Real-Time Pedestrian Detection Based on the Weak Saliency Map in Thermal Infrared Images
-
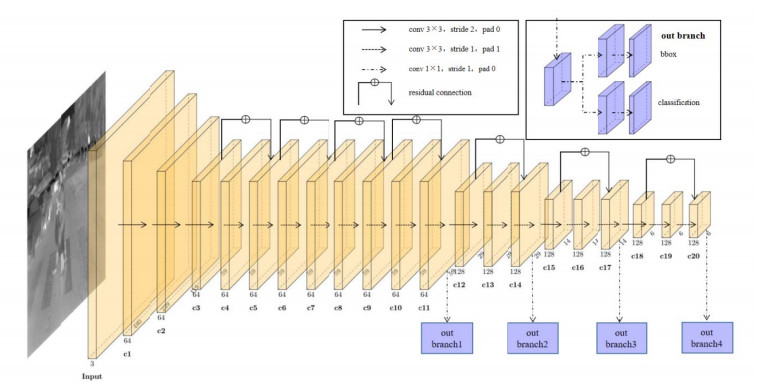
摘要: 针对现有热红外图像行人检测方法在精度和速度方面存在的问题,提出一种基于弱显著图的实时行人检测方法。该方法以轻量级LFFD(Light and Fast Face Detector)网络为基础,由两级改进网络即SD-LFFD(Saliency Detection-LFFD)和SF-LFFD(Saliency Fusion-LFFD)组成,首先以热红外图像作为输入经SD-LFFD网络产生初步行人检测结果和行人区域弱显著图,接着将该弱显著图与原热红外图像结合“点亮”潜在行人区域并经SF-LFFD网络产生新的行人检测结果,最后将两级改进网络的行人检测结果融合得到最终结果。在数据集CVC-09和CVC-14上实验结果表明,该方法与现有轻量级神经网络相比行人检测的平均精确率有大幅提升,且在有限硬件资源下可实现实时检测。Abstract: To address the low precision and speed of existing pedestrian detection methods for thermal infrared images, a real-time pedestrian detection method based on a weak saliency map is herein proposed. The proposed method comprises two improved networks, namely, SD-LFFD and SF-LFFD, which use lightweight LFFD as the basic network. First, the thermal infrared image is input into the SD-LFFD to produce the preliminary pedestrian detection results and a weak saliency map indicating the pedestrian regions. Then, the weak saliency map and the original thermal infrared image are combined to highlight the potential pedestrian regions and generate new results using the SF-LFFD. Finally, the pedestrian detection results obtained by the two improved networks are integrated to obtain the final results. The experimental results on the CVC-09 and CVC-14 datasets indicate that the proposed method significantly improves the average precision (AP) of pedestrian detection compared with that of existing lightweight neural networks, and that it achieves real-time detection with limited hardware resources.
-
Key words:
- thermal infrared image /
- pedestrian detection /
- saliency detection /
- real-time detection
-
表 1 CVC-09和CVC-14数据集的样本分布
Table 1. The distribution of samples in CVC-09 and CVC-14
Dataset Day Night Train set Test set Train set Test set CVC-09 4225 2882 3201 2883 CVC-14 3695 707 3390 727 表 2 行人检测AP值比较
Table 2. AP comparison for pedestrian detection
% Dataset TestScenario AP(IoU=0.5) ORI-LFFD SD-LFFD SF-LFFD SD-LFFD+SF-LFFD CVC-09 Day 74.15 73.25 76.05 78.46 Night 74.70 75.54 75.81 79.85 Total 73.82 74.01 75.52 78.74 CVC-14 Day 53.94 57.93 64.81 66.76 Night 75.70 76.17 83.61 83.94 Total 63.45 66.06 73.21 74.46 表 3 行人检测的速度对比
Table 3. Speed comparison for pedestrian detection
Method Model size/M Frame rate /fps Inference speed/ms Tiny-YOLOv3 33.99 18.31 54.61 SD-LFFD+SF-LFFD 14.45 31.25 32 -
[1] 刘峰, 王思博, 王向军, 等. 多特征级联的低能见度环境红外行人检测方法[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2018, 47(6): 137-144.LIU Feng, WANG Sibo, WANG Xiangjun, et al. Infrared pedestrian detection method in low visibility environment based on multi feature association[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2018, 47(6): 137-144. [2] CAI Y, LIU Z, WANG H, et al. Saliency-based pedestrian detection in far infrared images[J]. IEEE Access, 2017, 5: 5013-5019. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7904724 [3] Ko B C, Kim D Y, Nam J Y. Detecting humans using luminance saliency in thermal images[J]. Optics Letters, 2012, 37(20): 4350-4352. doi: 10.1364/OL.37.004350 [4] MA Y, WU X, YU G, et al. Pedestrian detection and tracking from low-resolution unmanned aerial vehicle thermal imagery[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(4): 446. doi: 10.3390/s16040446 [5] Jeon E S, Choi J S, Lee J H, et al. Human detection based on the generation of a background image by using a far-infrared light camera[J]. Sensors, 2015, 15(3): 6763-6788. doi: 10.3390/s150306763 [6] 李慕锴, 张涛, 崔文楠. 基于YOLOv3的红外行人小目标检测技术研究[J]. 红外技术, 2020, 42(2): 176-181. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWJS202002014.htmLI Mukai, ZHANG Tao, CUI Wennan. Research of Infrared Small Pedestrian Target Detection Based on YOLOv3[J]. Infrared Technology, 2020, 42(2): 176-181. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HWJS202002014.htm [7] LIU J, ZHANG S, WANG S, et al. Multispectral deep neural networks for pedestrian detection[J/OL]. arXiv preprint, 2016, https://arxiv.org/pdf/1611.02644.pdf. [8] Wagner J, Fischer V, Herman M, et al. Multispectral pedestrian detection using deep fusion convolutional neural networks[C]//24th European Symposium on Artificial Neural Networks, Computational Intelligence and Machine Learning (ESANN), 2016: 509-514. [9] Ghose D, Desai S M, Bhattacharya S, et al. Pedestrian Detection in Thermal Images using Saliency Maps[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, 2019: 988-997. [10] HE Y, XU D, WU L, et al. LFFD: A Light and Fast Face Detector for Edge Devices[J/OL]. arXiv preprint, 2019, https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.10633v1. [11] HOU Q, CHENG M M, HU X, et al. Deeply supervised salient object detection with short connections[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017: 3203-3212. [12] Socarrás Y, Ramos S, Vázquez D, et al. Adapting pedestrian detection from synthetic to far infrared images[C]//ICCV–Workshop Visual Domain Adaptation and Dataset Bias, 2013: 1-3. [13] González A, Fang Z, Socarras Y, et al. Pedestrian detection at day/night time with visible and fir cameras: A comparison[J]. Sensors, 2016, 16(6): 820. doi: 10.3390/s16060820 [14] Redmon J, Farhadi A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement[J/OL]. arXiv preprint, 2018, https://arxiv.org/pdf/1804.02767.pdf. -





 下载:
下载: