetic materials with an eye-safe UV Raman prototype developed for civil applications[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(1): 8. [55] Lamsal N, Barnett P, Angel S M, et al. Remote UV Raman spectroscopy for planetary exploration using a miniature spatial heterodyne Raman spectrometer[C]//Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, 2016: 1500-1510. [56] Lamsal N, Sharma S K, Acosta T E, et al. Ultraviolet stand-off Raman measurements using a gated spatial heterodyne Raman spectrometer[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2016, 70(4): 666-675. doi: 10.1177/0003702816631304 [57] Hopkins A J, Cooper J L, Profeta L T M, et al. Portable deep-ultraviolet (DUV) Raman for standoff detection[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2016, 70(5): 861-873. doi: 10.1177/0003702816638285 [58] Hufziger K T, Bykov S V, Asher S A. Ultraviolet Raman wide-field hyperspectral imaging spectrometer for standoff trace explosive detection[J]. Applied Spectroscopy, 2017, 71(2): 173-185. doi: 10.1177/0003702816680002 [59] Shkolyar S, Eshelman E J, Farmer J D, et al. Detecting kerogen as a biosignature using colocated UV time-gated Raman and fluorescence spectroscopy[J]. Astrobiology, 2018, 18(4): 431-453. doi: 10.1089/ast.2017.1716 [60] Gulati K K, Gulia S, Kumar N, et al. Real-time stand-off detection of improvised explosive materials using time-gated UV-Raman spectroscopy[J]. Pramana, 2019, 92(2): 1-5. [61] Cantu L, Gallo E, Duschek F. Remote Raman scattering detection of explosives[C]//ODAS (ONERA-DLR Aerospace Symposium)-MOTAR (Measurement and Optical Techniques for Aerospace Research), 2021: (DOI: https://elib.dlr.de/141626/).https://www.researchgate.net/publication/351072675_REMOTE_RAMAN_SCATTERING_DETECTION_OF_EXPLOSIVES. [62] Gallo E, Duschek F. Deep-UV remote Raman detection of chlorine[C]// OSA Optical Sensors and Sensing Congress, 2021: DOI: https://elib.dlr.de/143249/. [63] 卓立汉光. 紫外共振拉曼光谱系统—UV Raman100[EB/OL]. 仪器信息网, http://www.instrument.com.cn/netshow/SH100487/C95891.htm, 2018.Zolix Intruments CO., LTD. Ultraviolet Resonance Raman Spectroscopy System—UV Raman100[EB/OL]. Instrument, http://www.instrument.com.cn/netshow/SH100487/C95891.htm, 2018. [64] 黄保坤, 安虹宇, 范峰滔. 小型紫外拉曼光谱仪[J]. 光散射学报, 2017, 29(4): 348-353. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSSX201704011.htmHUANG B K, AN H Y, FAN F T. Mini UV Raman spectrometer[J]. The Journal of Light Scattering, 2017, 29(4): 348-353. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSSX201704011.htm [65] 王祺. 激光诱导击穿光谱和拉曼光谱远程探测系统研究[D]. 深圳: 深圳大学, 2016.WANG Q. Study of Combined Remote Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy And Raman Spectroscopy Detection System[D]. Shenzhen: Shenzhen University. 2016. [66] ZHANG W, ZHOU R, LIU K, et al. Sulfur determination in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy combined with resonance Raman scattering[J]. Talanta, 2020, 216: 120968-120976. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2020.120968 [67] SI G, FANGY, LIU J, et al. A new eye-safe compact UV-Raman spectroscopy setup for the proximal detection of hazardous chemicals[C]//AOPC 2021: Optical Spectroscopy and Imaging, 2021, 12064: 99-105. [68] Hagen N, Brady D J. Coded-aperture DUV spectrometer for stand-off Raman spectroscopy[C]//Next-Generation Spectroscopic Technologies Ⅱ, 2009, 7319: 73190D. [69] Yellampalle B, Martin R, Witt K, et al. Performance comparison of single and dual-excitation-wavelength resonance-Raman explosives detectors[C]//Chemical, Biological, Radiological, Nuclear, and Explosives (CBRNE) Sensing XVⅢ, 2017, 10183: 101830E. -





 下载:
下载: